Market Data

January 8, 2021
Steel Product Shipments and Inventories Through November
Written by David Schollaert
Overall, steel product shipments continued to improve through November, reporting an increase for the seventh consecutive month. Despite the gains, the improvement continues at a slower pace than the overall manufacturing economy. The market is still working to recover from the initial effects of the Covid-19 shutdowns back in April. As a result, despite the steady rebound, the market is still working towards pre-pandemic levels.
The Census Bureau provides monthly data on inventories, shipments and new orders for total U.S. manufacturing and for individual industries, one of which is steel products. Every two months, Steel Market Update analyzes Census data to provide a reality check for steel industry trade association data, which is most widely used to assess the state of the industry.
Total shipments and inventories are reported in millions of dollars, seasonally adjusted. Year over year through November, total manufactured product shipments declined by 1.3 percent, while steel product shipments declined by 0.6 percent. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the history of both since 2005. During the first wave of the global pandemic in April, total manufacturing shipments plunged by 19.4 percent and steel product shipments fell by 21.4 percent compared with the prior year. Steel has steadily recovered since, though at a slower pace than manufacturing overall.
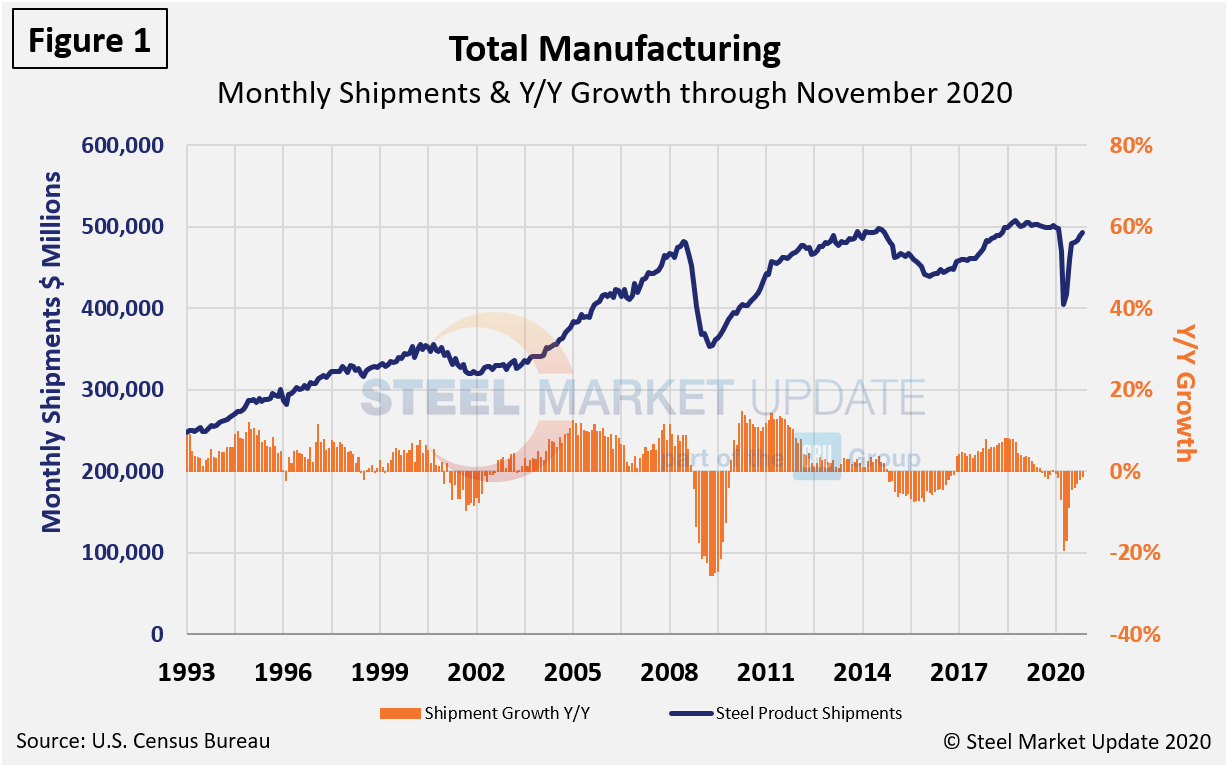
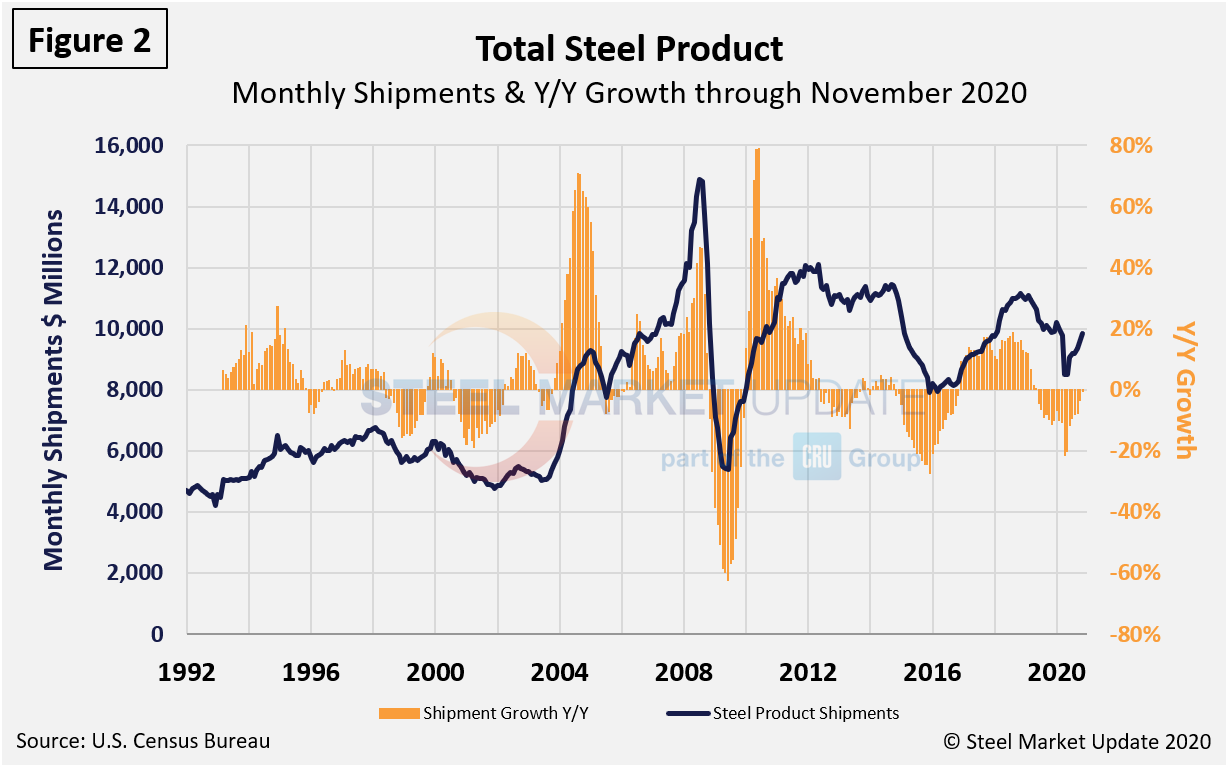
Figure 2 shows monthly steel product shipments in millions of dollars with the year-over-year growth through November. Through the first 11 months of 2020, shipments of steel products totalled $103.2 billion, down 11.3 percent from year-ago levels when shipments were $114.8 billion. Shipments of steel products most recently peaked in November 2018, then began a 17-month decline through April 2020. Although the growth rate has declined from 18.6 percent in August 2018 to just a negative 0.6 percent through November, shipments of steel products are up 13.7 percent since reaching bottom this past April.
Steel Market Update aims to provide information on the same subject from different sources for verification. The data in Figure 2 compares well over the long term with the AISI weekly crude steel production shown in Figure 3, which is more recent than the Census data. Figure 2 is in dollars and Figure 3 is in tons, yet they paint a similar picture. Despite the freefall that came to an end in late May, according AISI data shown in Figure 3 on a four-week moving average basis, a clear rebound has been seen since, but it pales in comparison to the drop. To date, crude steel production remained down by 13.9 percent in the week ending Jan. 2 year over year.
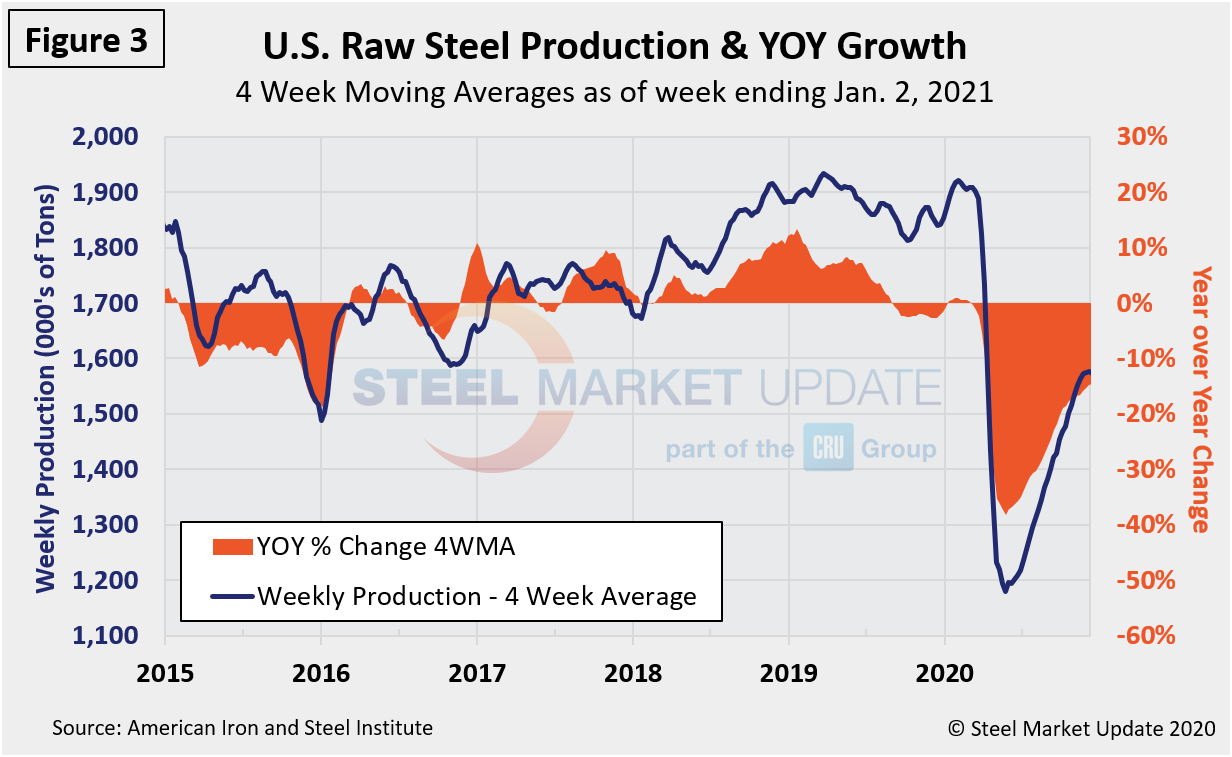
Figure 4 shows shipments and new orders on a monthly basis for all steel products since 2010. New orders declined much more than shipments in April, but were back in balance by June and have now exceeded shipments. However, with a slight curtailment in new orders, the gap has tightened over the past two months. This dynamic supports the near historic highs seen for flat rolled steel prices.
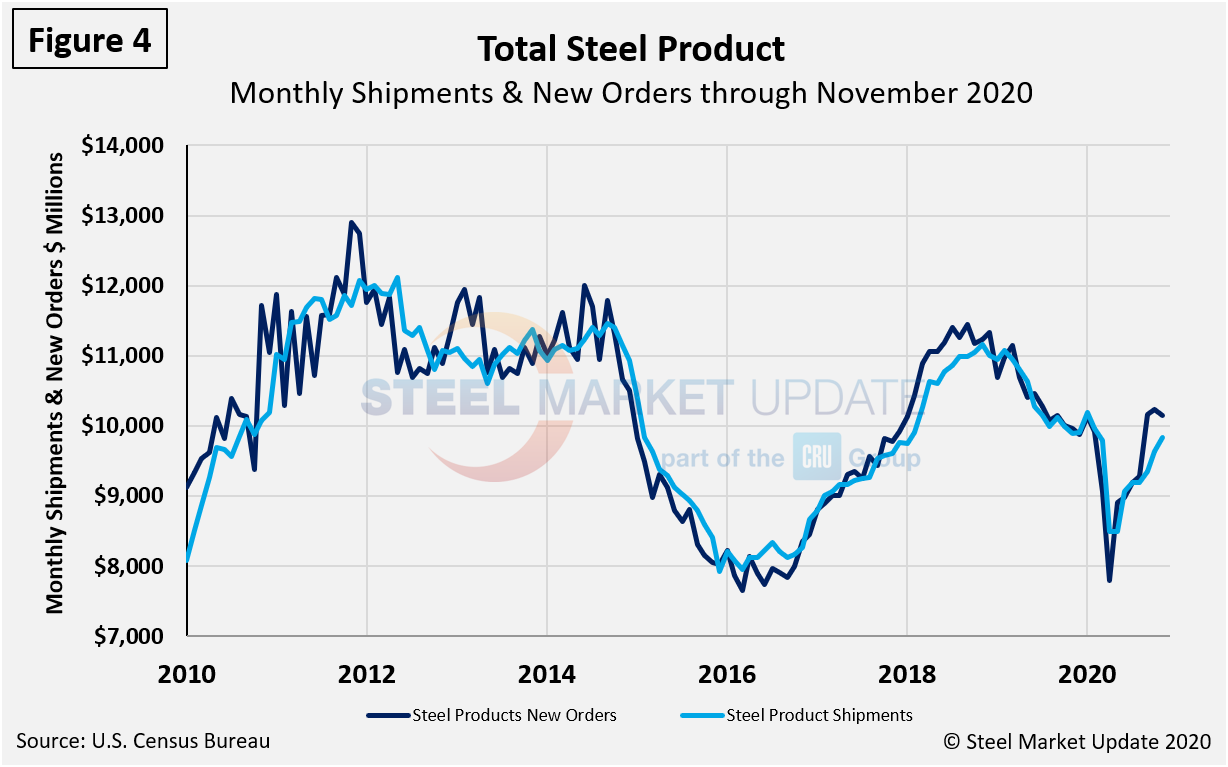
Figure 5 shows the same total shipment line as Figure 2, but now includes the inventory-to-shipment ratio. The IS ratio shot up in April, but has since declined to the recent norm. The IS ratio is a measure of how much inventory is necessary to support the level of shipments, thus the lower the IS ratio the better. Shipments have improved by nearly 14.0 percent since May.
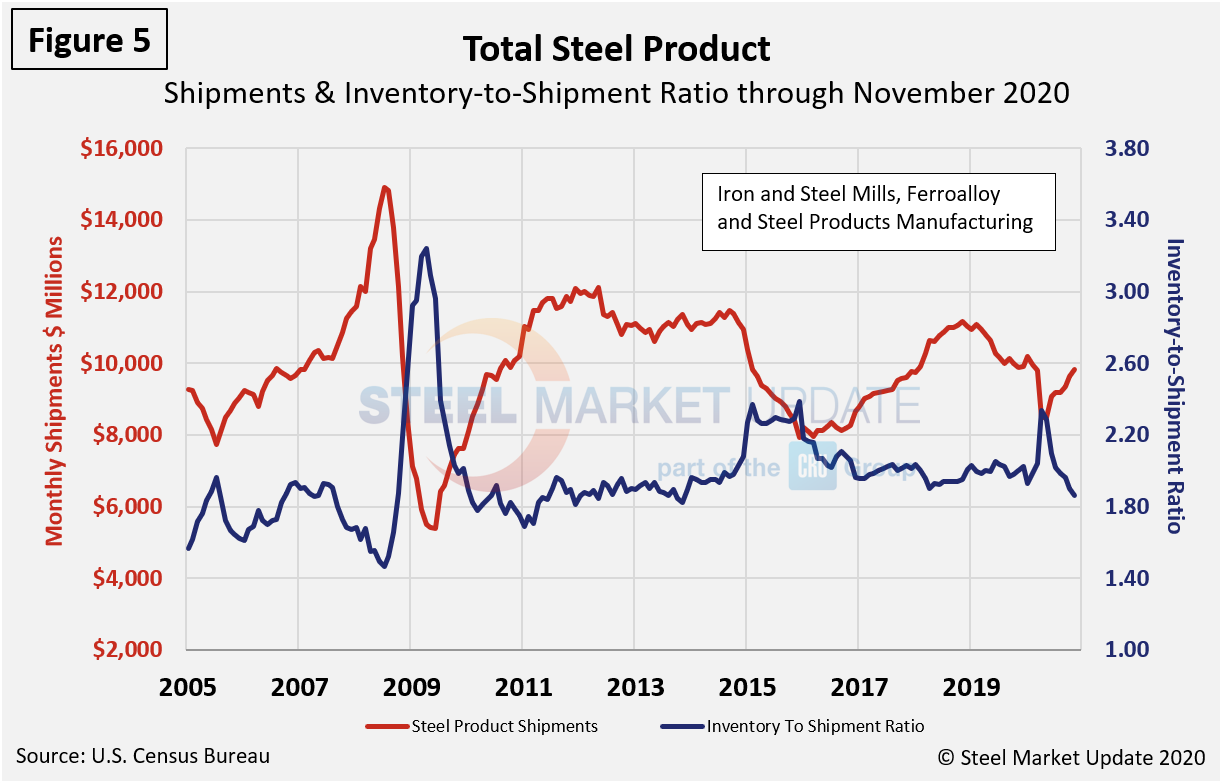
Figure 6 shows total inventory in millions of dollars and repeats the inventory-to-shipment ratio shown in Figure 5.
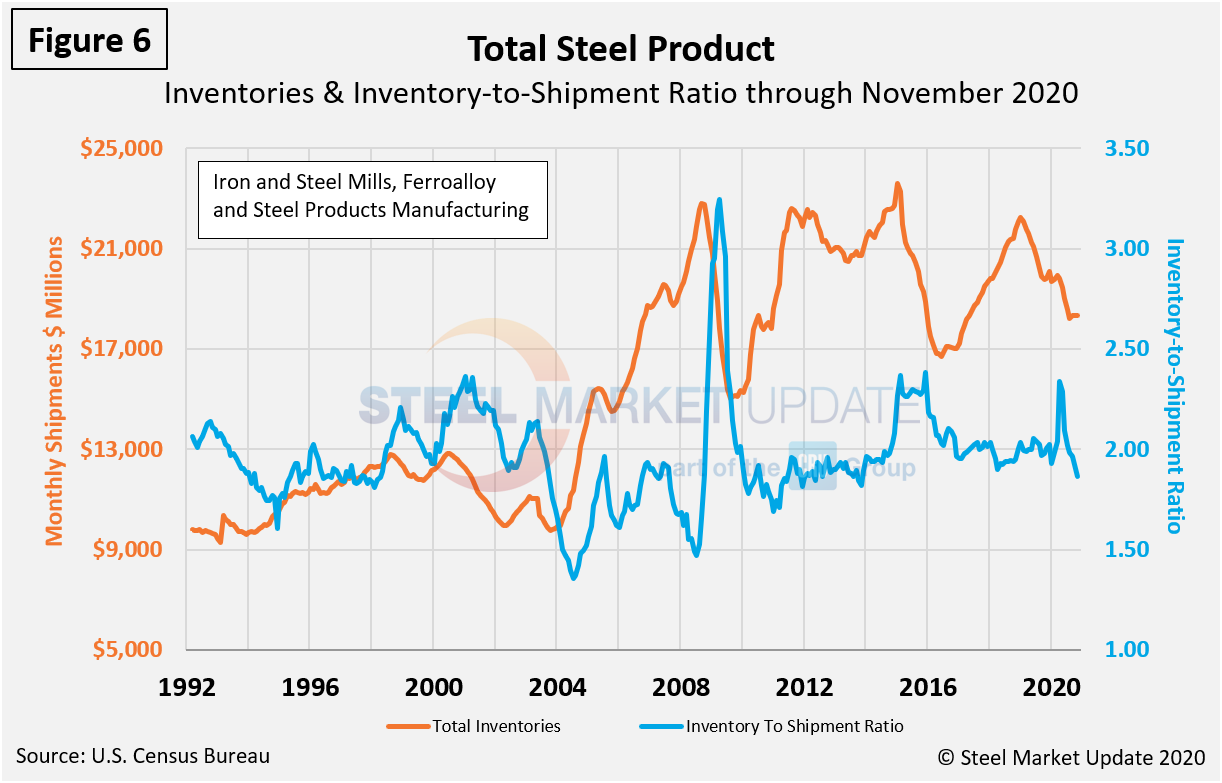
SMU Comment: The closest sample we have to the current decline in both manufactured and iron and steel product shipments was the recession of 2009. Despite the similarities, the current downturn hasn’t been as significant or as prolonged as it was 11 years ago. Data from the Census Bureau for steel product orders, shipments and inventories indicates that steel product shipments were hit harder than total manufacturing in April and May, but the steady rebound is where the contrast is most noteworthy. The inventory-to-shipment ratio of both total manufactured goods and products made from iron and steel peaked in April and declined through November 2020 and are now in line with pre-pandemic levels.
By David Schollaert, david@steelmarketupdate.com







