Government/Policy

December 13, 2018
Business Forward: Tariffs Causing “Demand Destruction”
Written by Sandy Williams
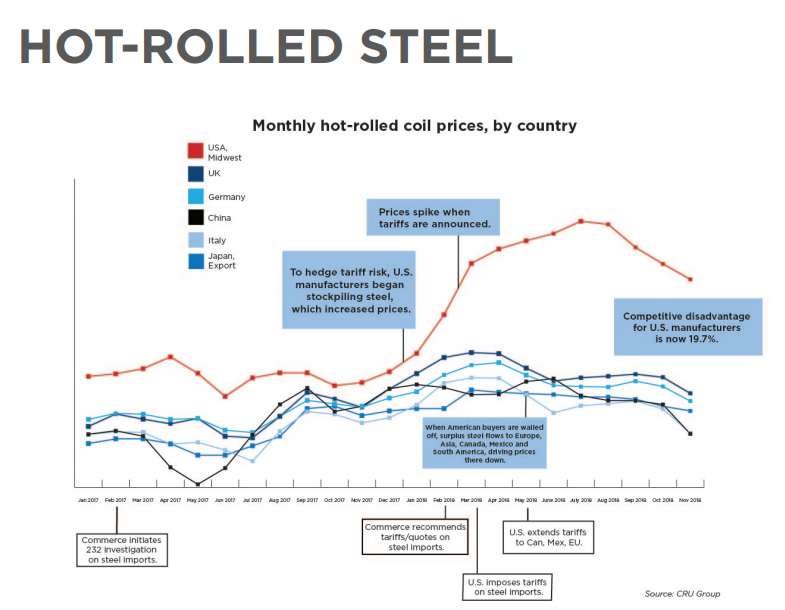
A new American Steel Index report by Business Forward shows U.S. steel prices have risen 7.4 percent since February, while foreign steel prices have fallen 9.8 percent. As a result, American manufacturers are paying 17.2 percent more for hot- and cold-rolled steel than their foreign competitors.
“President Trump’s tariffs on steel and aluminum are increasing consumer prices and hurting American exports,” said Business Forward President Jim Doyle. The long-term costs of tariffs are becoming clear, he added, as production moves overseas and firms cut back on capital investment.
The Section 232 tariffs are intended to reduce steel imports and strengthen U.S. manufacturing. Instead, the opposite effect is occurring as manufacturers switch strategies to importing more finished products from abroad while manufacturing less in the United States. Business Forward refers to this phenomenon as “demand destruction.”
“In order to have great manufacturing, a country or region must have cheap or affordable materials and energy,” said Josh Spoores, Principal Steel Analyst for CRU. “The U.S. has energy, but steel is not cheap. You also will see substitution and once that comes, it is challenging for a switch back.”
Business Forward maintains that the Trump administration’s defense of tariffs by comparing price increases for steel to finished product prices is wrong. “They should compare price increases with a manufacturer’s profit margin,” says Doyle. Higher steel prices are increasing input costs and negatively impacting profits for U.S. manufacturing firms.
Business Forward describes itself as a civic-minded, bipartisan advisory organization that works with business leaders across the country to advise Washington on how to create jobs and accelerate the economy.