Canada
June 11, 2018
Canada Trade Inequity: Fact or Hype?
Written by Sandy Williams
Is Canada really guilty of the trade inequity that President Trump charges? We looked at two product targets of the administration—dairy and automobiles—to find out.
The office of the U.S. Trade Representative estimates trade with Canada in 2017 totaled $673.9 billion–$341.2 billion in exports and $332.8 billion in imports, for a goods and services trade surplus for the U.S. of $8.4 billion.
The services part of that equation is what creates the surplus. Exports of services from the U.S., like travel, computer software and management services, totaled an estimated $58.7 billion in 2017, approaching double that of services imported from Canada at $32.8 billion. Removing services from the equation, the U.S had a trade deficit of $17.5 billion with Canada, according to Commerce data.

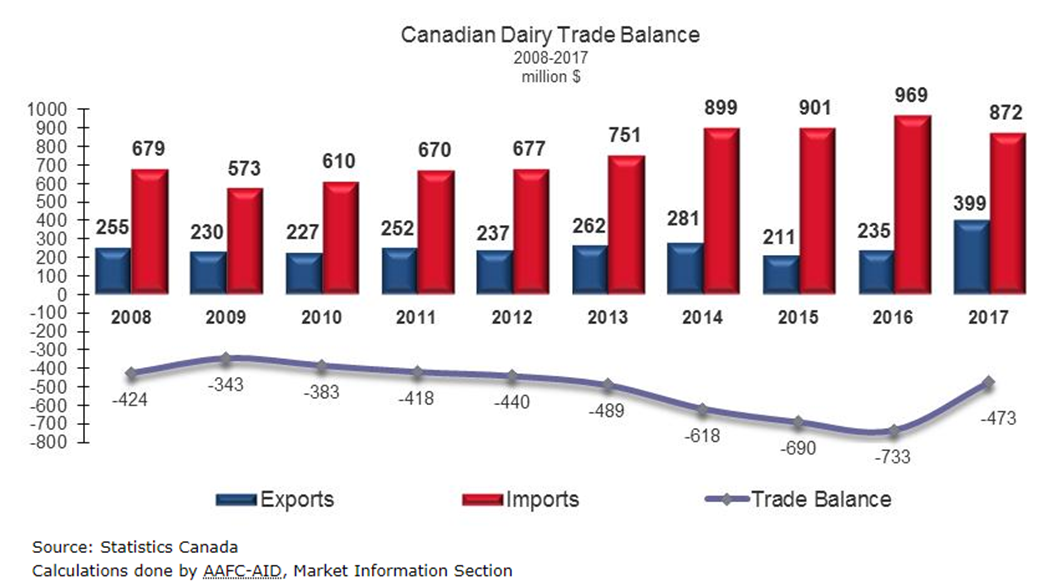
In the latest figures from 2016, however, the U.S. exported five times as much dairy to Canada as it imported. Despite paying higher prices, last year Canada bought $792 million worth of dairy products from the U.S. while exporting only $149 million to the U.S., according to data from the U.S. Dairy Export Council and the Canadian government.
The U.S. dairy industry hoped to take a larger part of the Canadian market through the NAFTA agreement, but was stymied by Canada’s “supply management program” that controls dairy supply and prices. Neighboring Wisconsin produces more dairy products than all of Canada and was a strong supporter of Trump. California, another sizable dairy region, exports about 12 percent of its products across the northern border.
When Canada included an ultra-filtered milk product under its supply management rules last year, the U.S. industry lost millions and exports of the product from Canada tripled. The dairy industry was a fervent lobbyist for a renegotiation of the North American Free Trade Agreement and Trump was willing to oblige his political constituency.
Now Trump is promoting a Section 232 tariff on automobiles and parts in response to Canada’s “massive tariffs” and “flooding” of the U.S. market with Canadian built vehicles. The USITC estimates vehicle imports from Canada to the U.S. totaled $56 billion in 2017.
“Autos [and related parts] represent just under 20 percent of our goods exports to the U.S. The products covered under the steel and aluminum tariffs are only about 4 percent,” said Royce Mendes, senior economist at CIBC World Markets in comments to CBC/Radio Canada.
“However, the U.S. administration should tread carefully. A major portion of the automotive products we ship south are made up of U.S. parts.”






