Government/Policy
March 29, 2022
Commerce Continues Plate Duties After Key Sunset Review
Written by Michael Cowden
The US Commerce Department has decided to continue anti-dumping duties on cut-to-length plate from a dozen nations.
It has also determined that countervailing duties – more than 250% – on plate from China should remain in place.
The Sun Doesn’t Set on Steel Duties
Those decisions follow an expedited “sunset” review that began on December 1, 2021.
Sunset reviews, conducted every five years, require US trade officials to decide whether duties should be extended or allowed to lapse (i.e., to sunset). In practice, the sun rarely sets on steel duties.
The sunset review period covered the years 2017-2021. That start date is because the Commerce Department on March 30, 2017, determined that plate from Austria, Belgium, Brazil, China, France, Germany, Korea, Italy, Japan, South Africa, Taiwan and Turkey had been dumped and so rolled out anti-dumping duties.
The result of the sunset review? “Commerce determines that revocation of the (duty) Orders would be likely to lead to continuation or recurrence of dumping,” according to an entry in the Federal Register dated Friday, March 25, 2022.
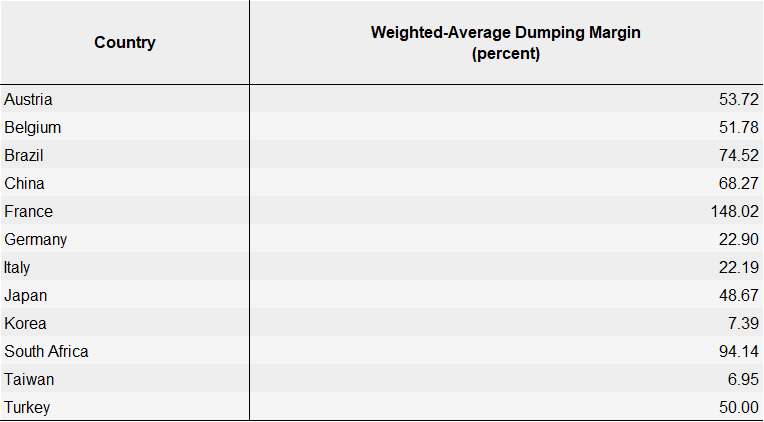
The Margins
Updated plate anti-dumping duty margins are below:
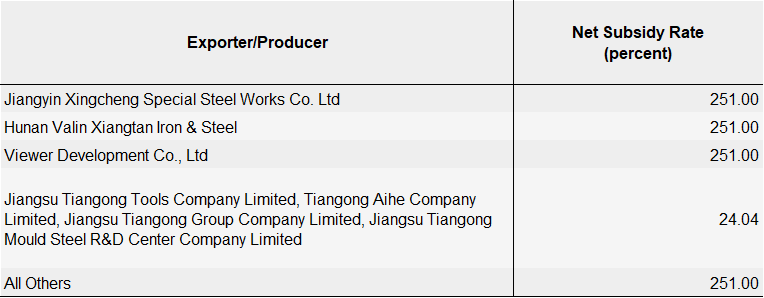
Commerce also decided to keep in place countervailing duties of as much as 251% to offset subsidies the department thinks Chinese plate producers would receive. Those margins are below:
The Background
Commerce in 2016 and 2017 decided a wave of trade petitions covering all major flat-rolled steel products – hot-rolled coil, cold-rolled coil, coated product, and plate – in favor of domestic mills. The scope of the plate case was notable in that it was brought against so many countries at the same time.
The tide of duties against some of the biggest importers to the US, rolled out under the Obama administration, reshaped the domestic steel industry dramatically. The landscape was again changed in a big way in 2018 with the Trump administration’s Section 232 tariffs and quotas.
The result of the combined trade actions: The US imported 40.3 million metric tonnes of flat-rolled steel in 2014. That figure fell 25 percent to 30.1 million in 2016, the year the big sheet cases were decided. And flat rolled imports have remained below 30 million tonnes since 2019 following the imposistion of Section 232.
Section 232 might capture more headlines. But the sunset reviews of the 2016-17 trade cases are important. And many of those reviews are slated to be completed this year.
“2022 is a critical year for sunset reviews of AD/CVD orders on steel products,” trade attorney Alan Price, a partner with the Washington law firm of Wiley Rein, said during a Community Chat in January. “Maintaining these orders is critical for the US steel industry, particularly as we see the world normalizing and imports ramping up into the United States.”
The Price and the Tons
Prices for steel sheet have been extraordinarily volatile this year. They started out 2021 falling fast before whipsawing back upward following the invasion of Ukraine by Russian forces on February 24.
Plate prices, in contrast, have been stable and have posted more modest gains. Plate tags started out the year at $1,795 per ton ($89.75 per cwt) and had increased 3.3% to $1,855 per ton when this article was filed, according to SMU’s interactive pricing tool.
As for import volumes, the US imported 470,730.77 metric tonnes of cut-to-length plate in 2021, according to Commerce Department figures. That’s up sharply from 278,233.54 tonnes in 2020 – the year when the pandemic hammered demand – but roughly on par with 483,767.39 tonnes in 2019, a comparatively normal year for steel.
By Michael Cowden, Michael@SteelMarketUpdate.com







