Government/Policy

March 8, 2018
Trump’s Tariffs Leave Market with Much Uncertainty
Written by Tim Triplett
Flanked by members of his administration and a group of steel and aluminum workers, President Trump signed measures today calling for a 25 percent tariff on imports of steel and a 10 percent tariff on imports of aluminum. But his comments leave the market far short of the clarity and certainty most had hoped for.
The tariffs apply to all countries, except Canada and Mexico, which would be exempt, at least as long as the NAFTA negotiations are under way. Unclear is Canada and Mexico’s status if U.S. negotiators don’t get the concessions they have been seeking and the U.S. pulls out of NAFTA.
The president also promised “flexibility and cooperation for those who are friends of ours,” suggesting that he would be willing to waive the tariffs on a country-by-country basis as the nation’s trading partners appeal for special treatment. “We will remain open to modifying the tariffs on individual nations as long as we know they are not a threat to our national security,” he said. The Commerce Department has 10 days to issue procedures for exclusion requests.
Word of Canada and Mexico’s exemptions, and the possibility of others, offers some consolation to U.S. rerollers and other mills that rely on imported slabs.
The tariffs are not to take effect for 15 days, which means companies in the United States now have 15 days to remove steel from ships and get customs clearance. Items on the water not arriving in time will need to go into bonded warehouses or pay the duty, said Washington trade attorney Lewis Leibowitz.
According to the proclamation signed by the president, the products covered by the tariffs include all steel products with the following HTS headings: HTS headings 7206.10-7216.50, 7216.99-7216.50, 7226.99-7301.10, 7302.10, 7302.40-7302.90, 7304.10-7306.90, with very narrow exceptions.
The tariffs take effect at 12:01 a.m. ET on March 23 (9 p.m. March 22 on the West Coast). They apply to entries or withdrawals from warehouses for consumption on or after the effective date. Goods shipped before March 8 will be covered if they are entered on or after the effective date. Goods not entered for consumption will not be subject to the tariffs, according to the proclamation (such as bonded warehouse entries, FTZ admissions, Temporary Importations under Bond, Transportation entries, etc.). It is not clear from the proclamation whether tariffs paid on entry may be recovered through duty drawback.
The Commerce Secretary is authorized to exclude products from the tariffs under the following criteria: The petition must come from “a directly affected party located in the United States.” Foreign exporters need not apply. “The proclamation does not state whether U.S.- based importers can apply, but if they are U.S. persons, it appears that they can,” Leibowitz said. Any steel article determined not to be produced in the United States in a sufficient and reasonably available amount and of satisfactory quality may be excluded by the Secretary of Commerce.
“I expect that there will be challenges to this proclamation in the U.S. and the WTO very soon,” Leibowitz added.
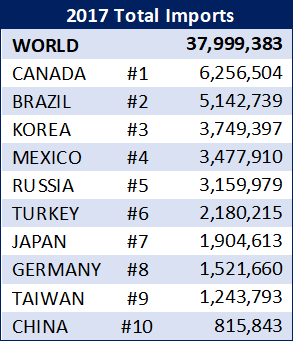
The table below shows the top 10 importers of steel to the U.S. in 2017, in net tons. Note that Canada was No. 1 and Mexico No. 4, accounting for about 25 percent of all U.S. imports last year.