Analysis

July 1, 2019
SMU Analysis: CPIP Data Shows Strength in State and Local Construction
Written by Peter Wright
Steel Market Update is please to share this Premium content with Executive-level subscribers. For more information on upgrading to a Premium-level membership, email Info@SteelMarketUpdate.com.
Private construction contracted in the three-month period including March, April and May, but state and locally funded work, including infrastructure, continued to boom.
The Construction Put in Place (CPIP) expenditures data for May was released on July 1. Through May, total construction saw slowing momentum every month this year as a result of negative growth of privately funded work. But infrastructure and state and local projects remain strong, according to Steel Market Update’s analysis of Commerce Department data
![]()
At SMU, we analyze the CPIP data to provide a clear description of activity that accounts for about 45 percent of total U.S. steel consumption. See the end of this report for more detail on how we perform this analysis and structure the data. In particular, note that we present non-seasonally adjusted numbers and we don’t include expenditures for residential improvements. Our rationale is that construction is highly seasonal and our businesses function in a seasonal world, and home improvements don’t consume much steel. The growth or contraction that we report in this analysis has had seasonality removed by providing only year-over-year comparisons. For these reasons our results may not align with other sources.
Total Construction
Total construction expanded by 2.7 percent in three months through May and by 3.9 percent in 12 months through May, both year over year. Since the three-month growth rate is lower than the 12-month rate, we conclude that momentum is negative. May construction expenditures totaled $96.835 billion, which breaks down to $67.3 billion of private work, $27.5 billion of state and locally funded (S&L) work, and $1.9 billion of federally funded work (Table 1). Growth trend columns in all four tables in this report show momentum.
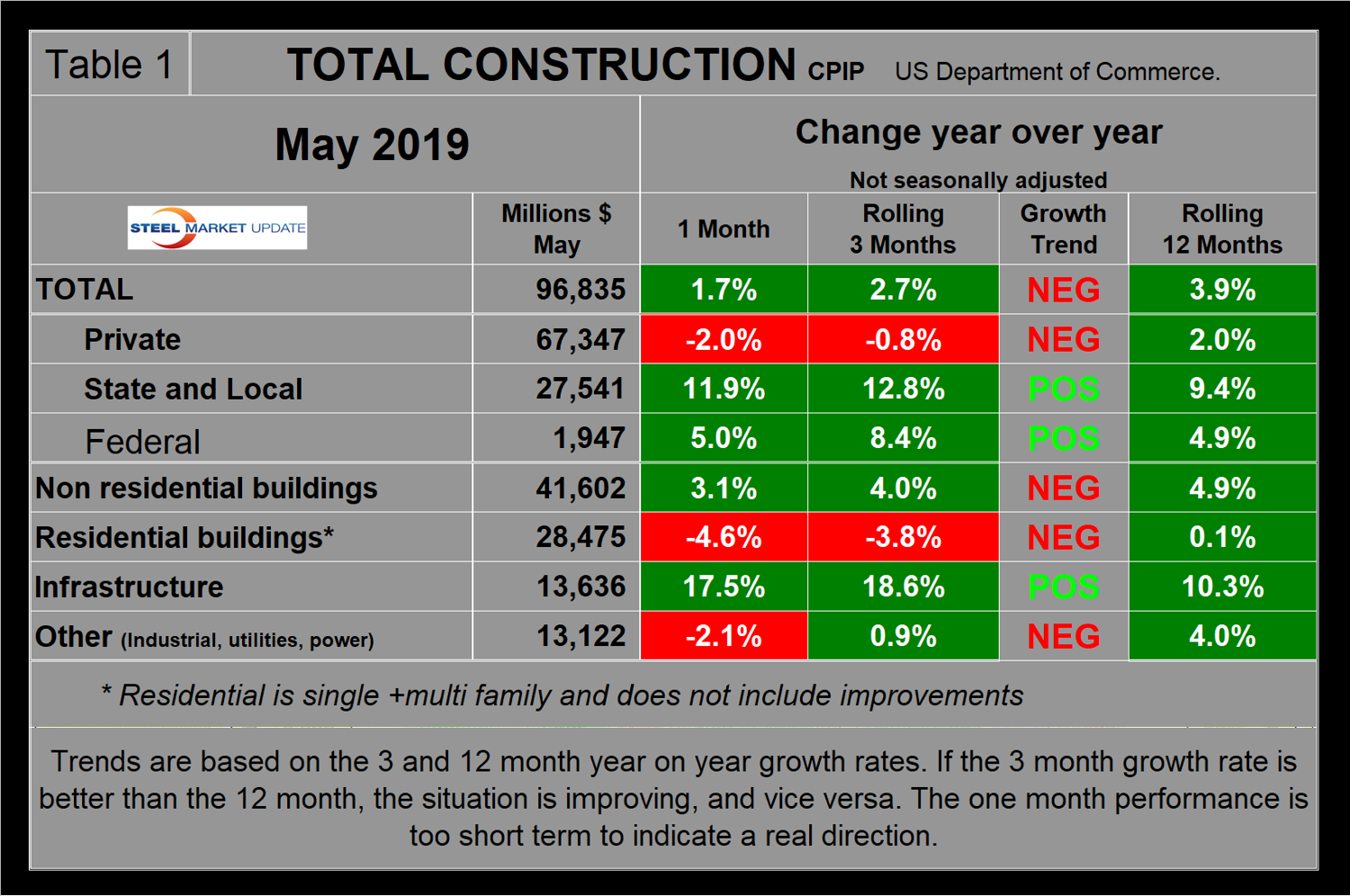
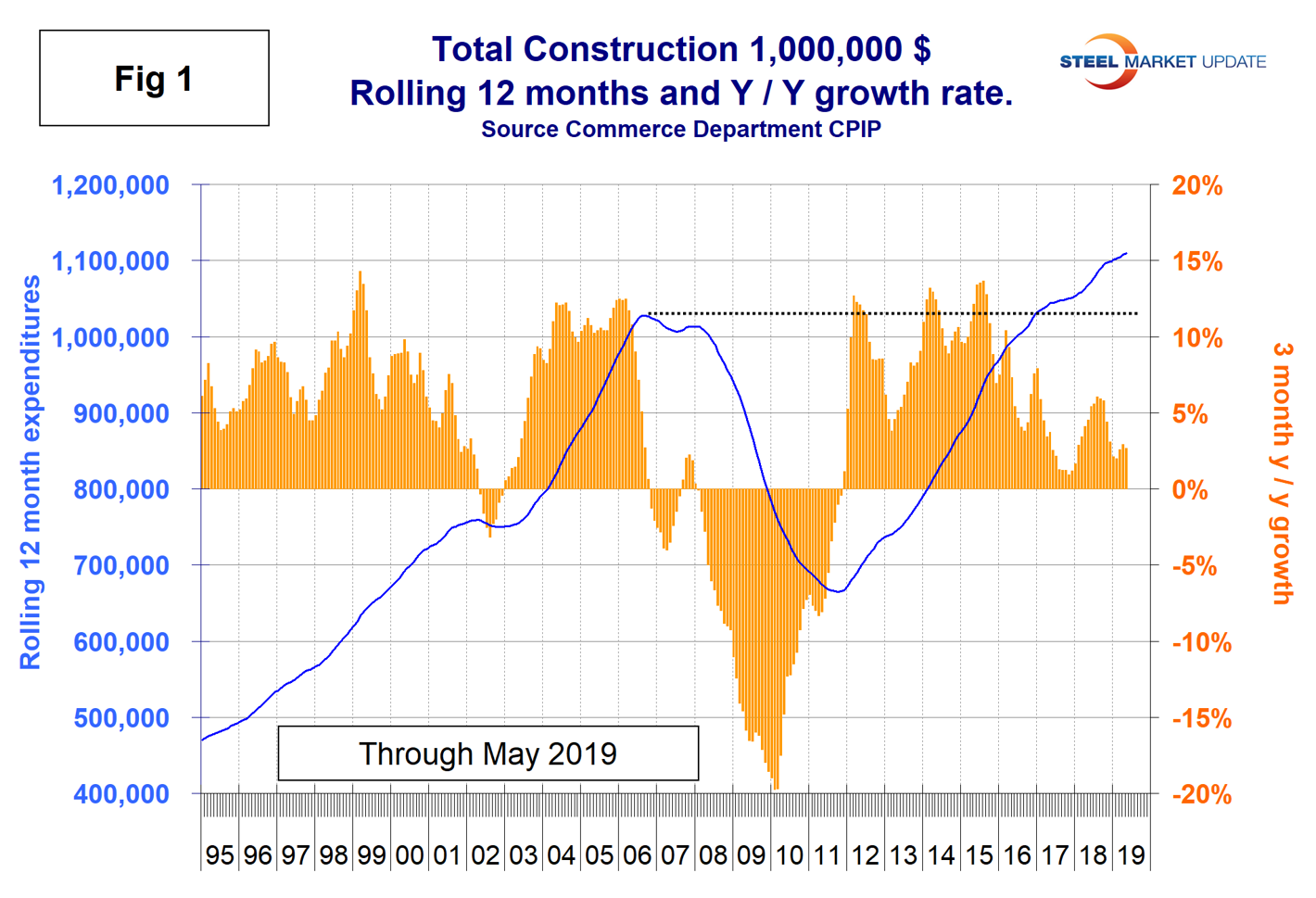
Figure 1 shows total construction expenditures on a rolling 12-month basis as the blue line and the rolling three-month year-over-year growth rate as the brown bars. Total construction in the 12 months through May hit an all-time high, but the brown bars show growth is lackluster.
Figures 1, 2, 6, 7 and 9 in this analysis have the same format, the result of which is to smooth out variation and eliminate seasonality. We consider four sectors within total construction: nonresidential, residential, infrastructure and other. The latter is a catchall and includes industrial, utilities and power. Of these four sectors, infrastructure and federal had positive momentum in May.
The pre-recession peak of total construction on a rolling 12-month basis was $1.028 trillion through November 2006. The low point was $665.1 billion in the 12 months through March 2011. In 12 months through May 2019, construction expenditures totaled $1.110 trillion. (This number excludes residential improvements; see explanation below.)
Private Construction
Table 2 shows the breakdown of private expenditures into residential and nonresidential and subsectors of both. The growth rate of private construction in three months through May 2019 was negative 0.8 percent, down from positive 4.9 percent in three months through last July. Growth has declined continuously in every one of those months as shown by the brown bars in Figure 2. April and May were the first months for private construction to experience negative growth since July 2011.
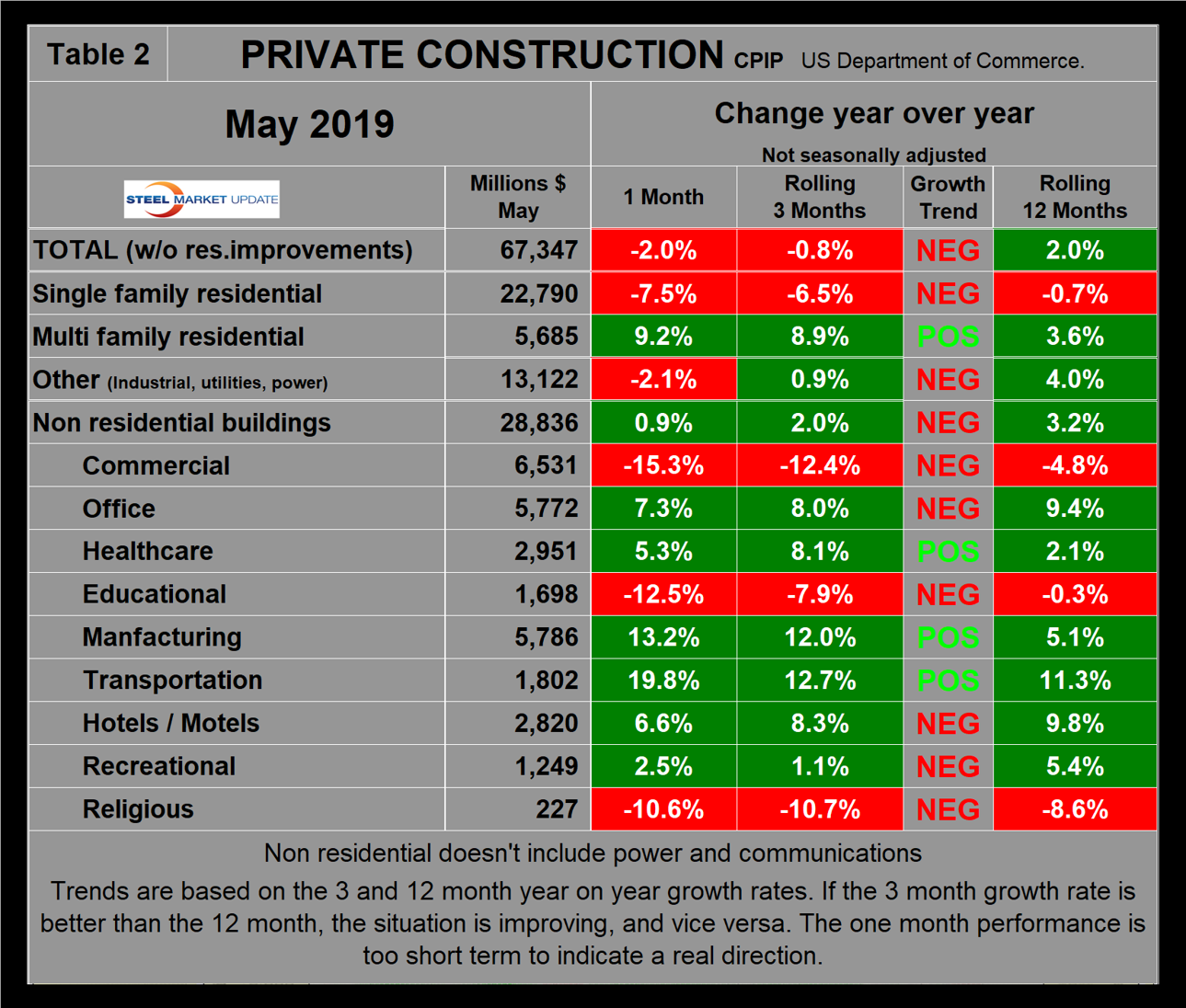
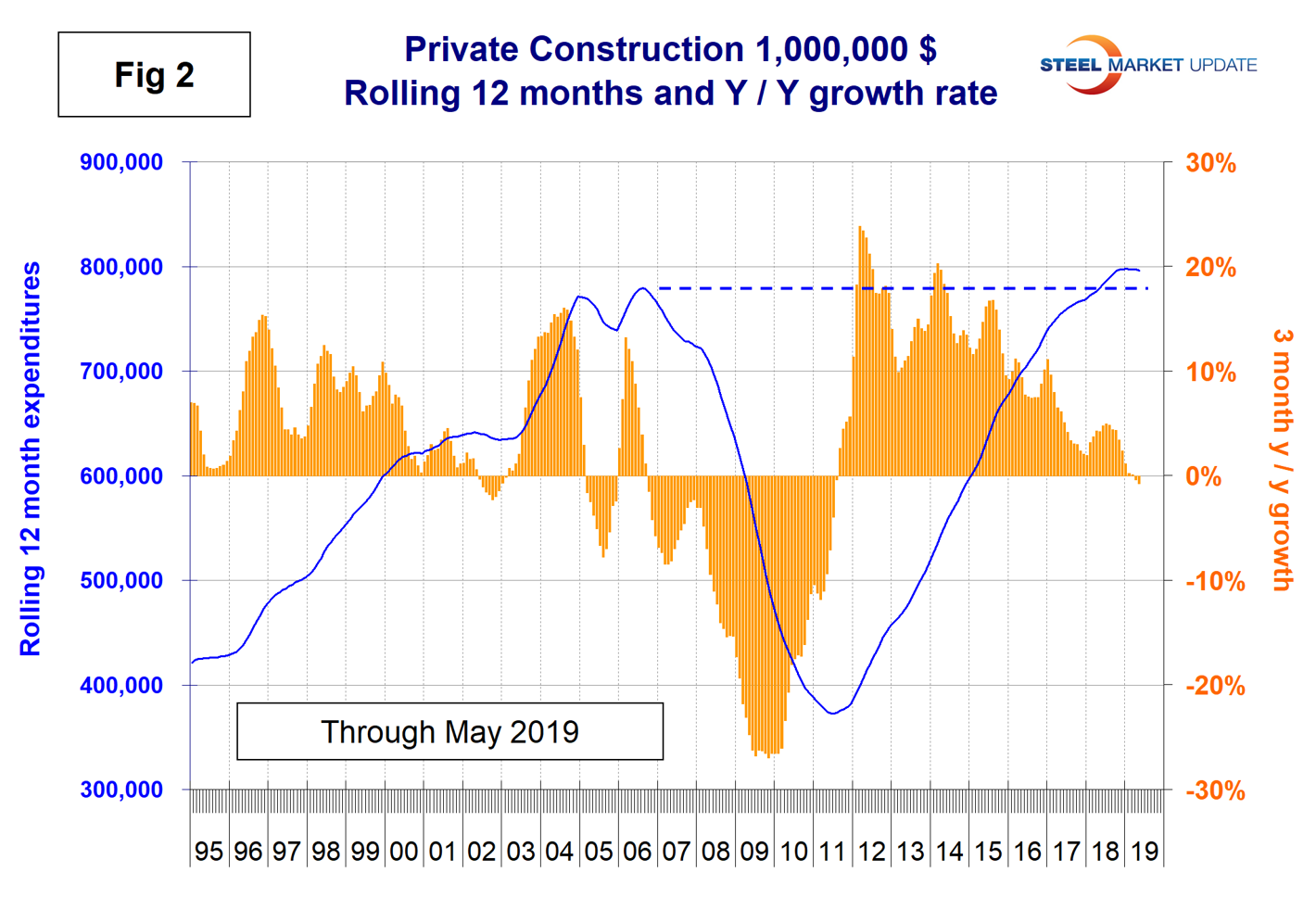
Within the nine sectors of private nonresidential building, momentum was mixed with three positive sectors and six negative.
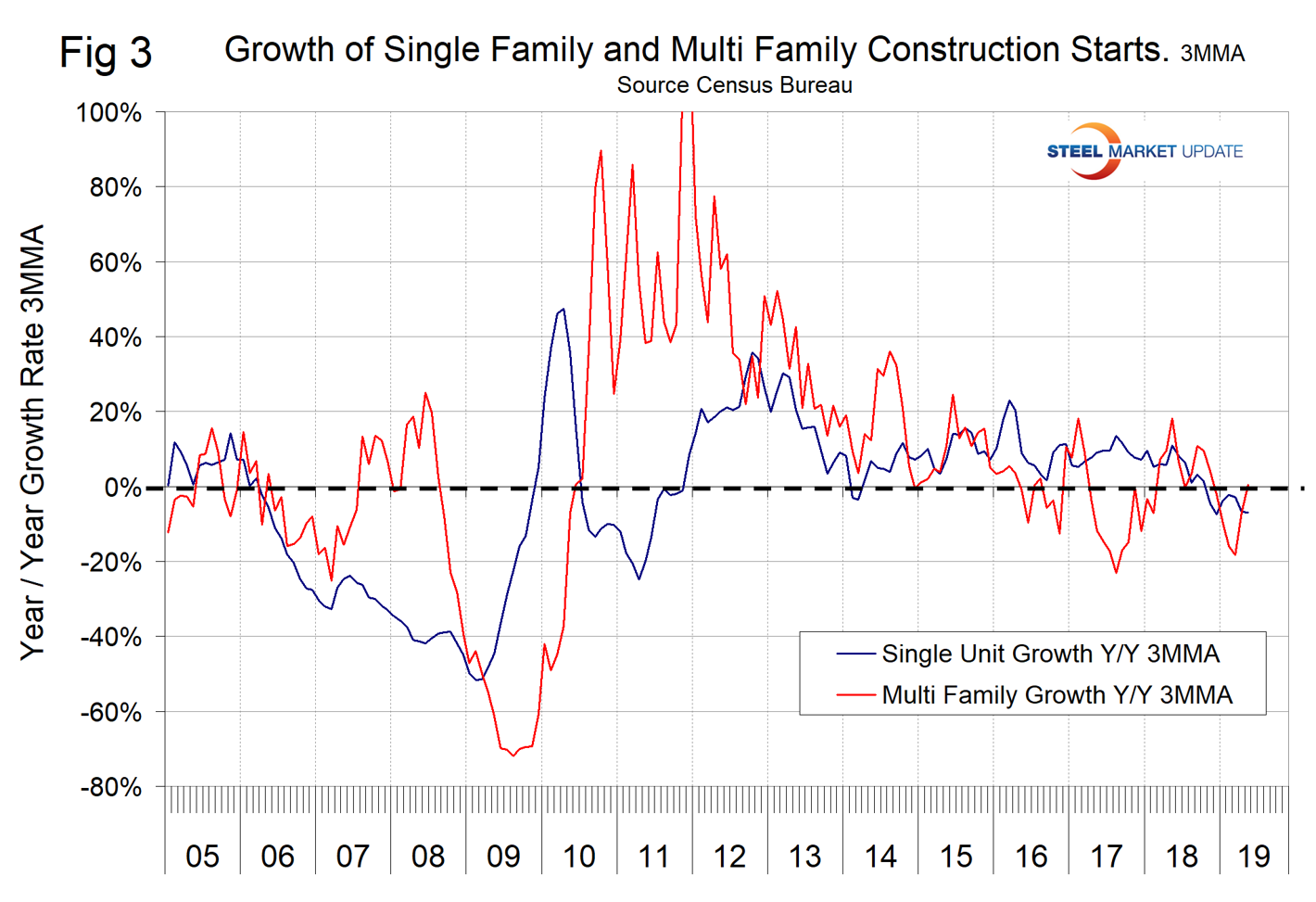
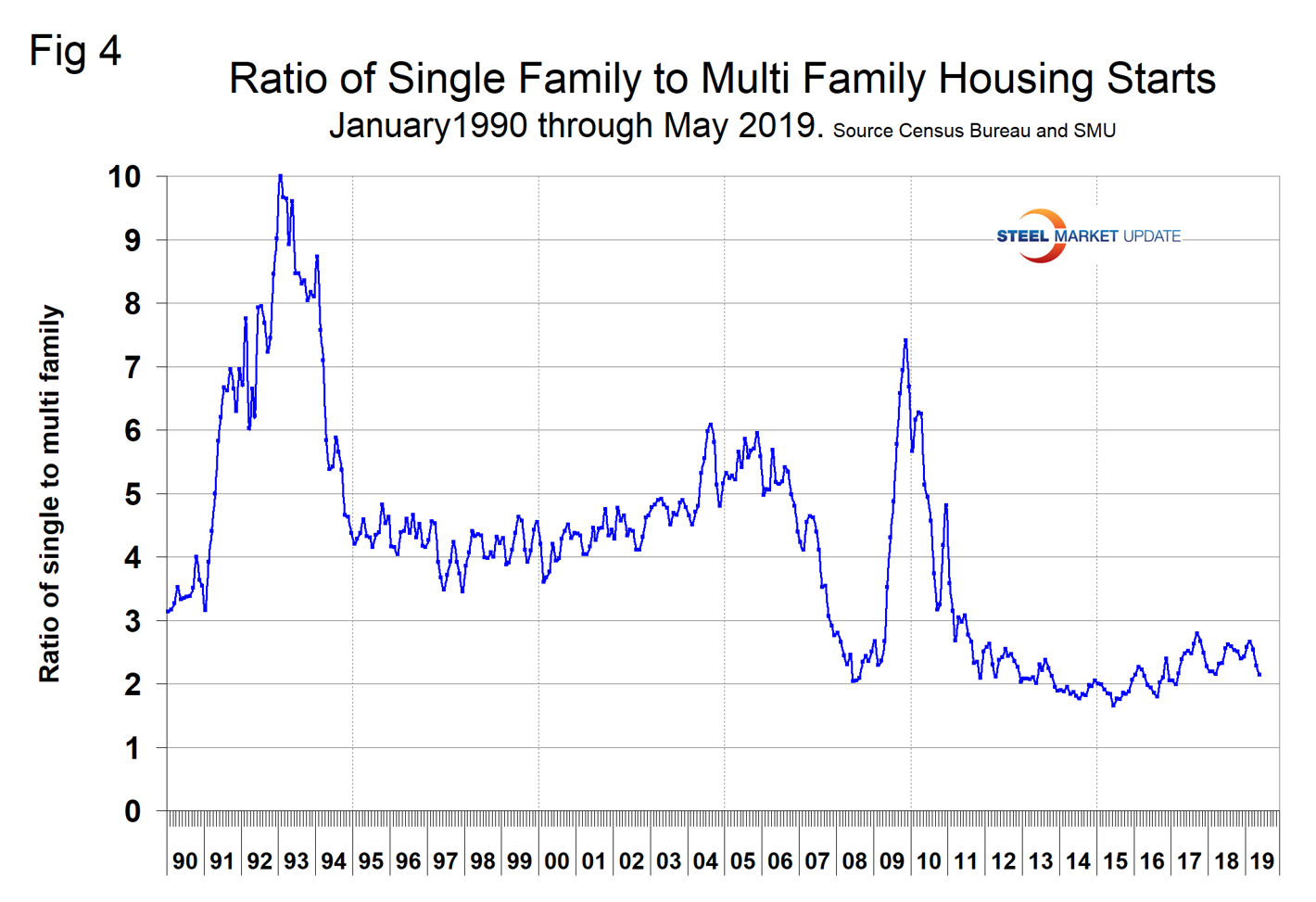
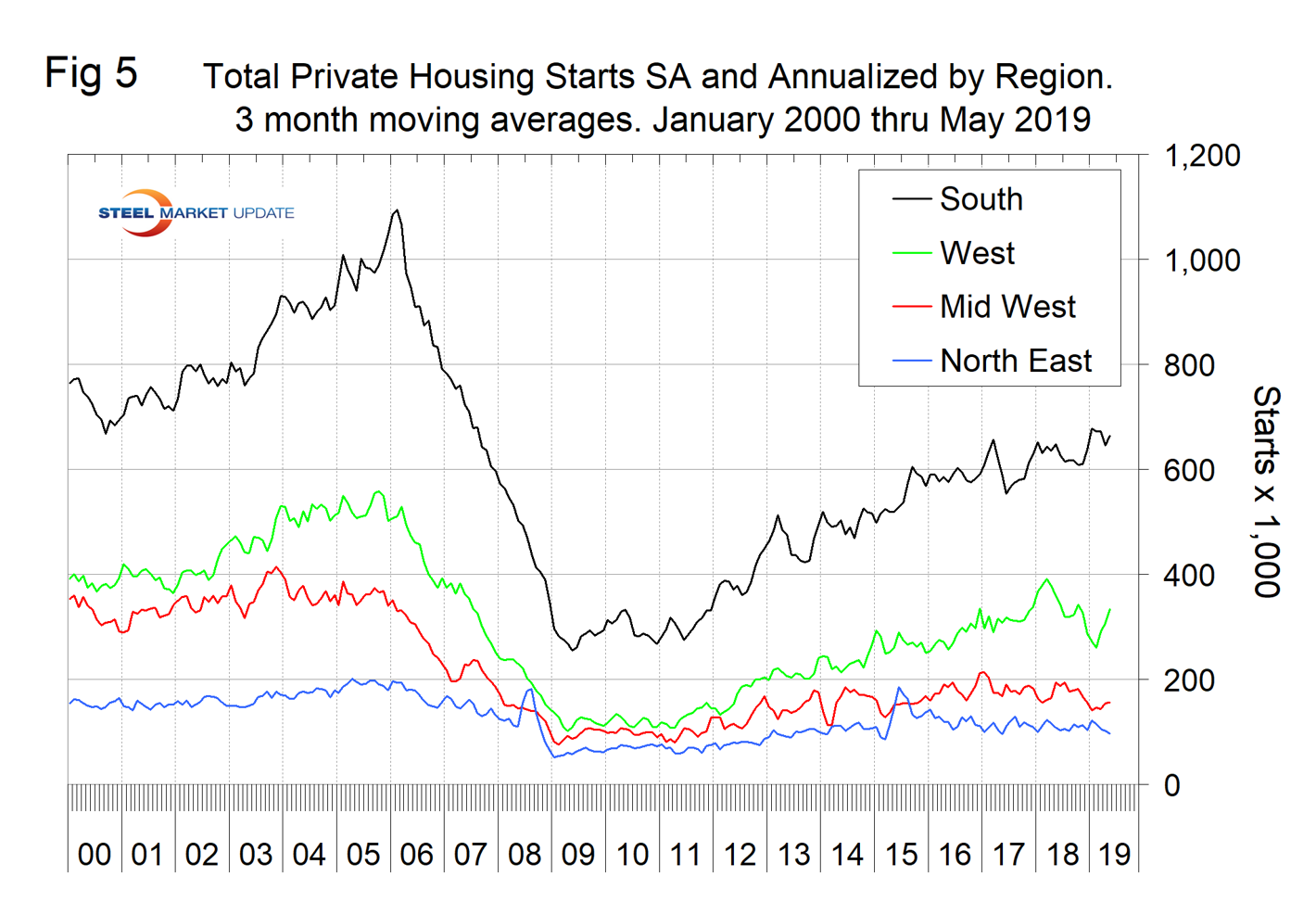
Excluding property improvements, single-family residential contracted by 6.5 percent in three months through May with negative momentum and multifamily residential grew by 8.9 percent with positive momentum. Total housing starts as reported by Census Bureau have been contracting on a year-over-year basis since October last year. The National Association of Home Builders optimism index improved in each of the months February through May this year, which flies in the face of negative data for CPIP and starts. The Census Bureau reports on construction starts in their housing analysis. In the starts data, the whole project is entered into the database when ground is broken. Construction put in place is based on spending work as it proceeds; the value of a project is spread out from the project’s start to its completion. Single-family starts declined by 7.0 percent in the three months through May year over year, which was about the same as the contraction rate of CPIP. Multifamily starts expanded by 0.5 percent, which was a much worse result than the rate of expansion indicated by the CPIP data. Figure 3 shows the growth of both housing sectors since January 2005 and Figure 4 shows the ratio of single-family to multi-family starts. The proportion of single-family has been gradually increasing since January 2015 when the ratio was 1.66 in favor of single units to 2.66 in February before declining to 2.14 in May 2019. Figure 5 shows total housing starts in four regions with the South being the strongest and the Northeast the weakest.
State and Local Construction
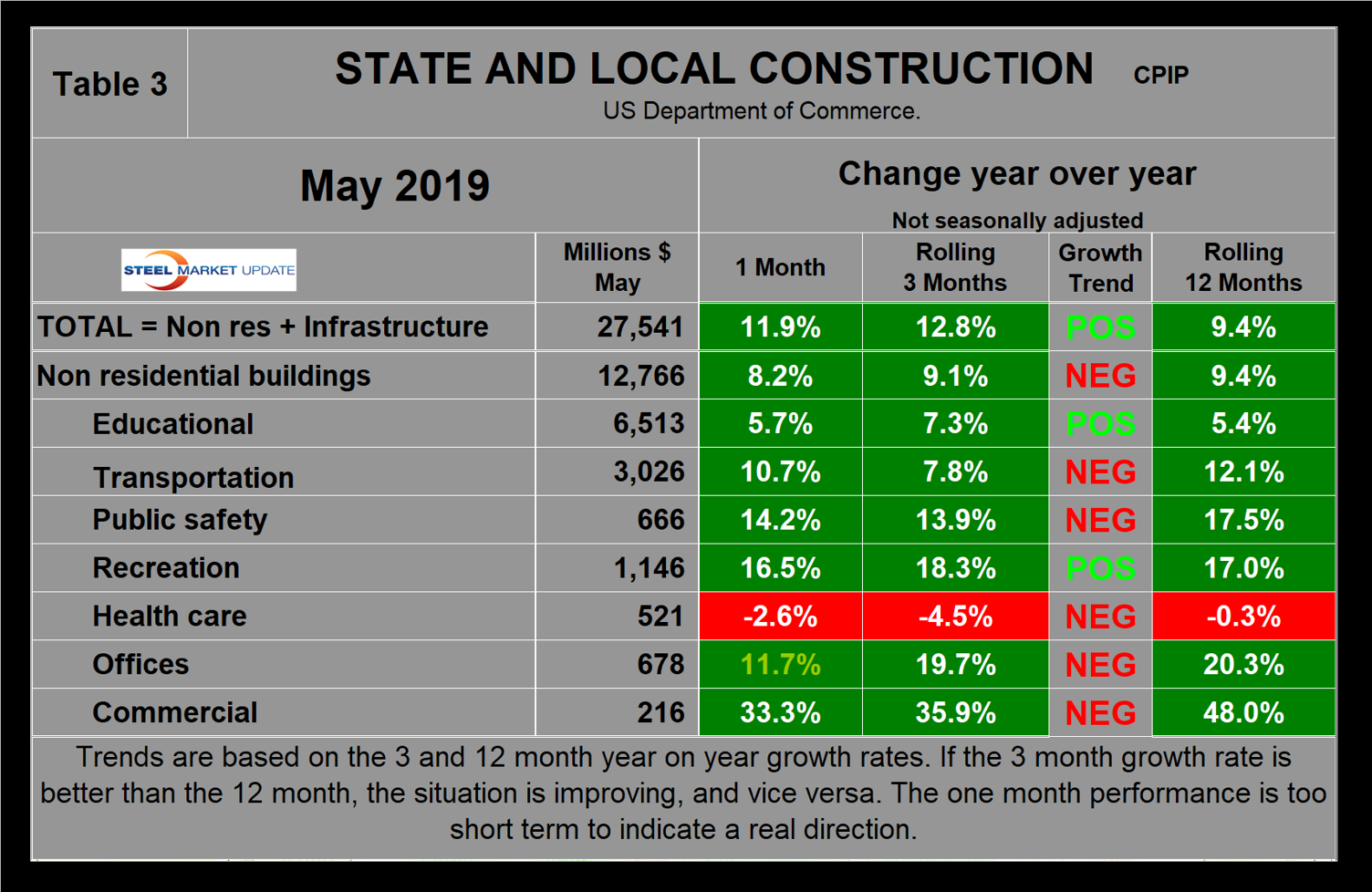
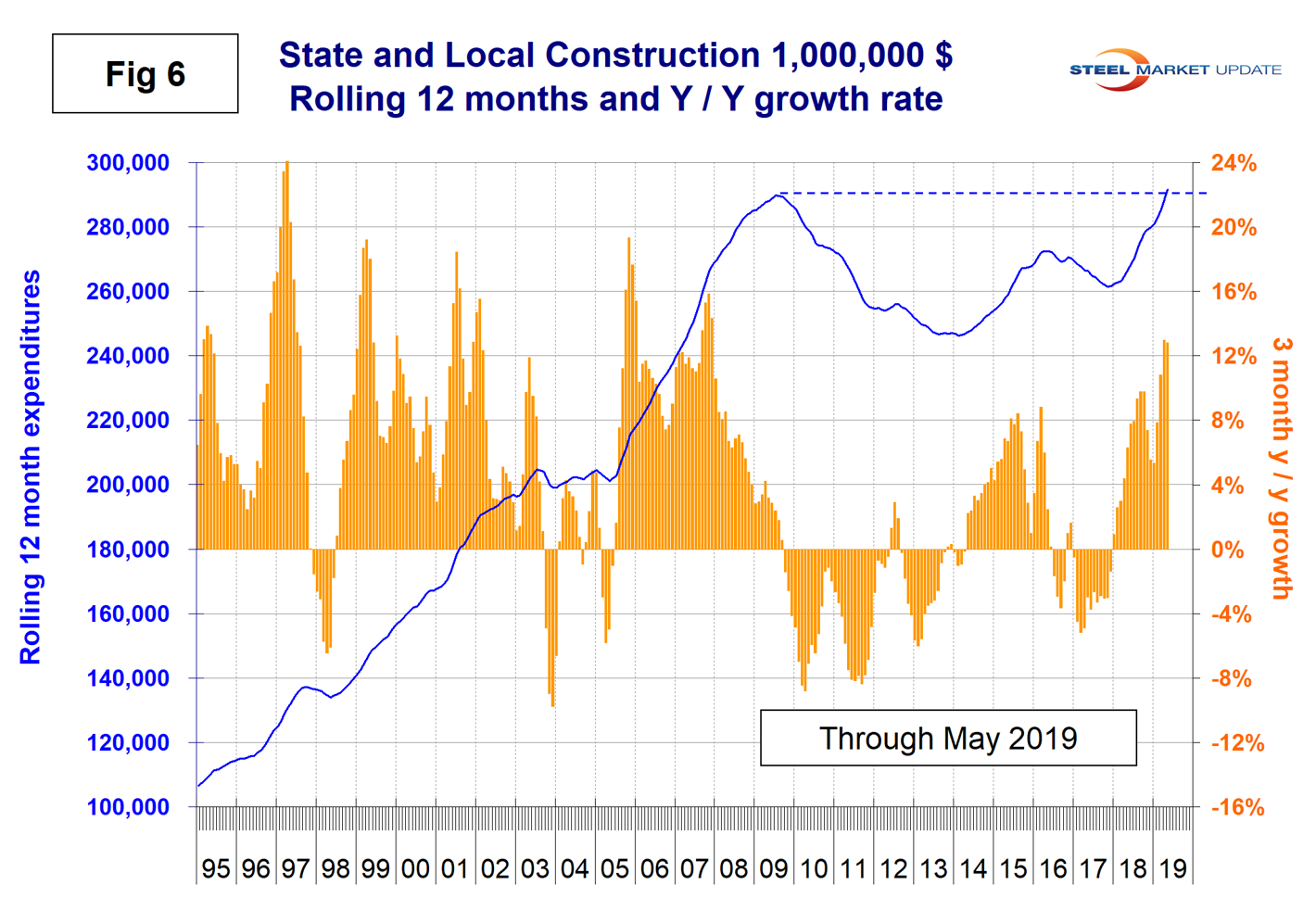
Apart from a slight dip in November and December last year, the growth rate of S&L work has improved steadily since January 2018. In May, the year-over-year growth rate on a rolling three-months basis was 12.8 percent, which completed three back-to-back months of double digit expansion (Table 3). S&L nonresidential building had slightly negative momentum in May, but still grew at 9.1 percent year over year. Educational was by far the largest subsector of S&L nonresidential building at $6.5 billion in May and experienced 7.3 percent positive growth on a rolling three months basis with positive momentum. Figure 6 shows the history of total S&L expenditures. May 2019 set an all-time record for S&L expenditures, breaking the previous best of July 2009. This has been an abrupt turnaround since the end of 2017.
Drilling down into the private and S&L sectors as presented in Tables 2 and 3 shows which project types should be targeted for steel sales and which should be avoided. There are also regional differences to be considered, data for which is not available from the Commerce Department.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure expenditures have had very robust growth in 2019. Year over year, the growth of infrastructure expenditures in three months through May was 18.6 percent with very positive momentum. On a rolling 12-months basis, infrastructure expenditures in May were at an all-time high. (Note: This is not seasonal as we are considering year-over-year data.) Highways and streets including pavement and bridges account for about two-thirds of total infrastructure expenditures. Highway pavement is the main subcomponent of highways and streets and had a 27.8 percent growth in three months through May. Bridge expenditures had negative growth in August through January, but picked back up to positive 3.8 percent in May (Table 4).
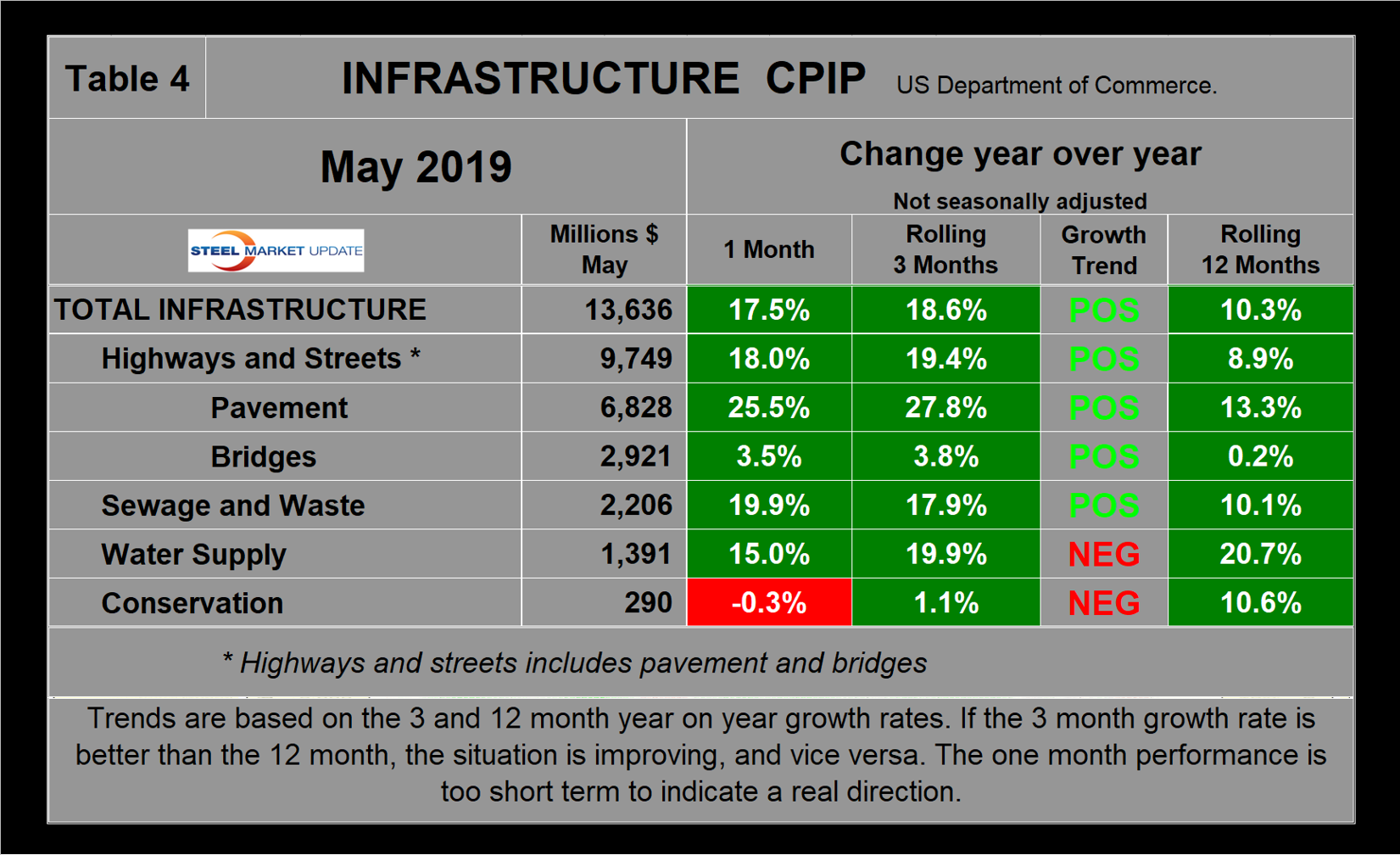
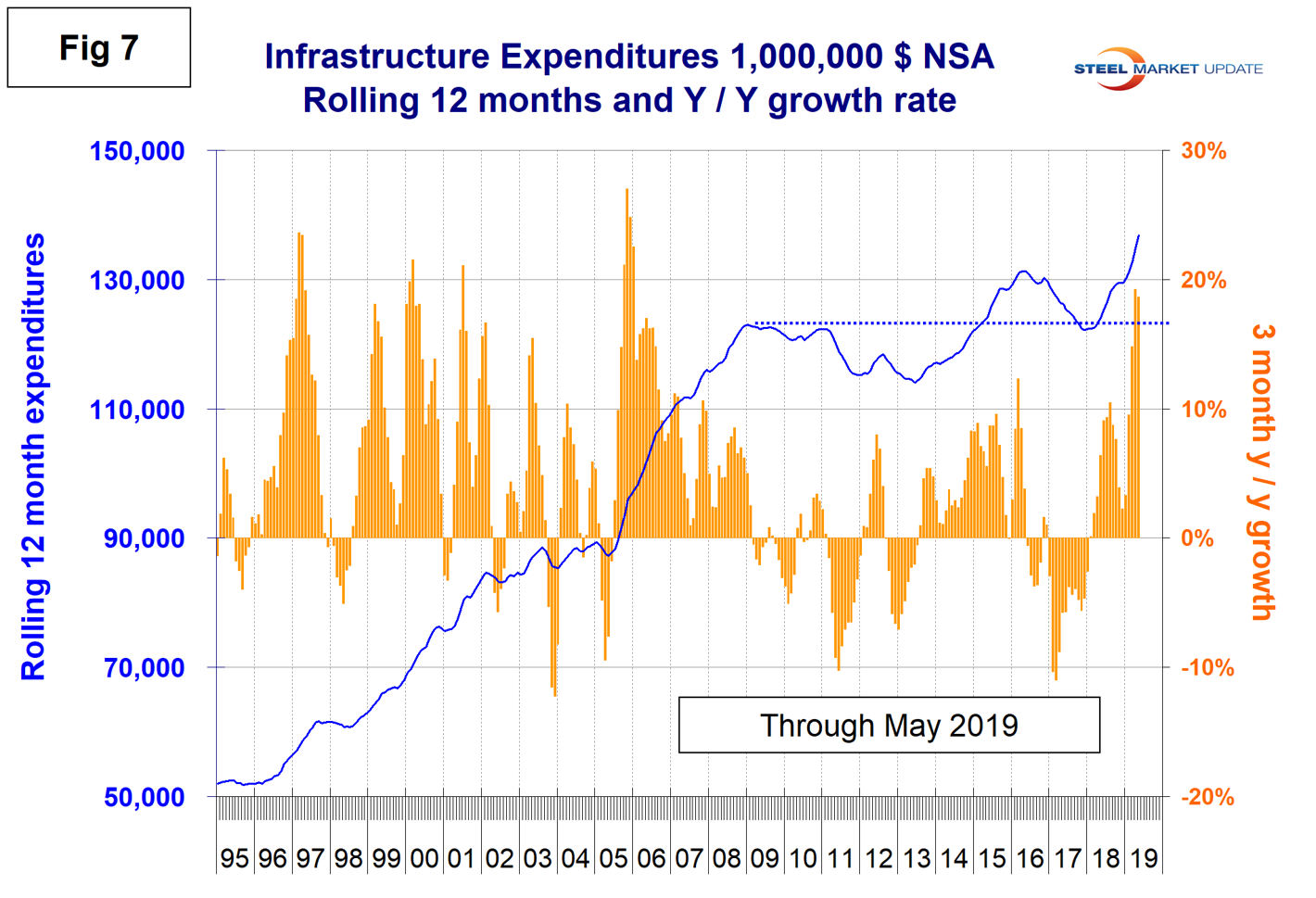
Figure 7 shows the history of infrastructure expenditures and the year-over-year growth rate.
Total Building Construction Including Residential
Figure 8 compares year-to-date expenditures for the construction of the various building sectors for 2018 and 2019. Single-family residential is dominant and in the 12 months of 2018 totaled $281.8 billion, up from $242.5 billion in 2016.
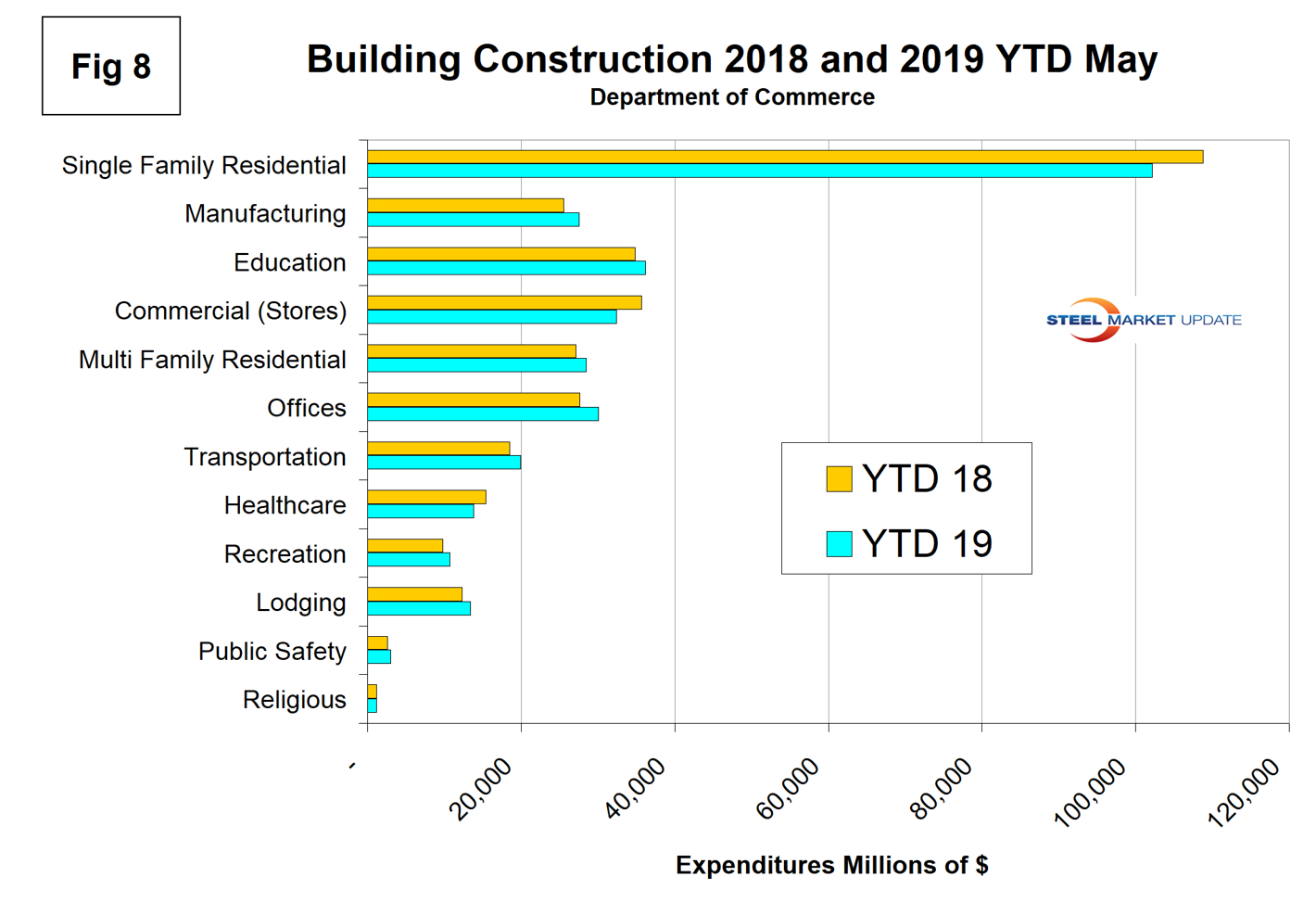
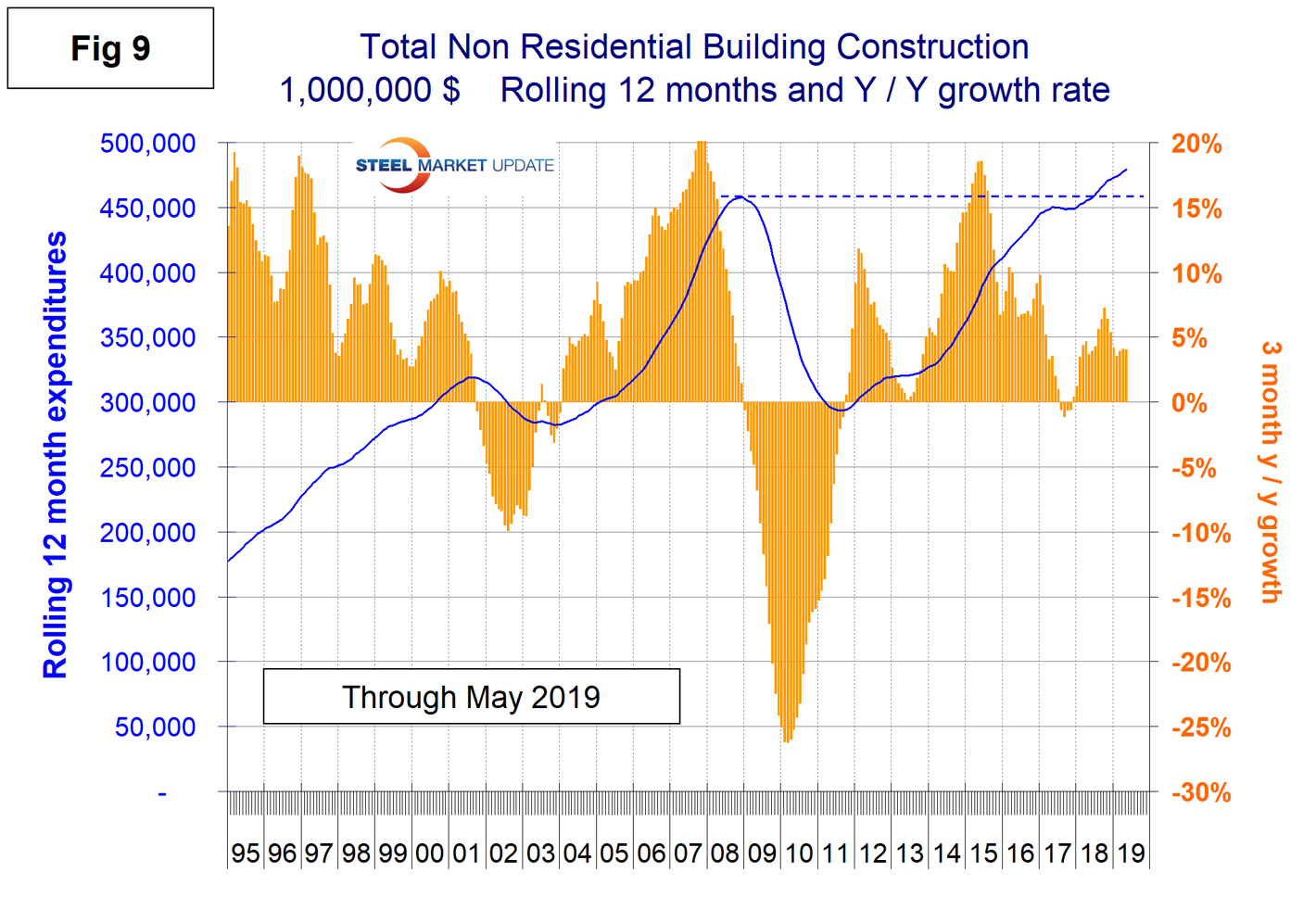
Figure 9 shows total expenditures and growth of nonresidential building construction. On a rolling 12-months basis, expenditures on nonresidential buildings including both private and S&L are at an all-time high and growth has been in the 5 percent range for over a year.
Explanation: Each month, the Commerce Department issues its Construction Put in Place (CPIP) data, usually on the first working day covering activity one month and one day earlier. There are three major categories based on funding source: private, state and local, and federal. Within these three groups are about 120 subcategories of construction projects. At SMU, we slice and dice the expenditures from the three funding categories to provide as concise a summary as possible of steel-consuming sectors. For example, we combine all three to reach a total of nonresidential building expenditures. CPIP is based on spending work as it occurs and is estimated each month from a sample of projects. In effect, the value of a project is spread out from the project’s start to its completion. This is different from the starts data published by the Census Bureau for residential construction, by Dodge Data & Analytics and by Reed Construction for nonresidential, and by Industrial Information Resources for industrial construction. In the case of starts data, the whole project is entered into the data base when ground is broken. The result is that the starts data can be very spiky, which is not the case with CPIP.
The official CPIP press release gives no appreciation of trends on a historical basis and merely compares the current month with the previous one on a seasonally adjusted basis. The background data is provided as both seasonally adjusted and non-adjusted. The detail is hidden in the published tables, which SMU tracks and dissects to provide a long-term perspective. Our intent is to provide a route map for those subscribers who are dependent on this industry to “follow the money.” This is a very broad and complex subject, therefore, to make this monthly write-up more comprehensible we are keeping the information format as consistent as possible. In our opinion, the absolute value of the dollar expenditures presented is of little interest. What we are after is the magnitude of growth or contraction of the various sectors. In the SMU analysis, we consider only the non-seasonally adjusted data. We eliminate seasonal effects by comparing rolling three-month expenditures year over year. CPIP data also includes the category of residential improvements, which we have removed from our analysis because such expenditures are minor consumers of steel.
In the four tables included in this analysis, we present the non-seasonally adjusted expenditures for the most recent data release. Growth rates presented are all year over year and are the rate for the single month’s result, the rolling three months and the rolling 12 months. We ignore the single month year-over-year result in our write-ups because these numbers are preliminary and can contain too much noise. The growth trend columns indicate momentum. If the rolling three-month growth rate is stronger than the rolling 12 months, we define that as positive momentum, or vice versa. In the text, when we refer to growth rate, we are describing the rolling three-month year-over-year rate. In Figures 1, 2, 6, 7 and 9 the blue lines represent the rolling 12-month expenditures and the brown bars represent the rolling three-month year-over-year growth rates.






