Market Segment

July 28, 2019
CRU: Turkish Steel at the Crossroads of the World
Written by Tim Triplett
By CRU Analyst Chris Bandmann
CRU is launching weekly Turkish HR coil export prices, enhancing the existing suite of weekly Turkish long product and scrap prices. This Insight being offered for these other markets has now been brought to flats – and offers a window into the world of Turkish hot rolled coil exports.
Turkey is the sixth largest exporter of steel in the world, supplying volume equal to 33 percent of China’s despite having a GDP just 7 percent the size. It is also the largest scrap buyer in the world, importing over three times the volume of scrap of the second biggest buyer and around five times as much as the EU’s total external trade.
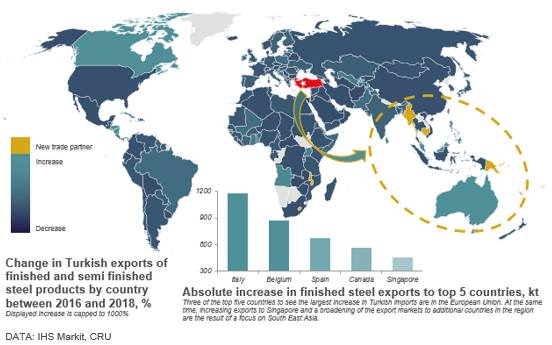
Other than the last two years, Turkish mills have both broadened their export markets and sought to increase sales to regions where they already had a presence. As shown on the map, this included selling larger volumes into Europe, as well as establishing customers in new countries in South East Asia.
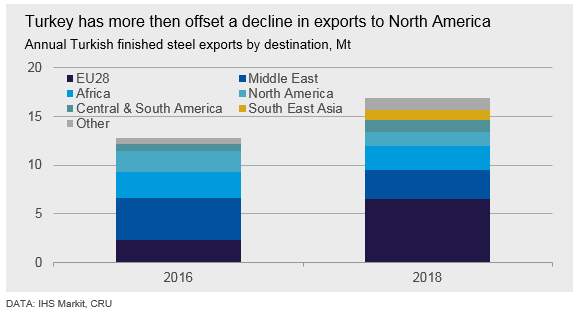
Turkey is a key cornerstone of the international steel trade. From North America to South East Asia, Europe to Africa – Turkish steel is influencing the markets. As such, Turkish prices are a driver of prices worldwide – and can act as a leading indicator for price changes in markets with which they trade. The key example here is EU domestic prices, though CIS export prices will often also be affected by movements in the Turkish price.
At the same time, the Turkish markets are high frequency markets, and prices can swing from week to week. While knowledge can be offered by an insight into these markets, they can be difficult to follow.
How did Turkey become such a major player in the international steel markets? The country has been aided by a couple of major factors, and developments in its domestic markets have enabled it to leverage these to its advantage.
Aided by Both Geography and Production Technology
The Turkish steel industry has several strengths. The geographical location of the country near the EU presents it with an easily accessible, large scale, high value export market, while neither the U.S. nor South East Asia necessitate prohibitively high freight costs. Most of the Turkish steel capacity is located close to a coast, allowing producers to switch between supplying domestic and export markets as necessary.
Beyond this, around 70 percent of Turkish steel is produced via the EAF route, offering mills flexibility in production.
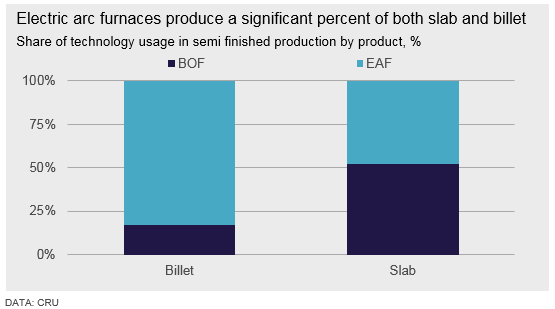
Unlike a blast furnace, an EAF can easily vary output according to market conditions, including short term shutdowns at times of market weakness. This also enables mills to choose between buying scrap and buying semi-finished products on the merchant markets, depending on relative price levels. However, the flexibility offered by an EAF can bring with it the trade-off of generally higher unit production costs, harming Turkish competitiveness in markets serviced by lower cost producers.
Some Turkish mills have strategic flexibility that extends beyond this. Mills operated by Çolakoğlu and Habaş are EAF-based, structurally short in steelmaking capacity versus rolling, and able to cast and roll both flat and long products. This provides a high degree of operational flexibility to quickly maximize margin opportunities in dynamic markets. Depending on the interplay between scrap and semis costs, and between flats and longs prices, the mills can choose to make more or less steel, purchase more or fewer semis, and route output preferentially to either sheet or longs markets. One example here might be a switch of production to sheet products once the EU quotas for long products have been filled.
Because of the Turkish steel industry’s heavy reliance on EAF, the country is the world’s largest scrap importer by volume. In 2018, Turkey imported a total of 20.7 Mt of material, compared to South Korea in second place with only around 6.1 Mt. Overall, Turkey was the recipient of around 22.4 percent of total world scrap exports.
As iron ore prices are currently inflated – with 62% Fe fines CFR China recently being assessed in excess of $110 /t – producers that rely on other feedstock will have a temporary cost advantage over those that rely on bulk raw materials. This will give Turkish mills an advantage in markets where they compete with producers using blast furnaces in the short term.
In the medium term, EAF-based producers in Turkey could see an additional market opportunity in the EU if a carbon border tariff adjustment were to be introduced there. EAF-based steel is much less carbon-intensive than BF/BOF-based steel. Consequently, Turkish flats exporters could find themselves at a cost advantage against both domestic EU flats mills, which are largely BF/BOF, and other key non-EU sources such as India. We discuss this issue further in a recent Insight, which Global Steel Trade Service subscribers can read here.
Weak Domestic Market has Contributed to Export Growth
Turkish mills have recently been struggling with weak domestic demand. CRU expects this to continue at least for the remainder of 2019. The Turkish domestic market hit a downturn last year, and quarterly demand for steel plummeted by 43 percent between 2017 Q4 and 2019 Q1. While some mills scaled back production, others switched their focus to the export markets instead, particularly the EU markets. At the same time, trade defense measures taken by the U.S. against Turkish steel meant that mills only had limited access to this traditionally strong market.
Historically, the U.S. market has offered Turkish mills the opportunity to make high margins, and so was Turkey’s largest trade partner between 2014-2017. The U.S. was the destination for an average of around 15 percent of total Turkish steel exports during this time, and annual shipments exceeded 2 Mt between 2015 and 2016.
Some Turkish mills had already been subjected to AD/CVD duties by the U.S. prior to the declaration of Section 232, and exports to the country had dropped. In 2016, Turkish steel represented a total of 8 percent of U.S. steel imports. This dropped to 6.5 percent in 2017 and 3.3 percent in 2018. The Section 232 measures caused this to decrease further, as Turkey uniquely received tariffs of 50 percent on its steel instead of the standard 25 percent. Year-to-date in 2019, Turkish steel made up close to 0 percent of total U.S. steel imports.
Having lost the U.S. market, Turkish mills attempted to find footholds elsewhere with varying degrees of success – and the propagation of Turkish steel across the world stage has brought with it significant price-setting power.
European Union: The EU remains Turkey’s primary export market, as it includes several of the country’s largest trade partners. In 2016, Turkey exported a total of 665 kt into the European Union. By 2018, this had risen to 1,861 kt.
The imposition of the EU’s safeguard measures against redirected steel imports will affect the Turkish hot rolled coil trade far less than the trade of other steel products. In the case of longs, as Turkish exports have picked up since the period used to set the levels of the quotas, the quota volumes it has received for long products have been insufficient for its needs. Notably, the Turkish quotas for both rebar and wire rod were filled within two weeks following their initial opening in February – quotas that were intended to last five months. The recent start of the next round of quotas has given Turkish mills some reprieve, but these will probably be exhausted soon, too.
However, Turkey can benefit from the hot rolled coil quota, which is the only product group to receive a single, global quota. Turkish mills will be able to sell hot rolled coil much more freely into the Union, thereby affecting domestic prices.
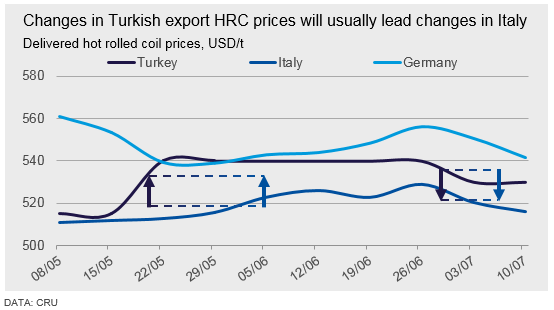
The local Italian and Spanish markets will usually be influenced by Turkish sheet prices, and as such changes to Turkish export prices will lead changes to Italian and Spanish domestic prices. The Italian market is both conveniently located for Turkish exporters and reacts quickly to cheap import prices. This affects greater Europe in turn, as other mills react in competition to lower prices from Italian mills.
For more information on the EU safeguard quotas, please see CRU’s regular Quota Watch publication as well as the following Global Steel Trade Service Insights here and here.
Africa and the Middle East: These regions are geographically close to Turkey as well as being developing markets with a growing demand for steel. Two of Turkey’s top ten export markets for steel, Israel and Yemen, are in these regions, and Israel was the single largest export market for long products in 2018.
However, while these regions are of great interest to Turkish mills, they cannot offer the volume of demand required alone. In 2018, Africa and the Middle East accounted for only 14 percent of total Turkish steel exports, where the EU28 accounted for around 39 percent.
Logistical issues such as efficiency in transporting steel to the more distant African countries with lower shipment sizes have required steel sellers to become creative. This includes the suggestion of pooling resources to buy a freight ship, which then has its cargo space doled out, but a solution has not yet presented itself.
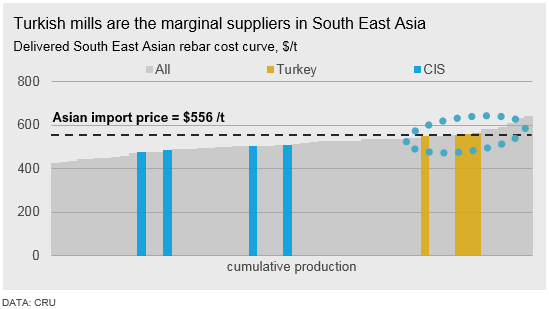
South East Asia: The South East Asian market is highly appealing – as a developing market, countries in the region have high and growing steel demand but have insufficient domestic capacity to account for this. However, Turkish mills must compete with Chinese and Russian mills in the region, competitors that have both the advantage of a lower cost base as well as lower freight rates. This has left Turkey as the marginal producer in the region, where they will enter and leave based on market conditions. As such, Turkish prices play a large role in setting the market price level in the region.
Renewed Push into the U.S.: Following the reduction of the U.S. tariffs on Turkish steel back to 25 percent, the markets were optimistic that mills could resume sales to the country. However, this optimism was short lived. U.S. steel mills reacted immediately, eating into their generous margins and lowering their prices to knock Turkey back out of the market. In addition to this, attractive offers from Italy meant that any U.S. buyers considering imports would prefer the EU country over Turkey.
The optimism soon dissipated, and while it may still be possible for Turkey to sell to the U.S., the price of scrap would need to fall to allow for finished steel prices to follow. Alternatively, if U.S. prices continue in their recent recovery, then the price level may rise to the level where sales can resume.
Gain Insight into a Price Influencer’s Markets
The production capabilities of the Turkish steel industry, the country’s advantageous location and recent developments in its domestic markets have contributed to the spread of Turkish steel around the world. Through this, Turkish mills influence prices as far away as the USA and South East Asia, and developments in the Turkish steel markets can have far-reaching effects.
CRU’s new price offering will help you keep ahead of these developments and offer an early insight into the movements of prices in the global steel markets.







