Overseas

February 3, 2022
Foreign vs. Domestic HRC Price Analysis: Foreign Advantage Shrinking
Written by Brett Linton
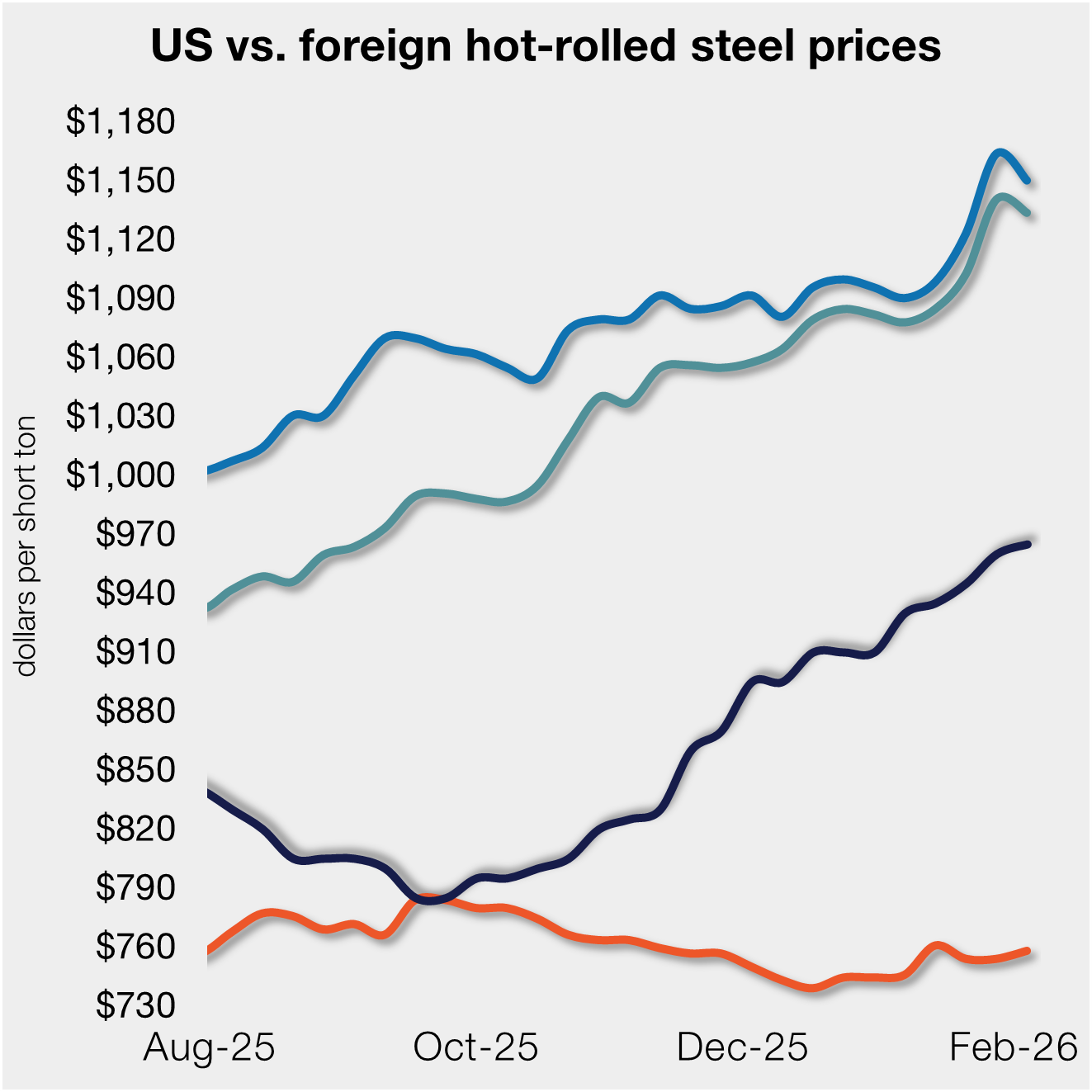
Hot rolled imports continue to tempt U.S. buyers with potential discounts of 14-23% over domestic prices, according to Steel Market Update’s latest foreign versus domestic price comparison. Foreign hot rolled steel prices are now theoretically $177-283 per ton cheaper than domestic steel, after taking freight costs, trader margins and tariffs into consideration. However, this foreign advantage has been declining since the September/October 2021 highs.
The following calculation is used by Steel Market Update to identify the theoretical spread between foreign hot rolled steel prices (delivered to U.S. ports) and domestic hot rolled coil prices (FOB domestic mills). This is only a “theoretical” calculation as freight costs, trader margins, and other costs can fluctuate, ultimately influencing the true market spread. This compares the SMU U.S. hot rolled weekly index to CRU hot rolled weekly indices for Germany, Italy, and Far East Asian ports.
Note that effective Jan. 1, 2022, the traditional Section 232 tariff no longer applies to most imports from the European Union. It has been replaced by a tariff rate quota (TRQ). Therefore, the German and Italian price comparisons in this analysis no longer include a 25% tariff, and comparisons to prior prices may be skewed. SMU still includes the 25% S232 tariff on foreign prices from other countries. We also add $90 per ton to all foreign prices in consideration of freight costs, handling, trader margin, etc., to provide an approximate “CIF U.S. ports price” that can be compared against the SMU U.S. hot rolled price. Buyers should use this $90 rate as a benchmark, and adjust up or down to their own shipping and handling costs if necessary. Note that we do not include any antidumping (AD) or countervailing duties (CVD) in this analysis.
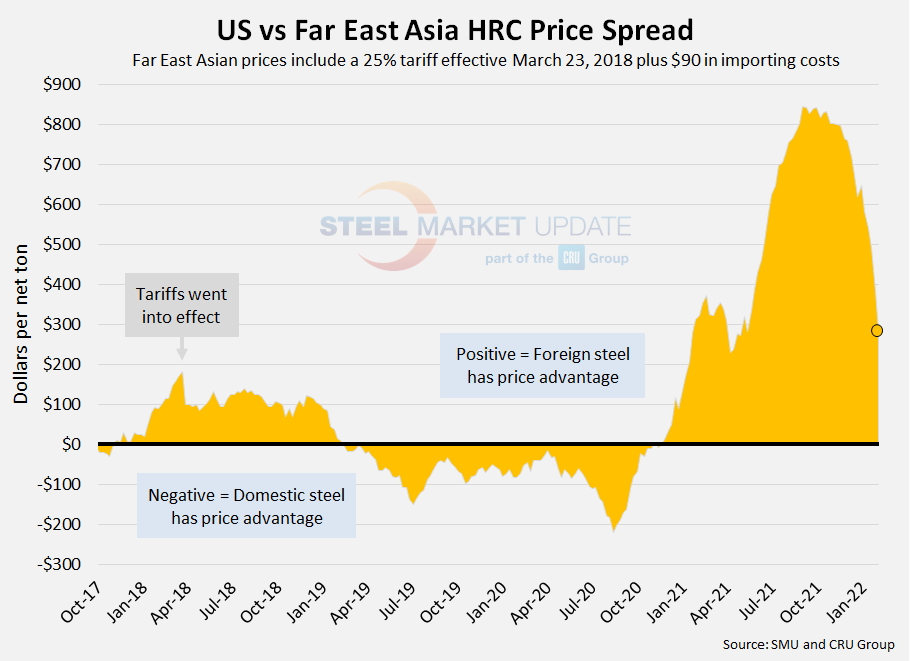
![]() Far East Asian HRC (East and Southeast Ports)
Far East Asian HRC (East and Southeast Ports)
As of Wednesday, Feb. 2, the CRU Far East Asian HRC price was unchanged at $689 per net ton ($760 per metric ton), also unchanged from one month prior. Adding a 25% tariff and $90 in estimated import costs, the delivered price of Far East Asian HRC to the U.S. is $952 per ton. The latest SMU hot rolled price average is $1,235 per ton, down $100 from one week ago, and down $300 from one month prior. Therefore, U.S.-produced HRC theoretically is now $283 per ton more expensive than imported Far East Asian HRC, down from $383 last week, and down from $583 one month ago. Recall that the early-September spread of $847 per ton was the largest theoretical spread between Far East Asian and domestic HRC prices in SMU’s four-year data history. Prior to 2021, the previous record high was $183 per ton in March 2018.
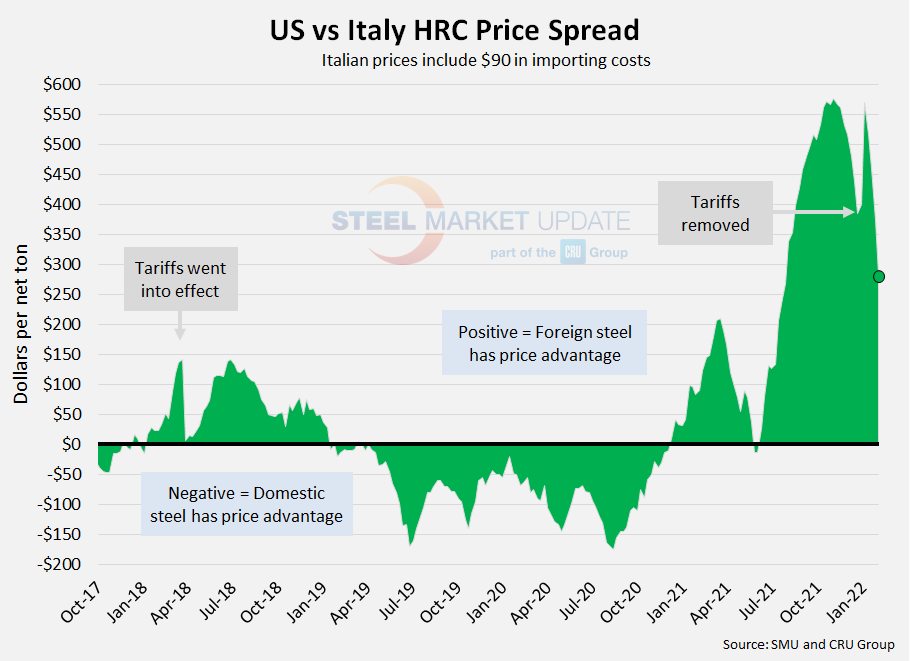
Italian HRC
CRU published Italian HRC prices at $863 per net ton ($951 per metric ton), down $9 from last week, and down $11 from one month ago. After adding import costs, the delivered price of Italian HRC is approximately $953 per ton. Accordingly, domestic HRC is theoretically $282 per ton more expensive than imported Italian HRC, down from $373 last week, and down from $571 one month ago. Prior to removal of the 25% tariff, the early-November spread of $577 per ton was the largest seen in SMU’s limited data history. Prior to 2021, the previous record high was $143 per ton in July 2016.
German HRC
The latest CRU German HRC price is $968 per net ton ($1,067 per metric ton), up $4 from last week, and up $6 from one month ago. After adding import costs, the delivered price of German HRC is approximately $1,058 per ton. Accordingly, domestic HRC is theoretically $177 per ton more expensive than imported German HRC, down from $281 last week, and down from $483 one month ago. Prior to removal of the 25% tariff, the mid-October spread of $504 per ton was the largest seen in SMU’s limited data history. Prior to 2021, the previous record high was $121 per ton in March 2018.

The graph below compares all four price indices and highlights the effective date of the tariffs. Foreign prices are referred to as “equalized,” meaning they have been adjusted to include importing costs (and tariffs in some cases) for a like-for-like comparison against the U.S. price.
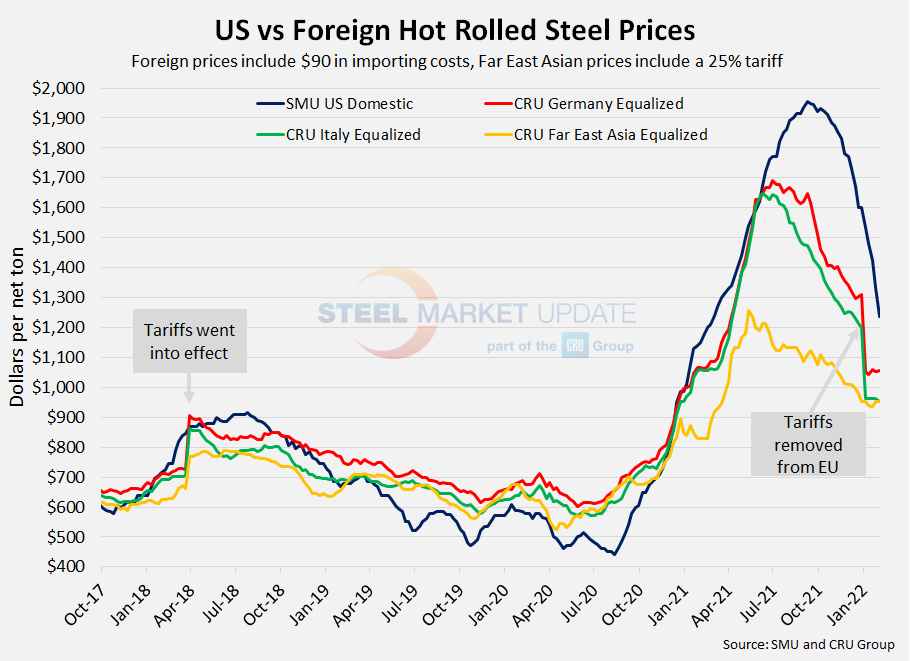
Note: Freight is an important part of the final determination on whether to import foreign steel or buy from a domestic mill supplier. Domestic prices are referenced as FOB the producing mill, while foreign prices are FOB the Port (Houston, NOLA, Savannah, Los Angeles, Camden, etc.). Inland freight, from either a domestic mill or from the port, can dramatically impact the competitiveness of both domestic and foreign steel. When considering lead times, a buyer must take into consideration the momentum of pricing both domestically and in the world markets. In most circumstances (but not all), domestic steel will deliver faster than foreign steel ordered on the same day.
By Brett Linton, Brett@SteelMarkeUpdate.com