Analysis

June 9, 2022
CPIP Data: Residential Construction Drives April Growth
Written by David Schollaert
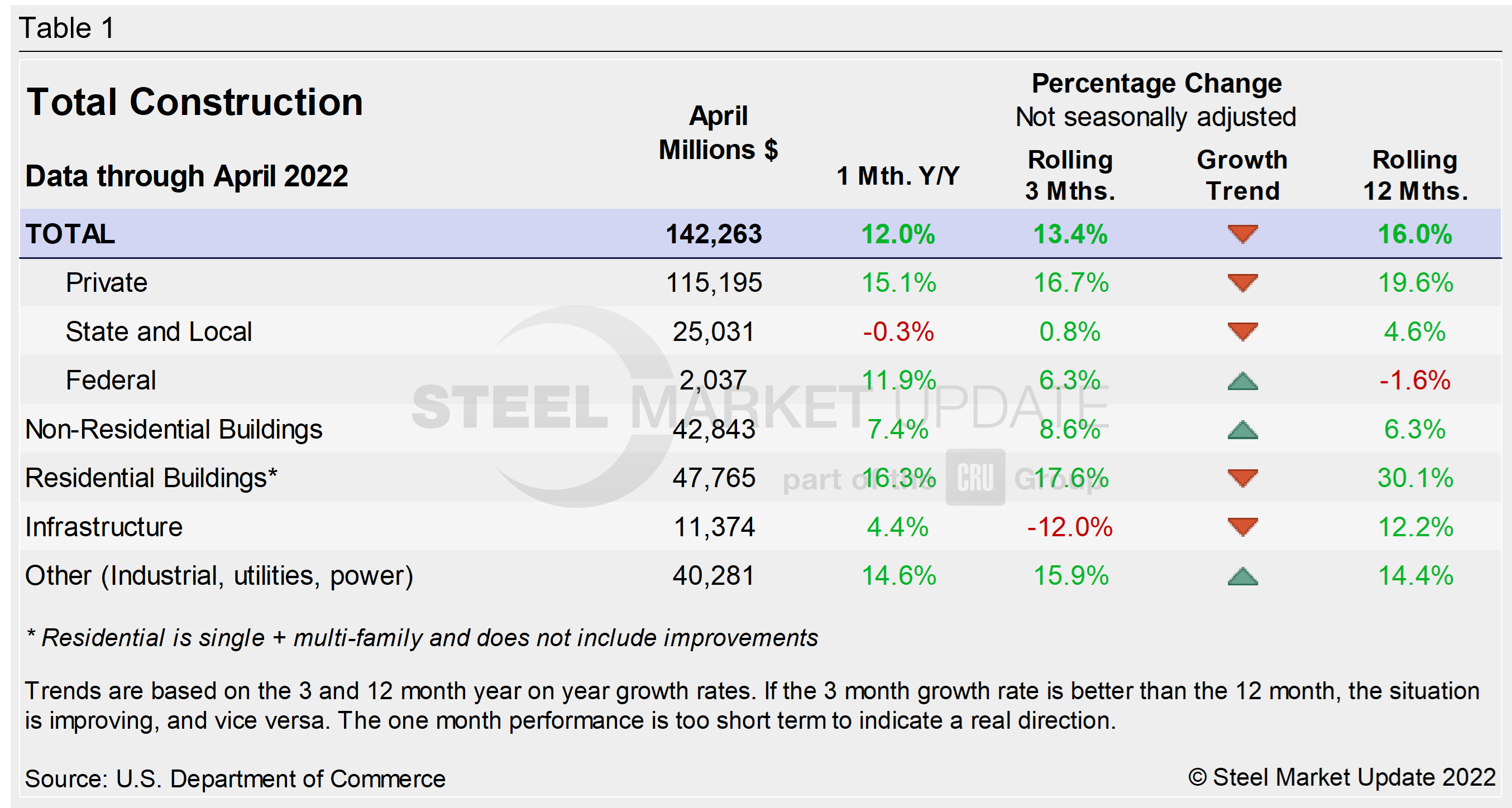
US construction spending in April totaled $1.744 trillion at a seasonally adjusted annual rate, just 0.2% above February’s upwardly revised $1.741 trillion. Investment in construction rose less than expected as an increase in private construction was partially offset by declines in public spending, the Commerce Department reported.
Construction spending in April missed expectations, easing from a 0.3% gain in March and behind earlier forecasts of roughly 0.5% growth. While month-over-month (MoM) growth disappointed in April, year-over-year (YoY) gains remain impressive. Construction spending in March was up 12.3% YoY – driven by residential (+18.4% YoY) growth.
The Census Bureau’s report on construction shows spending in the private sector increased 0.5% from March to April at an annual rate of $1.394 trillion. The residential share of that spending rose 0.9% MoM compared to a gain of 1.0% in March. The annual rate in April was $891.5 billion, up 19.6% compared to April 2021. The nonresidential component fell 0.2% from the prior month but is still 10.5% higher than the same year-ago period.
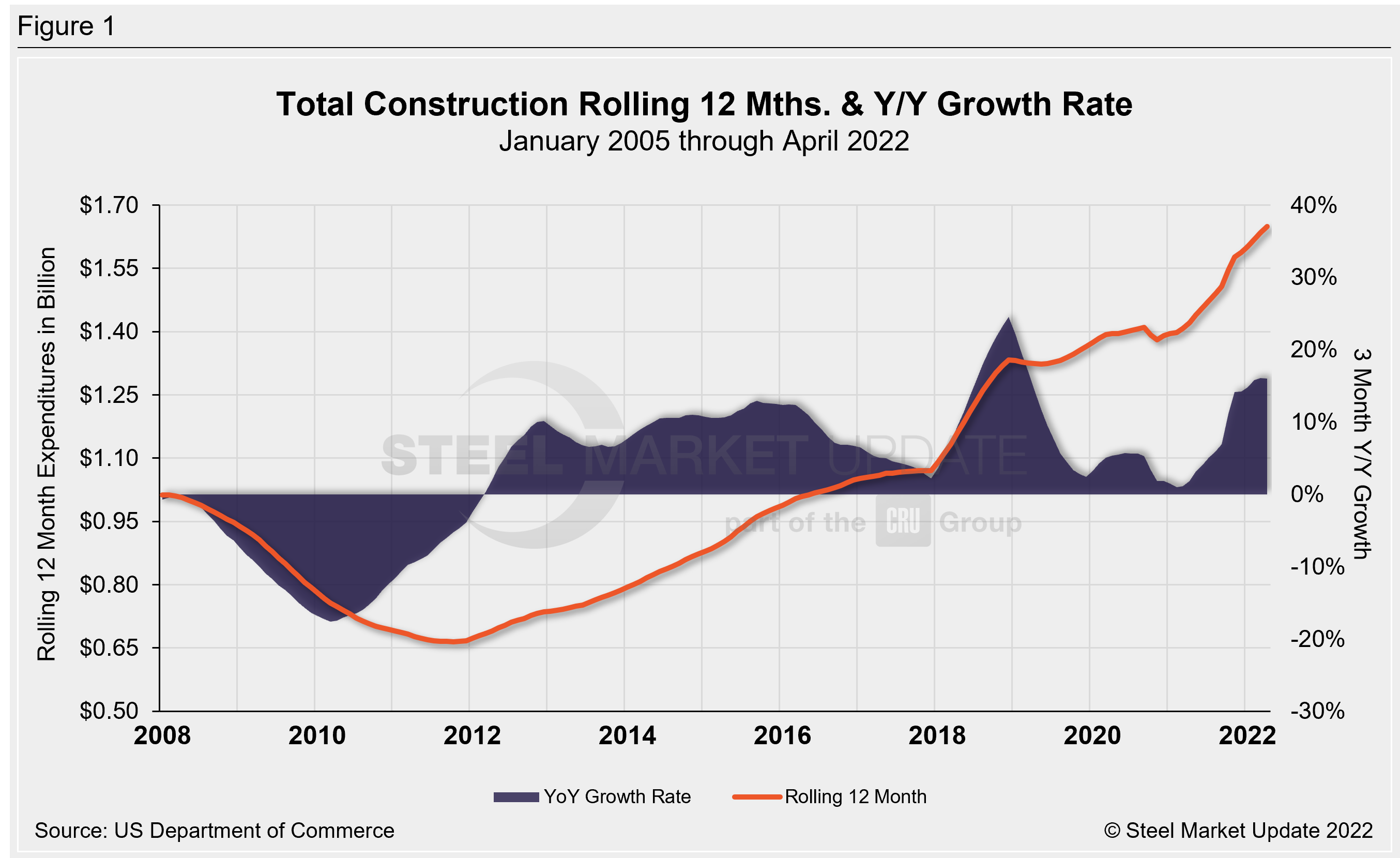
Total construction expenditures and their major categories are shown in Table 1 below. Figure 1 shows total construction and infrastructure expenditures. It details the year-on-year growth rate versus a rolling 12-month average.
Private Construction
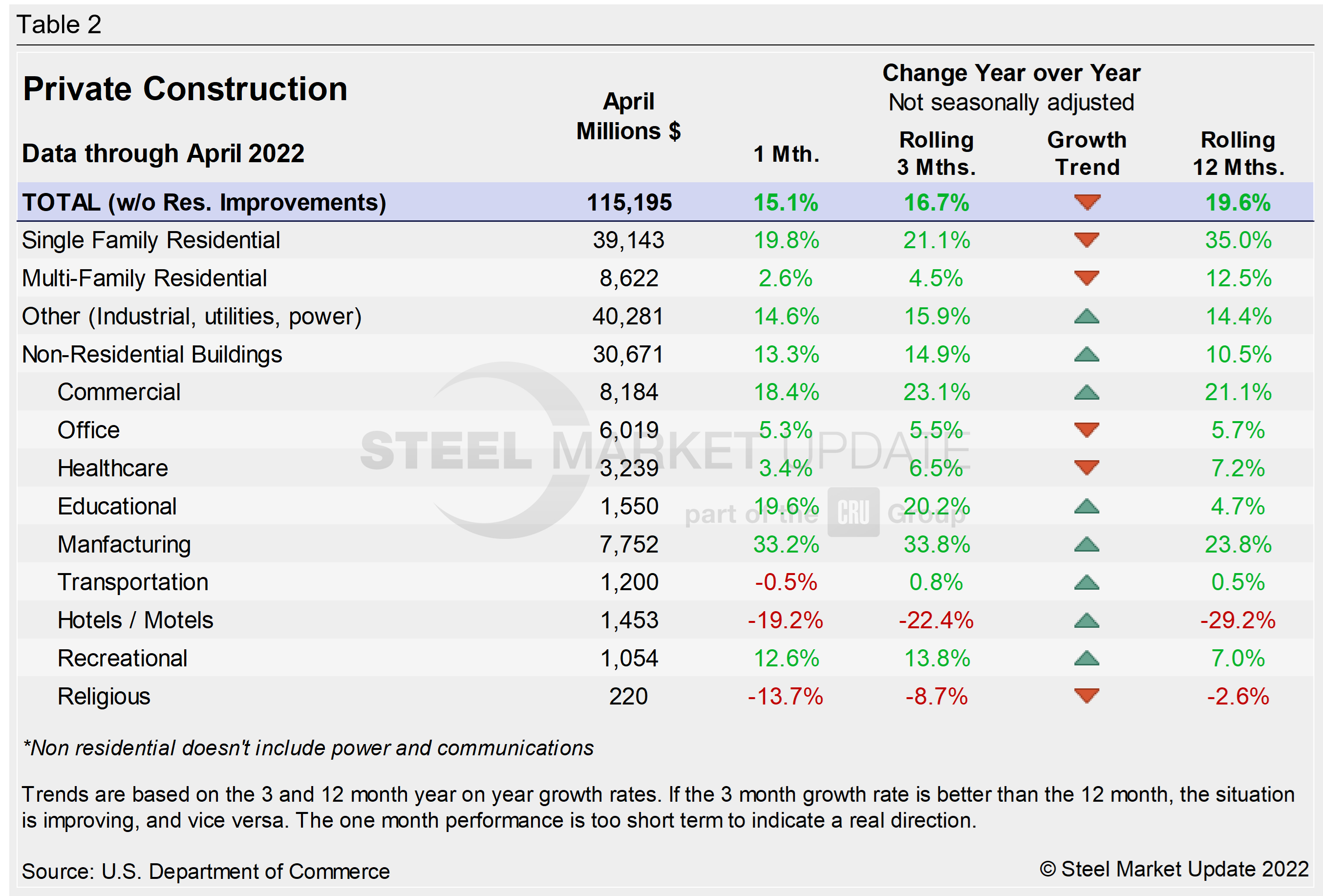
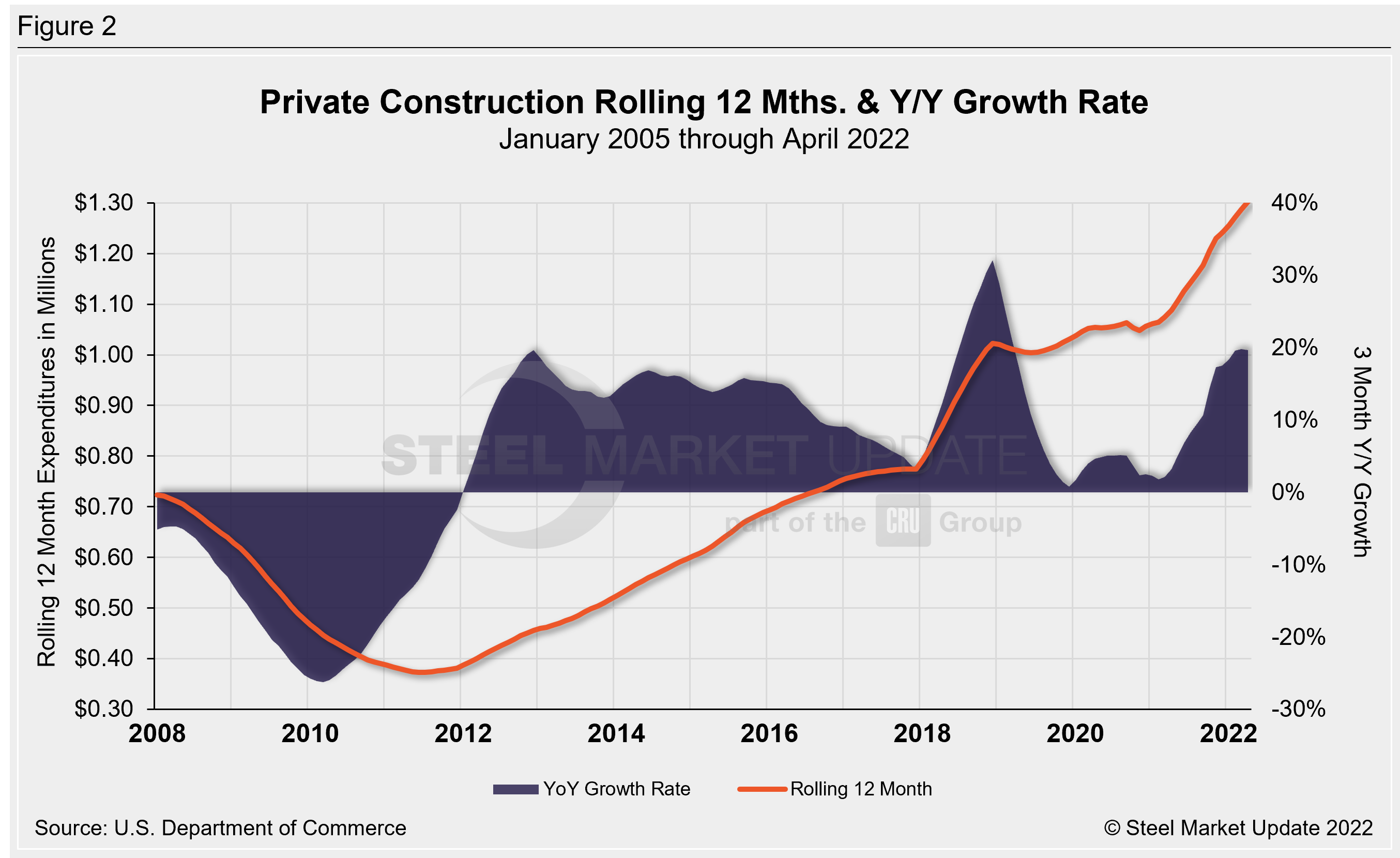
The breakdown of the $1.394 trillion private expenditures into residential and nonresidential, and their subsectors, are highlighted in Table 2 and Figure 2 below. Construction put in place in the private sector in April was up from March’s revised estimate of $1.388 trillion.
Within that category, residential construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $891.5 billion in April, 0.9% above the revised March estimate of $883.5 billion. Nonresidential construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $503.2 billion in April, 0.2% below the revised March estimate of $504.4 billion.
For the second straight month, residential claims the lion’s share of total private construction. It’s a staggering change with respect to the share of ‘total’ claimed by residential and nonresidential. Prior to the pandemic, the former almost always accounted for about 40% of total put-in-place construction, while the latter made up the other 60%.
The diverging trend with residential spending climbing and nonresidential slipping has residential investment accounting for more than half, nearly 55%, of all spending based on year-to-date, non-seasonally-adjusted data.
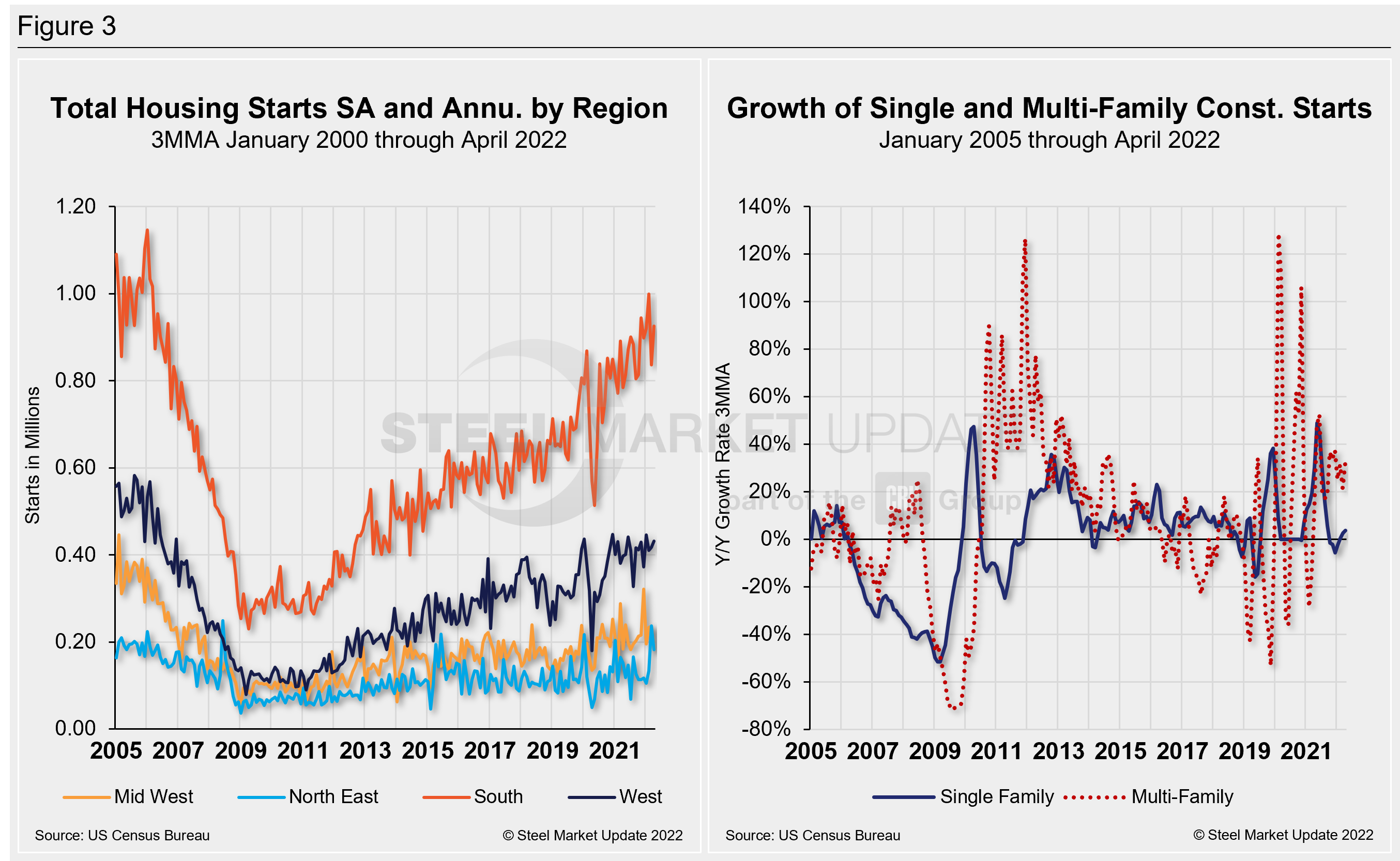
Despite April’s continued growth among residential segments, homebuilding remains constrained by higher prices for building materials. Total housing starts in four regions – the Midwest, Northeast, South and West – are displayed below (Figure 3). Figure three also displays the growth of single- and multi-family construction starts. Privately-owned housing starts in April were at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 1.724 million, down 0.2% from the revised March estimate of 1.728 million.
Regional results were split. The Midwest saw a 22% decline in April as starts totaled 184,000. The Northeast plunged 23.2%, with 182,000 starts. The West was up 3.3%, with 432,000 starts in April. And the South saw the largest percentage gain, a 10.6% jump with total starts of 926,000.
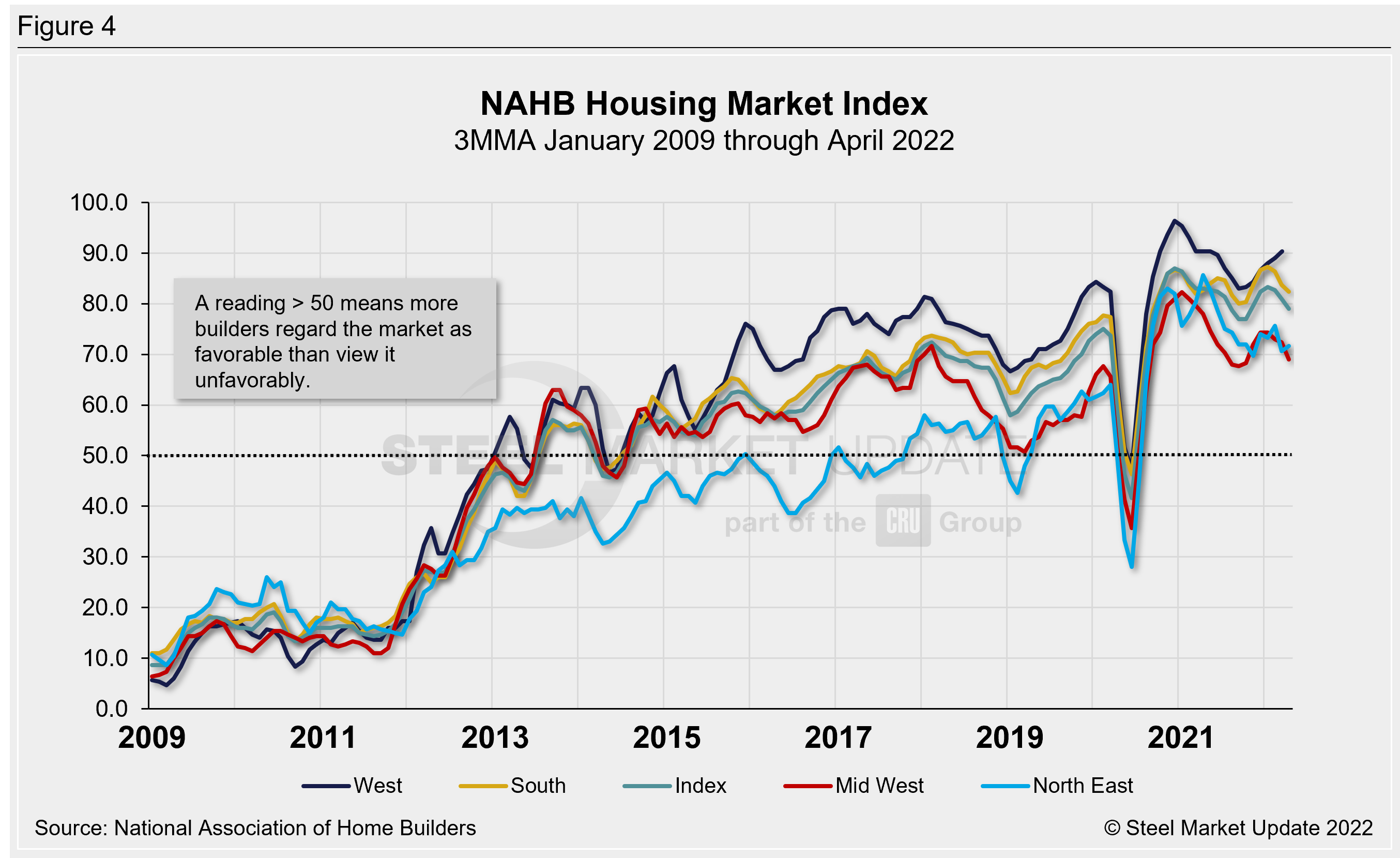
The National Association of Homebuilders (NAHB) said last month that building material production bottlenecks were raising construction costs and delaying projects. NAHB’s Optimism Index registered 77 in April, down slightly from 79 the month prior, and slipping for the fourth straight month. Advance reports indicate that the index may remain down in May (Figure 4).
State and Local Construction
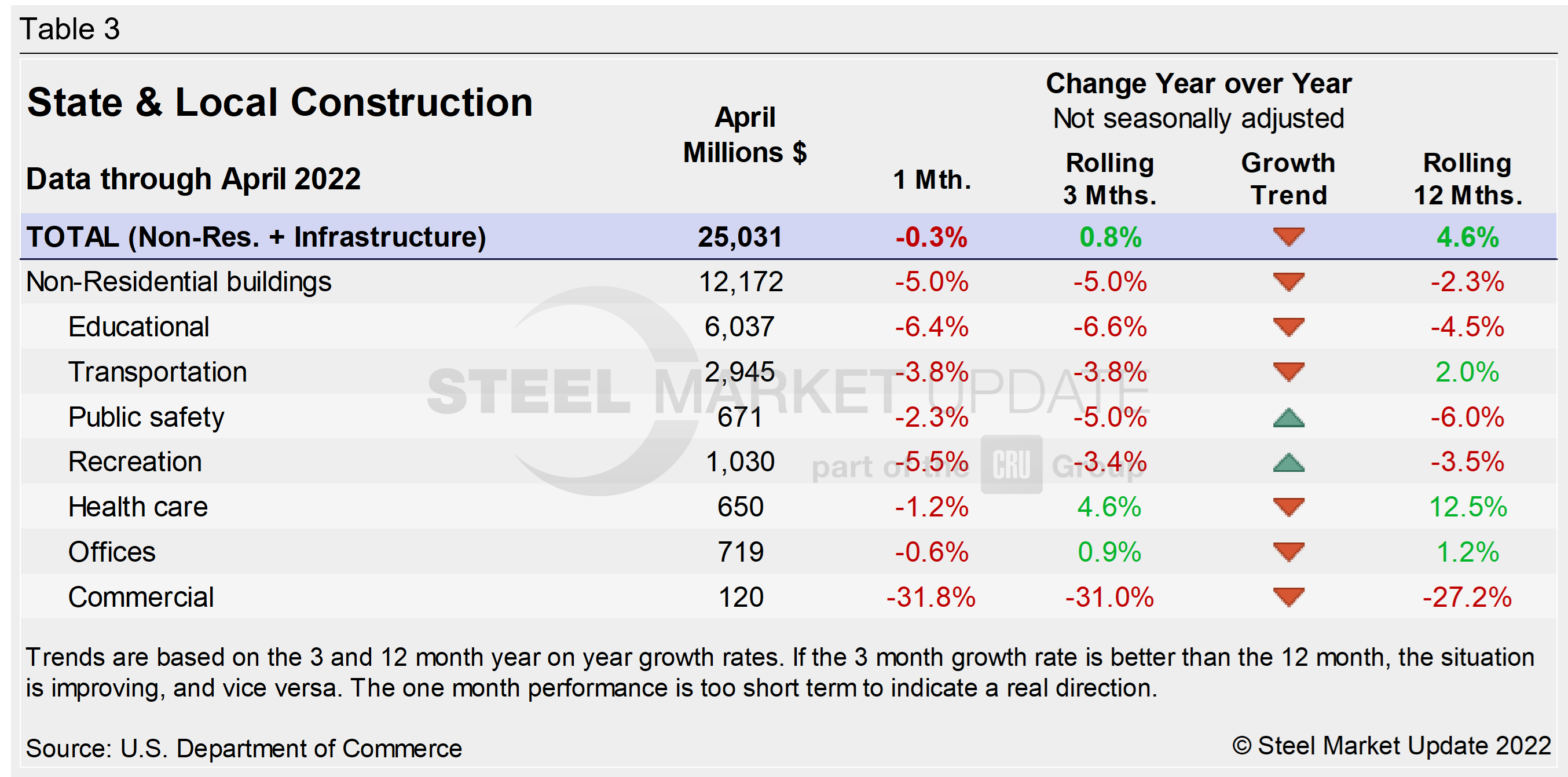
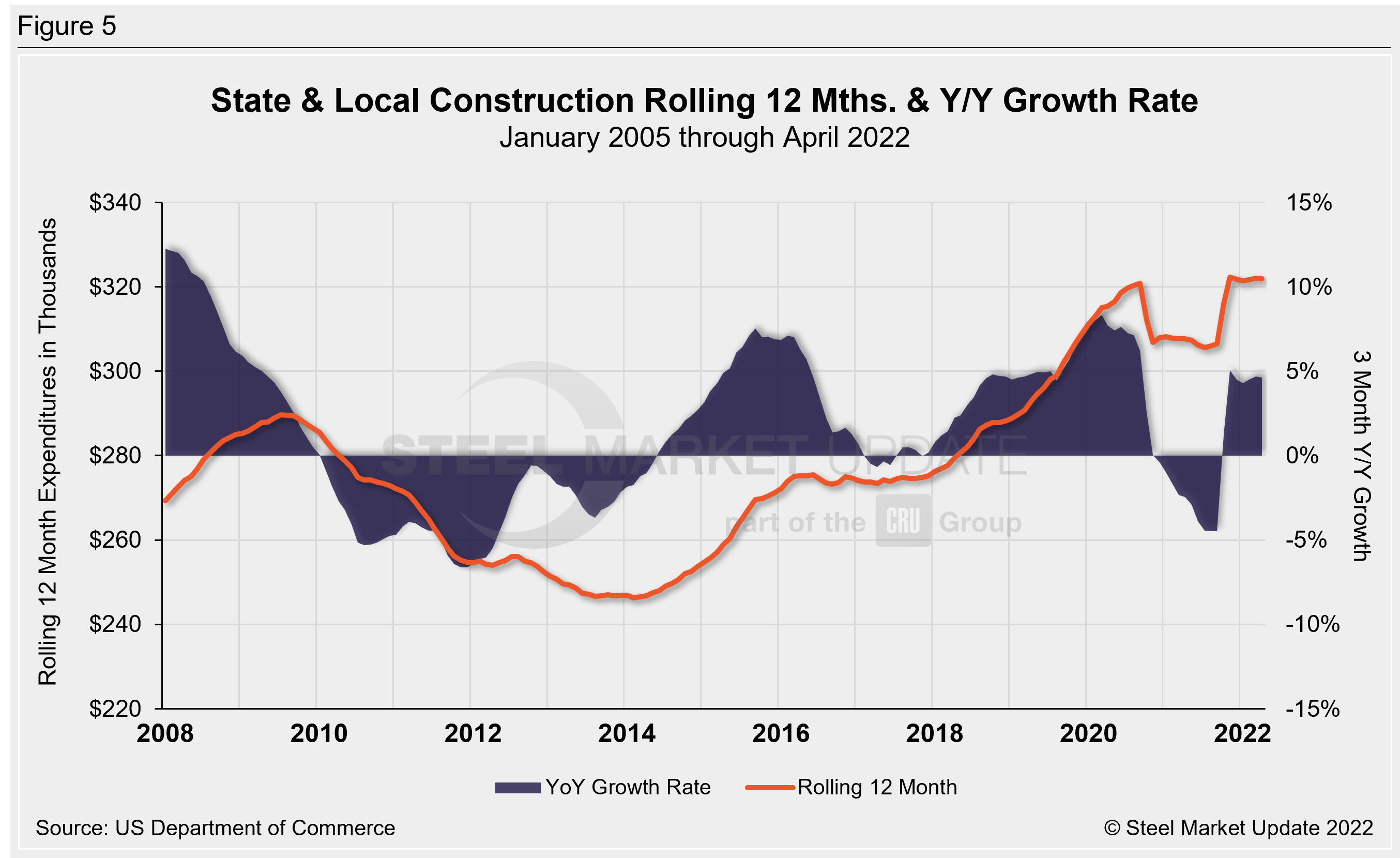
Publicly funded construction spending in April was $350.1 billion, at a seasonally adjusted rate, falling for the third straight month. April’s outlays slipped 0.7% below the revised February estimate of $352.7 billion. Spending on state and local government construction projects rose 10.5%, while federal government spending fell 8.9% month on month in April (see Table 3 and Figure 5 below).
Educational construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $79.6 billion, 0.7% below the revised March estimate of $80.1 billion. Highway construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $103.4 billion, 0.1% below the revised March estimate of $103.5 billion.
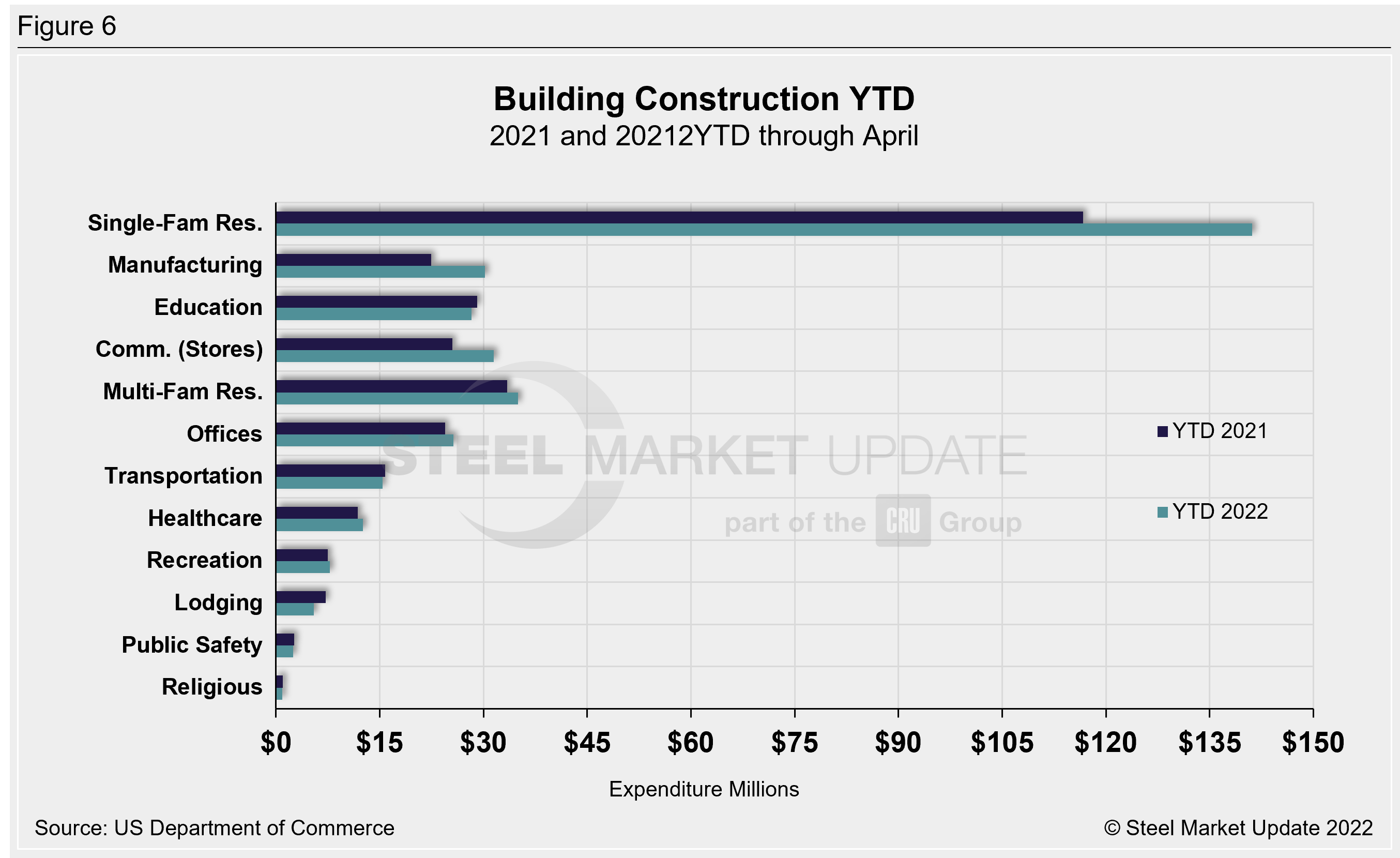
Year-to-date expenditures for construction of the various building sectors for 2021 and 2022 are compared in Figure 6. Single-family residential construction was dominant in 2021, with expenditures totaling $409.9 billion. The trend has continued into 2022: single-family residential totaled $141.1 billion through April, 20.9% above $116.7 billion a year ago. Manufacturing (+35%) saw the strongest subsector growth versus last year followed by commercial (+23.4%). Multifamily residential grew by 4.7% and totaled $34.9 billion when compared to the same year-ago period. Lodging is behind by double digits at 24.5% year on year, followed by religious and public safety, down by 10.5% and 7.4% respectively.
Explanation: Each month, the Commerce Department issues its Construction Put in Place (CPIP) data, usually on the first working day covering activity one month and one day earlier. There are three major categories based on funding source: private, state and local, and federal. Within these three groups are about 120 subcategories of construction projects. SMU analyzes the expenditures from the three funding categories to provide a concise summary of the steel-consuming sectors.
By David Schollaert, David@SteelMarketUpdate.com






