Government/Policy

December 15, 2019
CRU: Official “Phase 1” Deal Clears the Way for Expanded Trade in 2020
Written by Lisa Morrison
By CRU Principal Economist Lisa Morrison
On Dec. 13, U.S. Trade Representative, Robert Lighthizer, released a statement indicating that the U.S. and China had come to terms on a “phase 1” trade deal.
The opening sentence of the USTR press release states, “The United States and China have reached an historic and enforceable agreement on a Phase One trade deal that requires structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime in the areas of intellectual property, technology transfer, agriculture, financial services, and currency and foreign exchange.”
Critics will surely point to the lack of any specifics on progress made on the structural issues, which are at the heart of the U.S. Section 301 investigation with China. However, these are not issues that are easily resolved and any progress on the “easy wins” which reduces trade tension and defers further tariff escalation is certainly welcome.
Reporting from Reuters provides more detail than the USTR statement and indicates the deal will be signed during the first week of January. The key points are as follows:
• U.S. cuts the tariff rate from 15 percent to 7.5 percent on $120 bn in imports levied as of Sept. 1. The 25 percent tariffs scheduled for Dec. 15 on the remaining $250bn in imports from will not be implemented.
• China’s retaliatory tariffs scheduled to go into force on Dec. 15 are suspended.
• China will buy an additional $32 bn in U.S. agricultural goods—wheat, corn and rice— over the next two years. USTR indicated China will also increase purchases of U.S. manufactured goods, energy and services, but offered no details. China purchased $24bn worth of U.S. ag products in 2017.
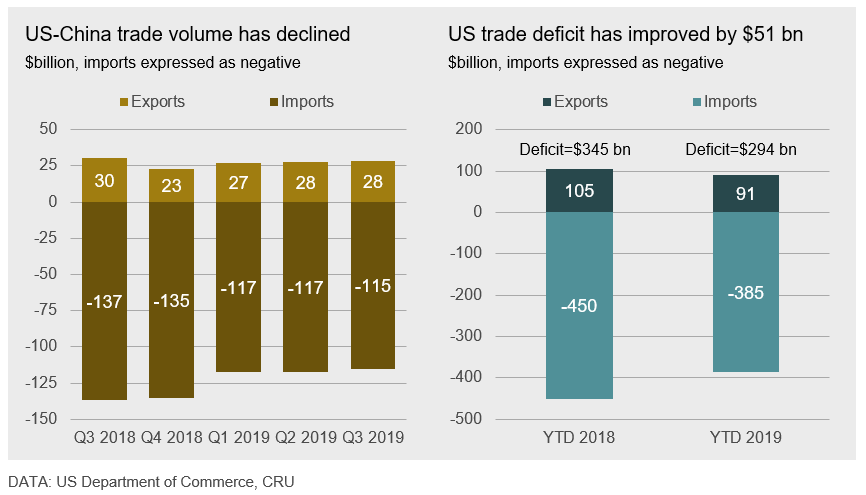
Data on the value of trade between the U.S.-China trade since Q3 2018 indicates that imports have declined by $22bn y/y and exports are lower by $2bn y/y. The U.S. trade deficit with China (right hand chart) indicates the gap has narrowed by $51bn thus far in 2019, or by 14.7 percent.
Request more information about this topic.
Learn more about CRU’s services at www.crugroup.com






