Market Segment

June 9, 2014
April Flat Rolled Utilization Rate 84.2% & Long Products 73.4%
Written by Peter Wright
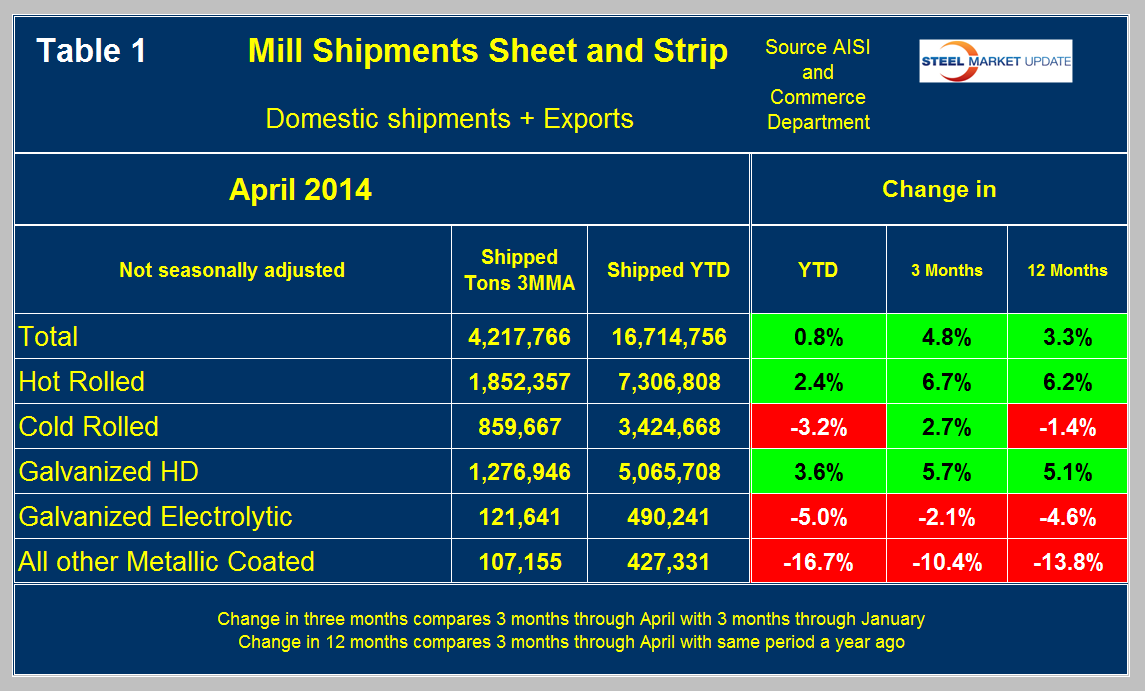
Total shipments of sheet and strip products including hot rolled, cold rolled and all coated products were up by 0.8 percent year to date (YTD) compared to the first four months of 2013. In the period January through April compared to the previous three months, the total tonnage was up by 4.8 percent. Comparing YTD shipments for 2014 and 2013 for individual products, hot band was up by 2.4 percent and hot dipped galvanized (HDG) by 3.6 percent. Cold rolled was down by 3.2 percent, electro-galvanized by 5 percent and other metallic coated (mainly Galvalume) by 16.7 percent, (Table 1).
Net imports were up strongly on all five of these product groups YTD which makes the performance of hot band and HDG impressive. We will be reporting on net imports in detail at this time next month.
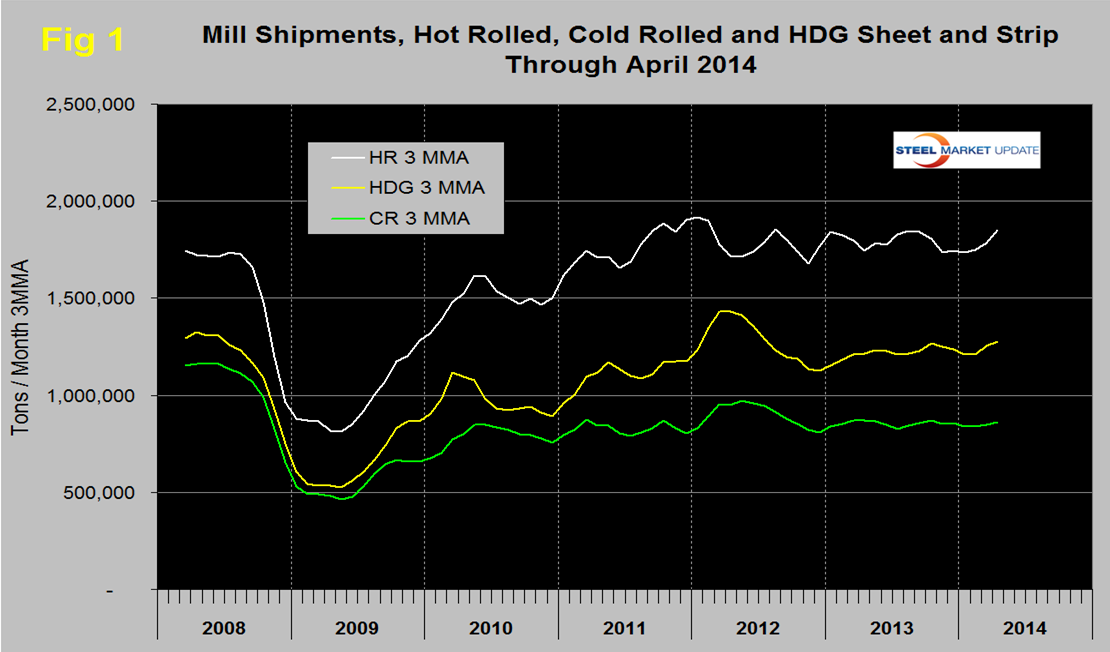
Figure 1 shows a six year trend for hot rolled, cold rolled and HDG. Following the post recession recovery, hot rolled has been little changed for two years but with another good month could break out of the range that has prevailed for that time period. Shipments of hot dipped galvanized sheet and strip declined strongly in Q2 through Q4 2012 but has been improving steadily for 18 months. Cold rolled shipments have shown little direction for almost two years. This analysis is based on shipments to domestic locations plus exports and uses the AISI AIS10 monthly report and Commerce Department trade data.
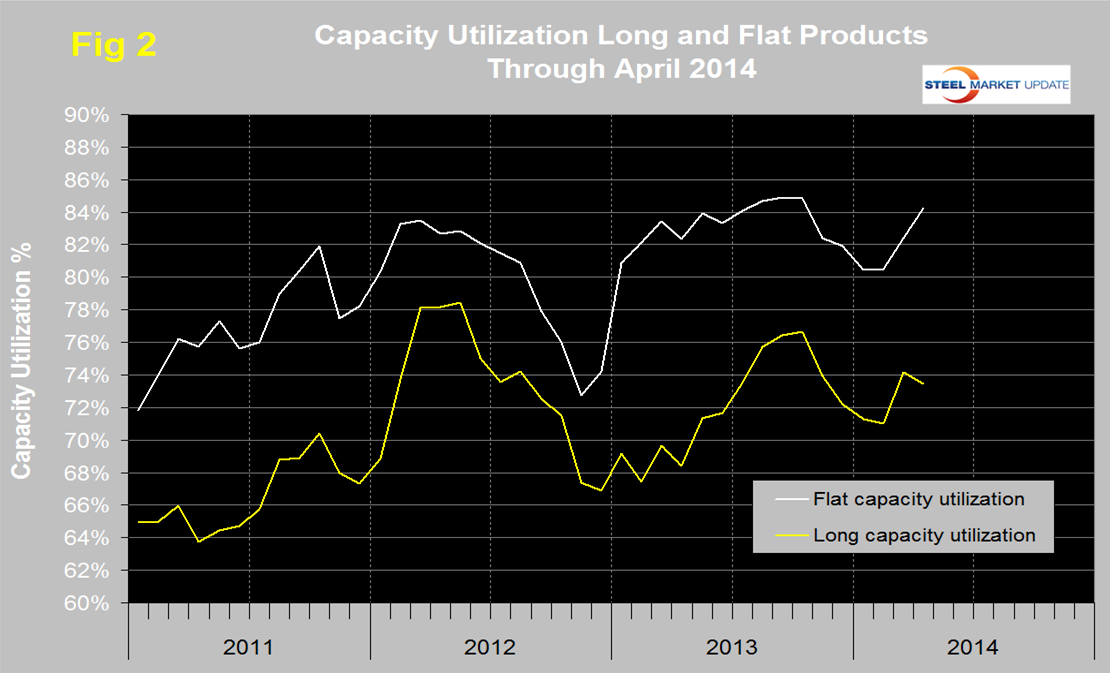
Capacity utilization of the flat rolled mills continues to outperform long products by a wide margin, (Figure 2). On a three month moving average basis, the capacity utilization of the flat rolled mills in April was 84.2 percent compared to 73.4 percent for the long product mills.
The logic of these capacity utilization calculations is as follows: Calculate total steel mill capacity using the crude production tonnage divided by capacity utilization reported by AISI weekly. Multiply that number by 0.9 to get the rolled product capacity. This has to be an industry wide rationalization because integrated hot mills with thick slab feed have a lower mill yield than thin slab compact strip mills. Subtract the rolled product capacity of the long product mills which we feel we have a good handle on from SMA data which leaves flat rolled capacity. Then calculate flat rolled capacity utilization using shipment data from the AISI AIS10 report. Note the resulting utilization rate is for rolled products not for crude steel. Please feel free to challenge this logic if you see fit. This is definitely not an exact science.