Market Data

July 8, 2022
Employment by Industry: Service, Manufacturing, Add Jobs in June
Written by David Schollaert
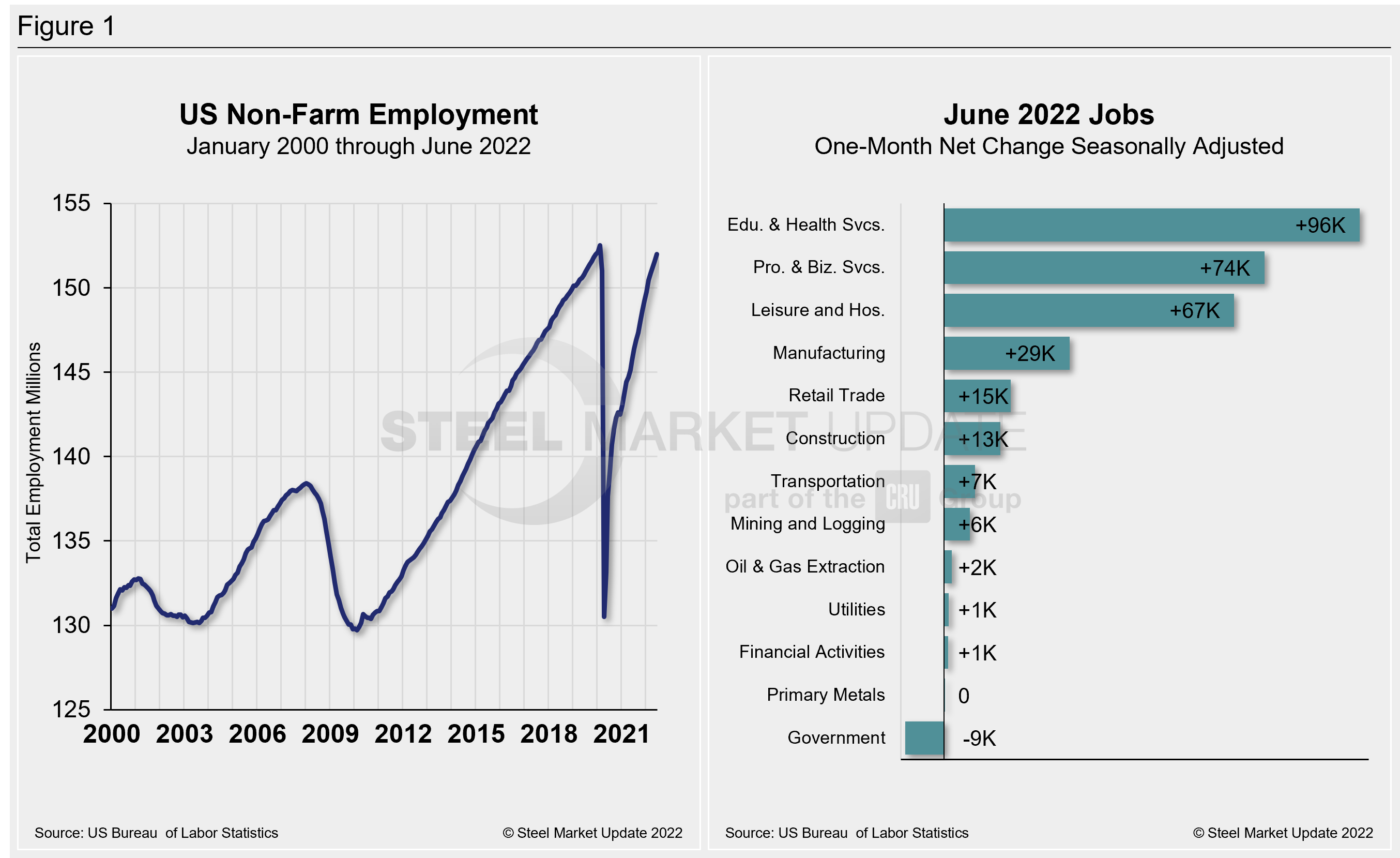
The US labor market added 372,000 jobs in June, an unexpected boost in hiring. It was ahead of most expectations and only slightly down from May’s revised 384,000 additional payrolls. The result kept the unemployment rate unchanged month on month (MoM) at the pandemic-era low of 3.6%, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported.
Payroll gains were better than economists had forecast, a signal that the labor market remains robust despite recession fears.
The report showed that job gains were not as widespread as they have been in recent past, though. Some industries saw more of a slowdown than others in June. Construction companies added just 13,000 jobs during the month – less than half as many as the month before – as homebuilding has declined in response to rising mortgage rates.
In June, professional and business services led will the job gains with 74,000. Leisure and hospitality, which includes restaurants and bars, the sector hit hardest by Covid, added 67,000; health care, 57,000; transportation and warehousing, 36,000; and manufacturing, 29,000.
Among those out of the labor force, some 610,000 people could not look for work in June because of the pandemic, up from 455,000 in the previous month. It is the first increase in this measure since the Omicron variant swept the nation in January.
Shown below in Figure 1 is the total number of people employed in the nonfarm economy as well as the month-on-month net change in total jobs in May.
Designed on rolling time periods of 1 month, 3 months, 1 year, and 2 years, the table below breaks total employment into service industries and goods-producing industries, and then into private and government employees. Most of the goods-producing employees work in manufacturing and construction. Comparing service and goods-producing industries in June shows both increased by just 0.2%. The steady and repeated gains have pushed both above pre-pandemic levels, where they’ve been for the past three straight months. Note, that the subcomponents of both manufacturing and construction shown in this table do not add up to the total because we have only included those with the most relevance to the steel industry.
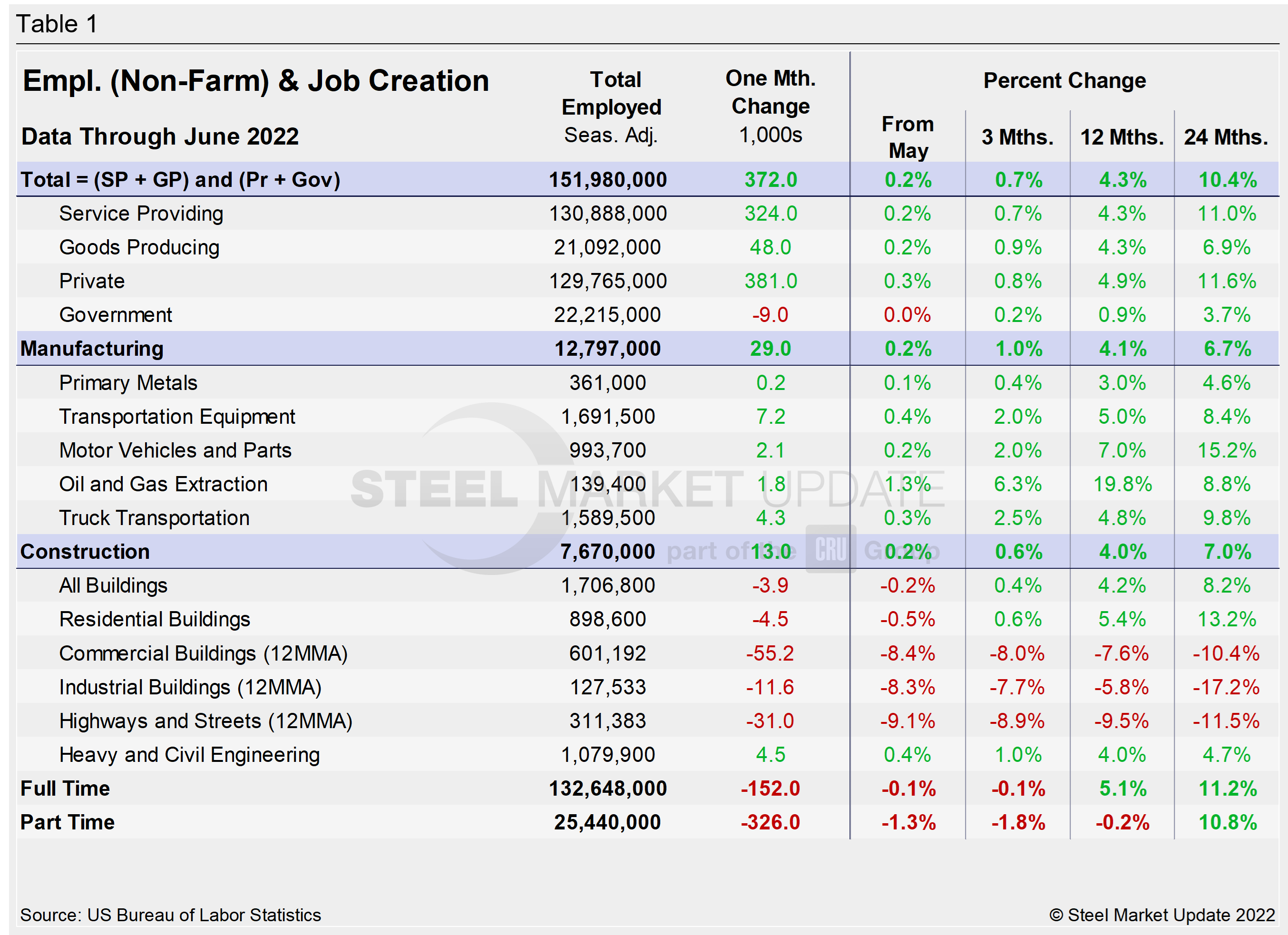
Comparing June to May, manufacturing employment was just 0.2% higher, a bit better than the 0.1% growth the month prior. Construction saw a 0.2% increase as well MoM, slower than the 0.5% gain in May. The construction sector, which had been driven by the residential market, is experiencing the impact of rising interest rates and inflation. That is undercutting homebuilding and overall commercial and industrial buildings. Only heavy and civil engineering saw a boost in June, propping up the overall sector slightly. The struggles reflect the obstacles still facing the US economy and domestic job creation.
The three-month and 12-month comparisons show a decent recovery. But some still lag the 24-month pre-pandemic comparisons by a wide margin. In the year-over-year (YoY) contrast, manufacturing is up 9.5% and construction is up 4.1%.
Manufacturing employment added 29,000 jobs in June, a stronger pace than the 18,000 added in May but well behind the 55,000 added in April. Construction was little changed at 13,000 new payrolls, down more than 50% from 34,000 added in May but far better than 3,000 total jobs lost in April.
Construction and manufacturing unemployment diverged in June. Construction unemployment fell 1.8% MoM from 392,000 in May to 385,000 in June. Manufacturing unemployment was up 10.2% MoM following a 13.7% decline the month prior. Manufacturing unemployment rose from 422,000 in May to 465,000 in June. Both sectors have been heavily impacted by supply-chain disruptions and labor force constraints.
The history of employment and unemployment in manufacturing and construction since January 2010 is shown below side-by-side in Figure 2, seasonally adjusted.
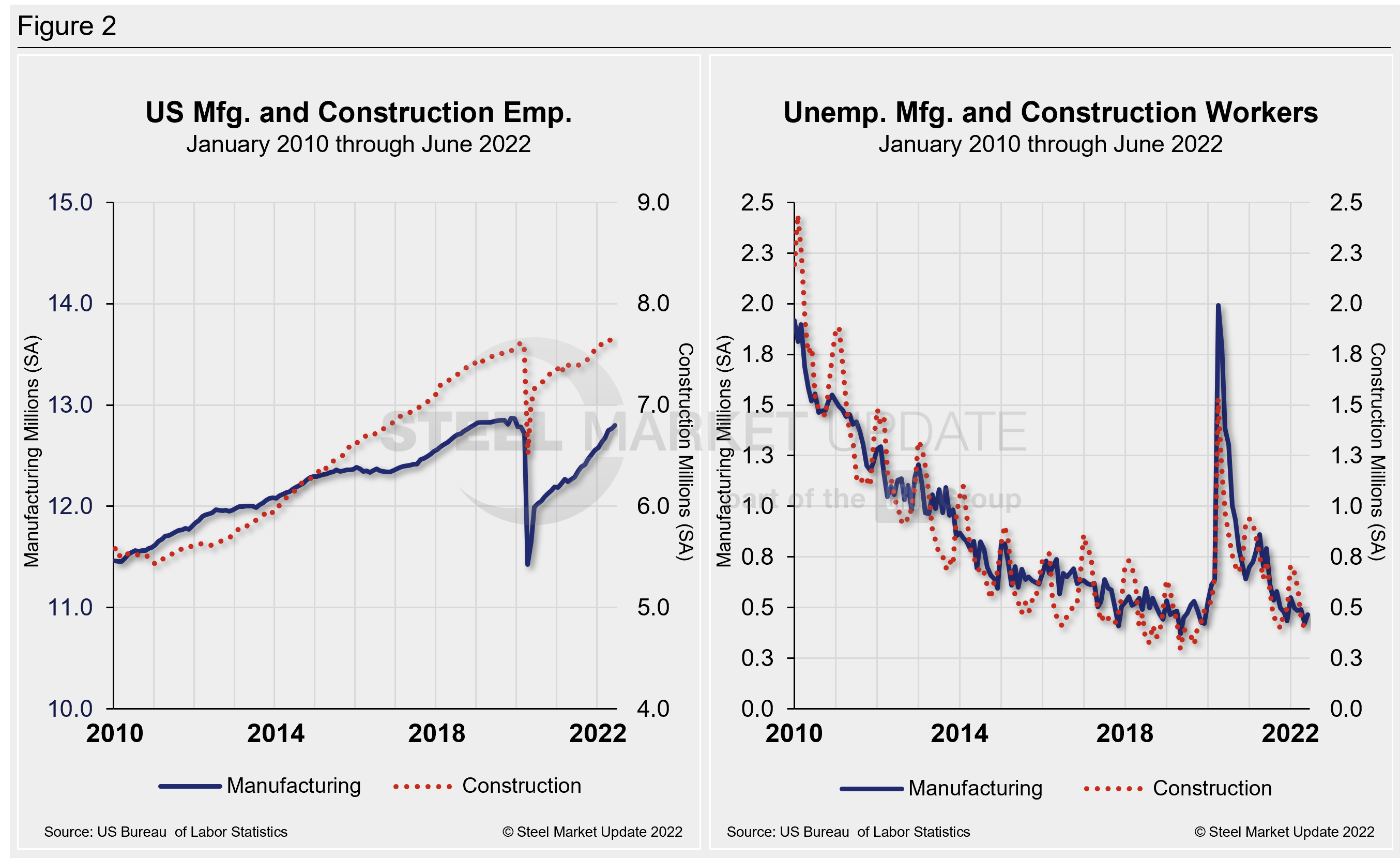
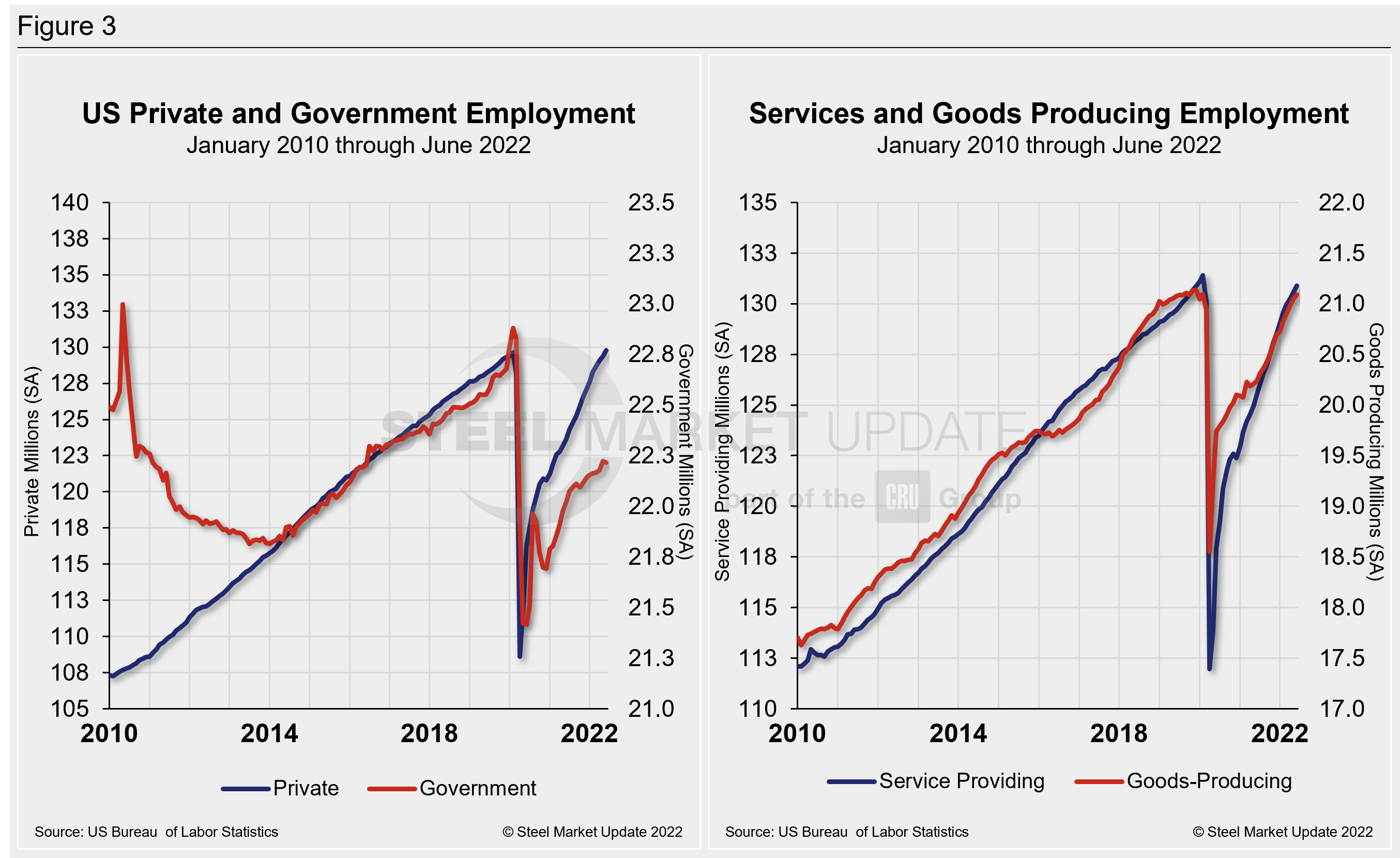
Figure 3 details employment comparisons between private and government jobs, as well as services and goods-producing jobs.
Explanation: On the first or second Friday of each month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the employment data for the previous month. Data is available at www.bls.gov. The BLS employment database is a reality check for other economic data streams such as manufacturing and construction. It is easy to drill down into the BLS database to obtain employment data for many subsectors of the economy. The important point about all these data streams is not necessarily the nominal numbers, but the direction in which they are headed.
By David Schollaert, David@SteelMarketUpdate.com







