CRU
November 1, 2024
CRU: What will the US elections mean for climate policy?
Written by Frank Eich
SMU is pleased to share this Insight piece from CRU economists. You can visit the CRU website to learn about its global commodities research and analysis services.
The US presidential election will take place this Tuesday, Nov. 5, with opinion polls indicating a tight race between the two main contenders, Democrat Kamala Harris and Republican Donald Trump, who have diametrically opposing views on the green transition. On the same day, 34 out of the 100 seats in the US Senate are up for election. In this policy Insight, we suggest that the election outcome clearly matters for climate policies, but perhaps less than suggested by current rhetoric.
Please also see our accompanying Insight, shared by SMU last week, which focuses on the likely broader economic implications of a Harris or Trump win.
Climate change is not a top priority in the US presidential election
Does it matter for US climate policies whether a Democrat or a Republican wins the US presidential election? A superficial look at previous US administrations’ involvement in global climate efforts suggests that it does: The country entered the Paris Agreement in September 2016 under then President Barack Obama, a Democrat, before withdrawing in 2020 under Republican President Trump, just to rejoin once again under outgoing Democrat President Biden, also a Democrat.
US climate policies clearly matter globally – the country is the second largest greenhouse gas emitter globally (after China and ahead of India) and by far the largest oil producer, ahead of Saudi Arabia and Russia. In 2021, the current Biden Administration committed to at least halving emissions by 2030 from its 2005 level, reaching 100% carbon pollution-free electricity by 2035 and net zero by 2050 at the latest. At COP28 in late 2023, the US government, alongside other governments, agreed to submit more ambitious Nationally Defined Contributions in 2025.
The 2022 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is the flagship climate policy launched under the outgoing Biden Administration. The IRA opened a new chapter in US environmental policies, promising nearly $370 billion over 10 years in targeted incentives to support clean technology investment in an effort to reduce emissions and put the US at the forefront of green technologies of the future.
Recent opinion polls by nonpartisan think tanks such as the Pew Research Center and pollsters such as YouGov suggest though that US voters are currently more concerned about the state of the economy and cost of living, healthcare and abortion, crime, and Supreme Court appointments than climate change. Even for traditional Democrat voters, who are generally far more concerned about the environment than Republican voters, climate change does not appear to be a top election priority.
Harris and Trump hold opposing views on the future of the energy transition and how to address climate change
The differences between the Democratic and Republican parties’ election platforms on climate change could not be more stark. “Tackling the climate crisis, lowering energy costs, and securing energy independence” is one of the nine policy priorities in the Democratic Party’s 2024 election platform. The Democratic Party wants the US to lead the world in clean energy production and adoption, pledging additional financial incentives and streamlined permitting processes to make this vision a reality.
Democrats are determined to lower energy costs for households by providing tax credits and rebates to improve home insulation or purchase plug-in hybrids or fully electric cars. They also intend to create new jobs in the clean energy sector. Another focus of their policy is to reduce pollution by investing in transportation infrastructure (America’s largest emitting sector) by strengthening environmental and safety standards to reduce toxic pollutants like smog, soot, and methane, and even setting a national drinking water standard. They are also committed to “making polluters pay” and strengthening civil and criminal enforcement of environmental law. Click here to expand the image below.
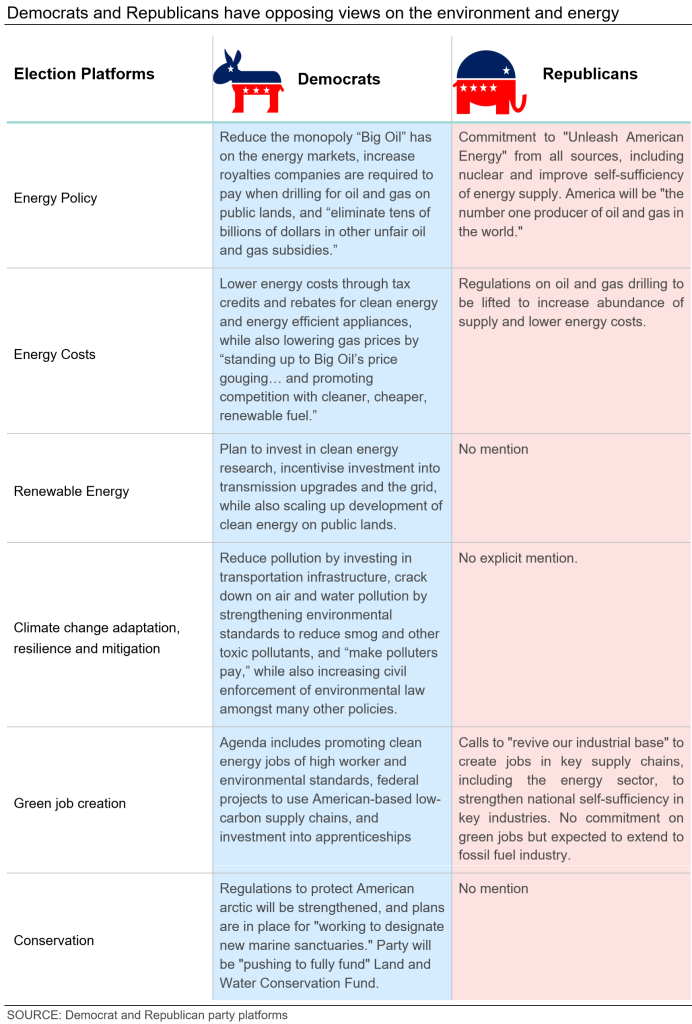
By contrast, climate change action is not featured in the Republican Party’s 2024 election platform. Instead, under the title “America First: A Return to Common Sense,” the Republicans make 20 promises, including No. 4: “Make America the dominant energy producer in the world, by far,” and No. 15: “Cancel the electric vehicle mandate and cut costly and burdensome regulations.”
According to the Republican Party, committing to these promises will help to defeat inflation and bring down prices, thereby addressing the cost-of-living crisis. Achieving this will require increasing American energy production from all sources, including nuclear power. Moreover, ending “market-distorting restrictions on oil, natural gas, and coal” will, according to the Republicans, help to support economic growth and prosperity.
A Trump victory would make withdrawal from the Paris Agreement likely but not necessarily spell the end of the IRA
If only for symbolic reasons, we would expect Trump, should he be elected as the 47th US president, to again withdraw the country from the Paris Agreement. When he withdrew it previously, it was widely feared that this could jeopardize global climate efforts. This fear proved unwarranted, with the global community raising its climate ambitions in subsequent COPs even without US participation.
Since then, the world has moved on, with China increasingly taking the lead in climate change mitigation efforts, the EU implementing its Green Deal, and many other governments stepping up their climate change efforts. We expect that global climate efforts and institutions are now established enough to withstand a potential US withdrawal from the Paris Agreement.
With respect to domestic climate policies, a Trump win would not necessarily spell the end of the IRA, as the financial support on offer has proven to be popular with households and industry, including in Republican-leaning states with strong manufacturing centers. As a result, even if the Republicans took the US Senate – the Democrats currently hold a narrow majority – there might not be enough support to repeal the IRA even if Trump wanted to do so. Click here to expand the image below.
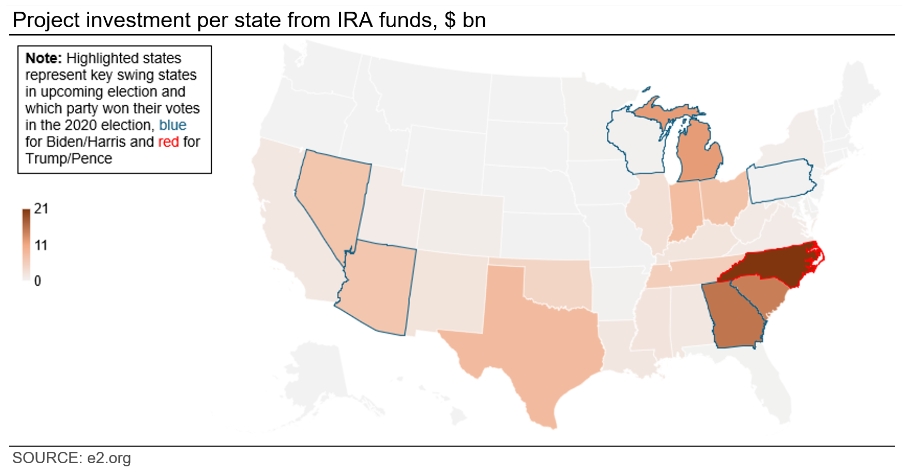
Instead of abolishing the IRA outright, Trump can be expected to reprioritize some of the incentives on offer and roll back environmental regulations, including on energy efficiency standards. Federal programs to support energy saving projects might also be cut.
Even if Harris wins, a federal carbon tax is unlikely, but there might be bipartisan support for a carbon border tax
As more countries launch domestic carbon pricing schemes, the US is increasingly an outlier in terms of lacking national-level carbon pricing. We expect this will remain the case after the election, as there is no bipartisan consensus on a federal-level carbon pricing scheme regardless of who wins.
This is not an issue on the state level. Democrat-led states are expected to further develop their existing carbon pricing schemes, despite regular pushback and occasional setbacks, to meet their own emission reduction and climate change targets (e.g. California has committed to reaching net zero by 2045). Click here to expand the image below.
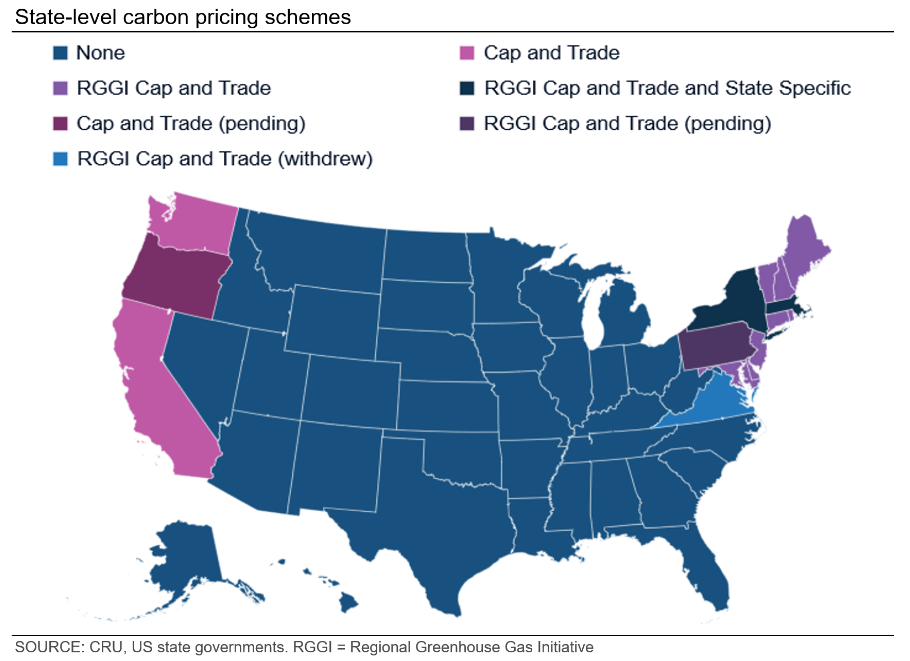
Closely linked to domestic carbon pricing schemes are carbon border adjustment mechanisms (CBAM). The EU’s CBAM, launched in late 2023 to complement the EU Emissions Trading Scheme, is the prime example, but other jurisdictions are currently considering their own variants.
While the absence of a domestic federal carbon price means that there is no domestic benchmark to set a US carbon border tax, US policymakers have considered workarounds, and there is growing bipartisan support for a US carbon adjustment mechanism, with four bills related to climate and trade (n.b. PROVE IT Act, Foreign Pollution Fee Act, Clean Competition Act and Market Choice Act) introduced in US congress in 2023 alone.
Such a policy could be attractive in terms of industrial policy – US industry generally emits less than competing industries elsewhere, and as such, has much to gain from such a levy – and could help to raise urgently needed revenue for the government to narrow the fiscal deficit.
The election outcome will shape US climate policies but perhaps less than suggested by current rhetoric
The outcome of the US presidential election will undoubtedly shape future US climate policies but perhaps by less than suggested by current political rhetoric. This is partly because much of the climate and environmental agenda rests with state governments and not the federal government, consumers and investors are generally supporting the green transition (despite some setbacks to the ESG agenda), and a Trump victory would probably not mean an outright end to the IRA. Moreover, regardless of who enters the White House, there is little appetite for a domestic carbon pricing scheme, but an emissions-based carbon border tax might see the light of day.
Additional authors contributing to this Insight: CRU Sustainability Analysts Lottie Zayed and Samuel Dath


