Government/Policy

August 6, 2019
New S301 Tariffs Will Not Directly Hit Chinese Steel Industry
Written by Tim Triplett
By CRU Analyst Alexander Ordosch
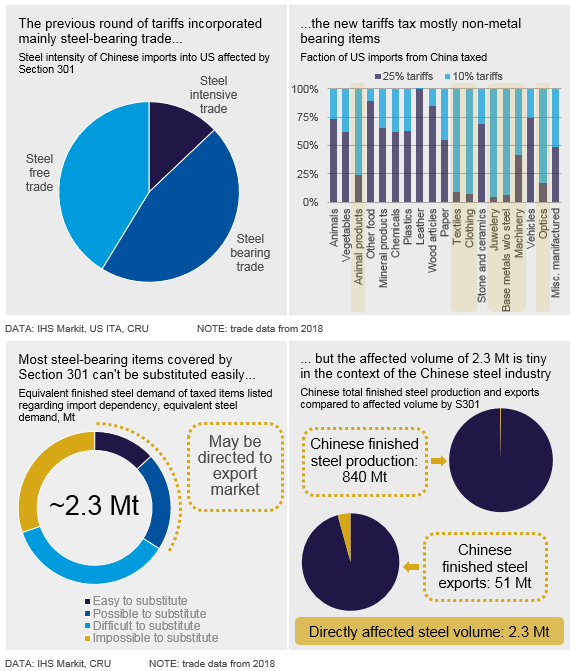
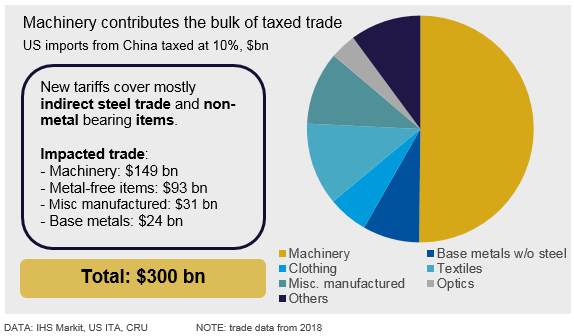
On Friday, Aug. 2, the U.S. government announced 10 percent tariffs on an additional $300 billion in Chinese imports that are not already covered by Section 301 (S301) tariffs. About 50 percent of the new tariffs cover steel-bearing machinery, while the rest are non-steel-containing items such as food, clothing, base metals and optics. The new tariffs will have a negligible direct impact on the Chinese steel industry, but broader consequences are a downside risk.
Section 301 tariffs have been in place for nearly a year now, having been imposed in September 2018. These tariffs of 25 percent cover $200 billion of trade that is mainly mechanical and electrical machinery and some direct steel trade, while mostly sparing non-steel items. From next month, September 2019, tariffs will be imposed on the other half of U.S. imports from China, but at a lower rate of 10%. The new duties affect mostly machinery, but also cover metal-free items like food, textiles and clothing, steel-free metal-bearing items from base metals and jewelry.
The new tariffs will impact machinery trade, which is steel intensive. The U.S. is dependent on these imports and we believe there are limited options to substitute for machinery sourced from elsewhere. Therefore, while imports from China will likely decrease, they will not fall dramatically. Previously, we estimated that Section 301 tariffs would impact just 2 Mt of Chinese steel demand (i.e. in the manufacture of machinery), steel which would then potentially be directed to the export market. This figure is negligible in the context of the Chinese steel industry, which produced about 840 Mt of finished steel and exported about 51 Mt in 2018. Overall, the new Section 301 tariffs may add another 300-400 kt/y to Chinese steel exports.
That said, Chinese steel demand can be influenced by indirect factors like loss of confidence in the Chinese economy or reduced investment. This would then have a much larger impact on Chinese steel export volumes as steelmakers compensate for lower domestic steel demand by directing material to the export market.