Overseas
February 27, 2024
Cold-rolled imports still significantly cheaper than domestic product
Written by David Schollaert
Foreign cold-rolled coil (CR) remains much less expensive than domestic product even as prices in the US have declined at a rapid pace over the past month, according to SMU’s latest check of the market.
All told, US CR prices are now 24.5% more expensive than imports. The premium is up marginally from 24.1% last week but down from a high of 31.5% in early January. And while imported cold-rolled coil has become less attractive over the past month due to sharp price cuts in the US, offshore CR is still a great value given the wide spread.
In dollar-per-ton terms, US CR is now on average $232 per short ton (st) more expensive than offshore product, up $67 week over week (w/w) on average. This is still $37/st lower than a month ago when the average premium for US CR over imported cold band was $269/st.
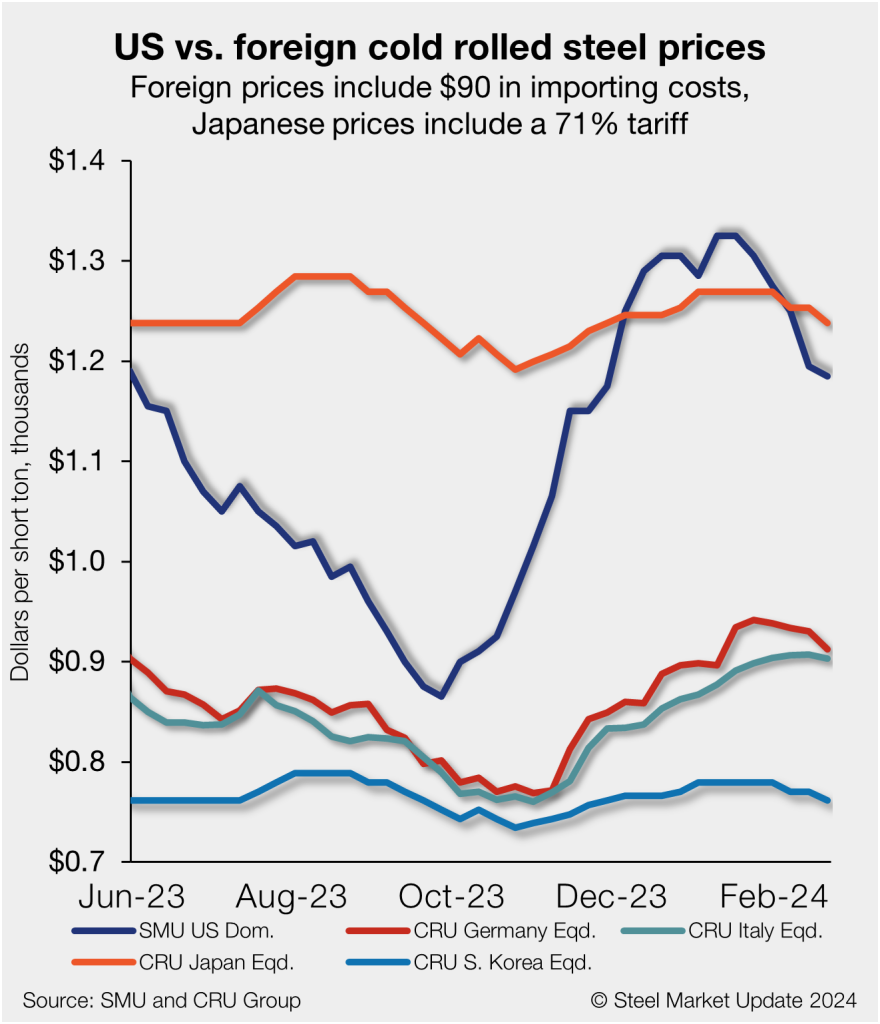
This week, domestic CR tags were $1,185/st on average based on SMU’s latest check of the market on Tuesday, Feb. 20. And even while US prices are now at their lowest level since early late November, they continue to carry a large premium over imports.
Methodology
This is how SMU calculates the theoretical spread between domestic CR prices (FOB domestic mills) and foreign CR prices (delivered to US ports): We compare SMU’s US CR weekly index to the CRU CR weekly indices for Germany, Italy, and East Asia (Japan and South Korea). This is only a theoretical calculation. Import costs can vary greatly, influencing the true market spread.
We add $90 per short ton to all foreign prices as a rough means of accounting for freight costs, handling, and trader margin. This gives us an approximate CIF US ports price to compare to the SMU domestic CR price. Buyers should use our $90-per-st figure as a benchmark and adjust up or down based on their own shipping and handling costs. If you import steel and want to share your thoughts on these costs, please get in touch with the author at david@steelmarketupdate.com.
East Asian cold-rolled coil
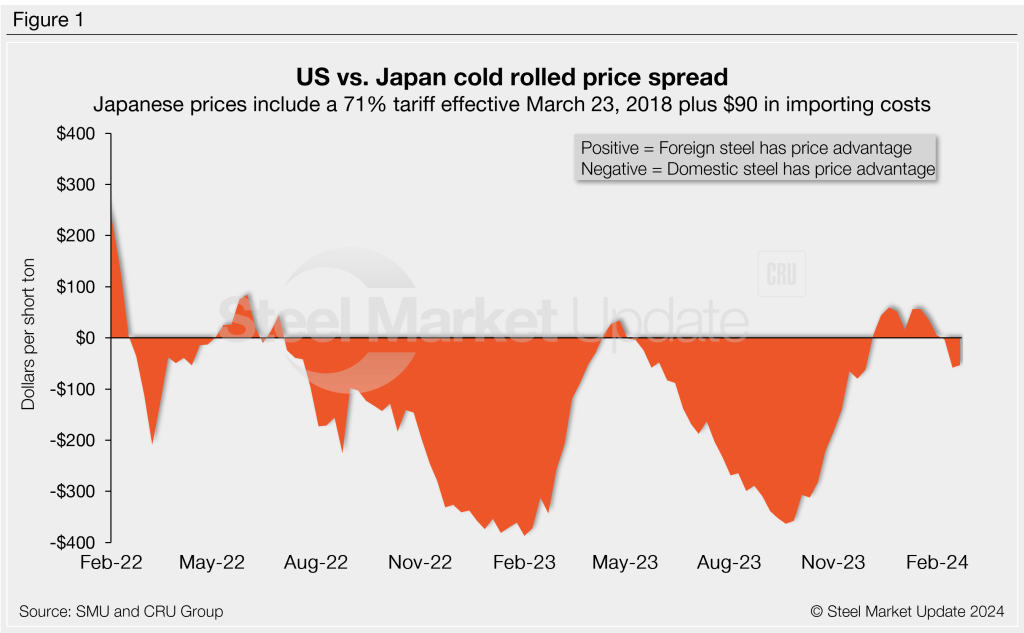
As of Thursday, Feb. 22, the CRU Asian CR price was $671/st, down $9/st w/w and down just $18/st from a month prior. Adding a 71% anti-dumping duty (Japan theoretical), and $90 per ton in estimated import costs, the delivered price to the US is $1,238/st.
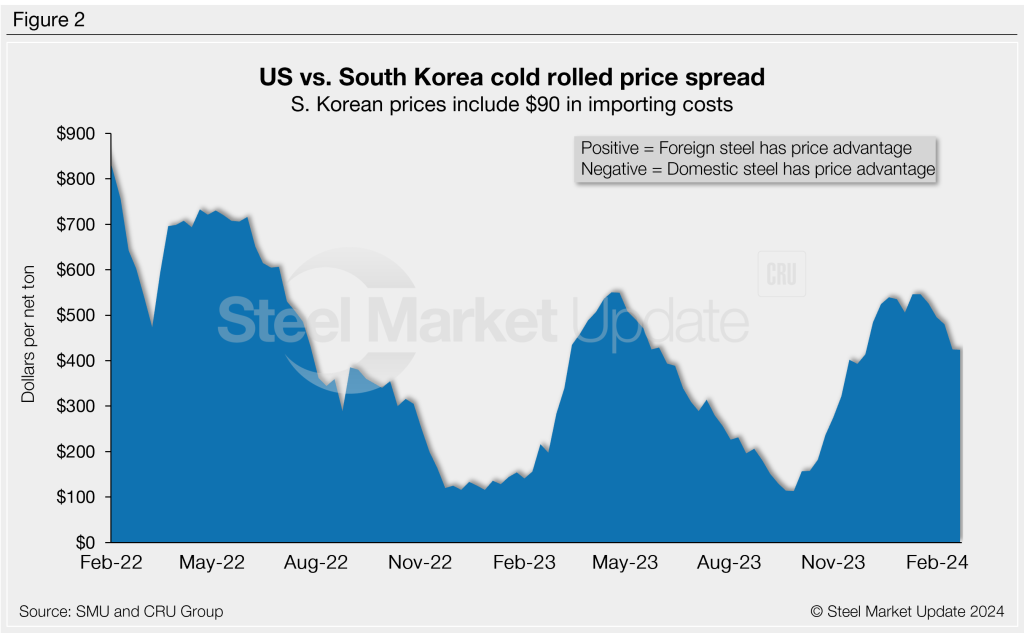
The South Korean theoretical price is $761/st. The latest SMU cold-rolled average is $1,185/st, down $10/st w/w, and down $120/st compared to one month ago.
The result: US-produced CR is now theoretically $53/st cheaper than steel imported from Japan but $424/st more costly than cold-rolled imported from South Korea.
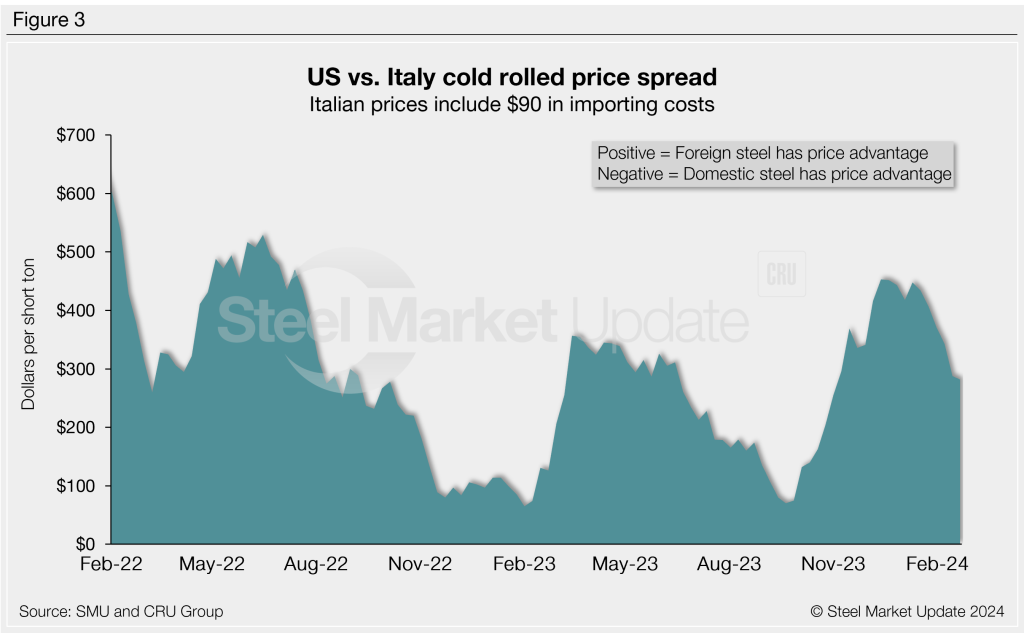
Italian cold-rolled coil
Italian CR prices were down $4/st to roughly $813/st this week. Despite that decline, Italian prices are still up $5/st from a month ago. After adding import costs, the delivered price of Italian CR is in theory $903/st.
That means domestic CR is theoretically $282/st more expensive than CR imported from Italy. The spread is down just $6/st from last week, but the domestic cold band price premium over offshore product from Italy is down $171/st from a recent high of $453/st in mid-December.
German cold-rolled coil
CRU’s German CR price ticked down $18/st vs. the week prior to $822/st. After adding import costs, the delivered price of German cold rolled is in theory $912/st.
The result: Domestic CR is theoretically a whopping $273/st more expensive than CR imported from Germany. The spread is now $155/st below a recent high of $428/st during the first week of 2024.
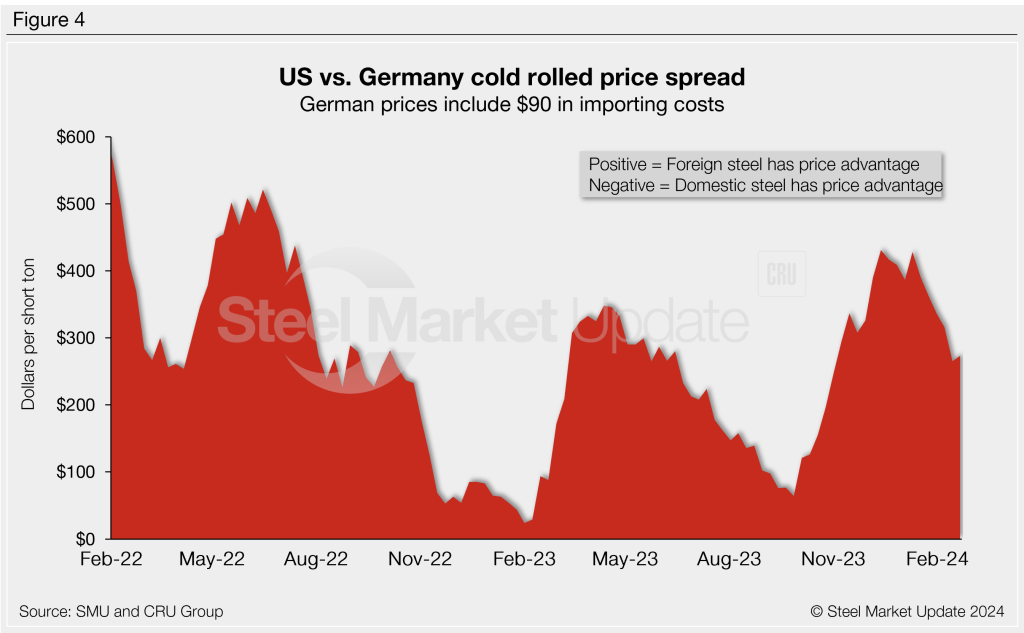
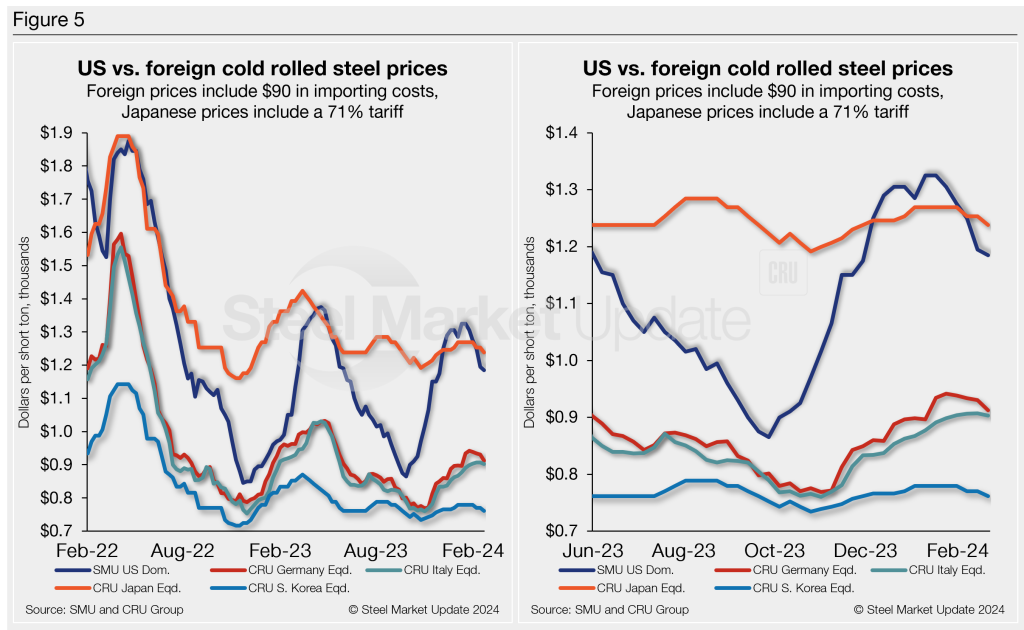
Figure 5 compares all five price indices. The chart on the left shows historical variation from Feb. 1, 2022, through present. The chart on the right zooms in to highlight the recent volatility in US pricing since June 2023.
Notes: We reference domestic prices as FOB the producing mill, while foreign prices are CIF the port (Houston, NOLA, Savannah, Los Angeles, Camden, etc.). Inland freight from either a domestic mill or a port is important to keep in mind when deciding where to source from. It’s also important to factor in lead times too. In most market cycles, domestic steel will deliver more quickly than foreign steel.
Section 232 tariffs are no longer considered in these prices. That’s because, effective Jan. 1, 2022, the blanket 25% Section 232 tariff was removed from most imports from the European Union. It as replaced by a tariff rate quota (TRQ). Therefore, the German and Italian price comparisons in this analysis no longer include a 25% tariff. A similar TRQ with Japan went into effect on April 1, 2022. South Korea is subject to a hard quota rather then the 25% tariff.