Market Data

October 5, 2018
Net Job Creation Through September 2018
Written by Peter Wright
The employment situation in the United States is excellent and continues to improve.
Rising employment and wages are the main contributors to GDP growth because personal consumption accounts for almost 70 percent of GDP. Steel consumption is related to GDP; therefore, this is one of the indicators that helps us understand the reality of the steel market. Net job creation in September as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) on Friday was 134,000, which was almost exactly half the August increase. This deterioration was partly due to August being revised up by 69,000. In addition, July was revised up by 18,000.
Figure 1 shows the three-month moving average (3MMA) of the number of jobs created monthly since 2000 as the brown bars and the total number employed as the black line. These numbers are seasonally adjusted by the BLS, which has been criticized in the past for the ineffectiveness of its seasonal adjustment calculations.
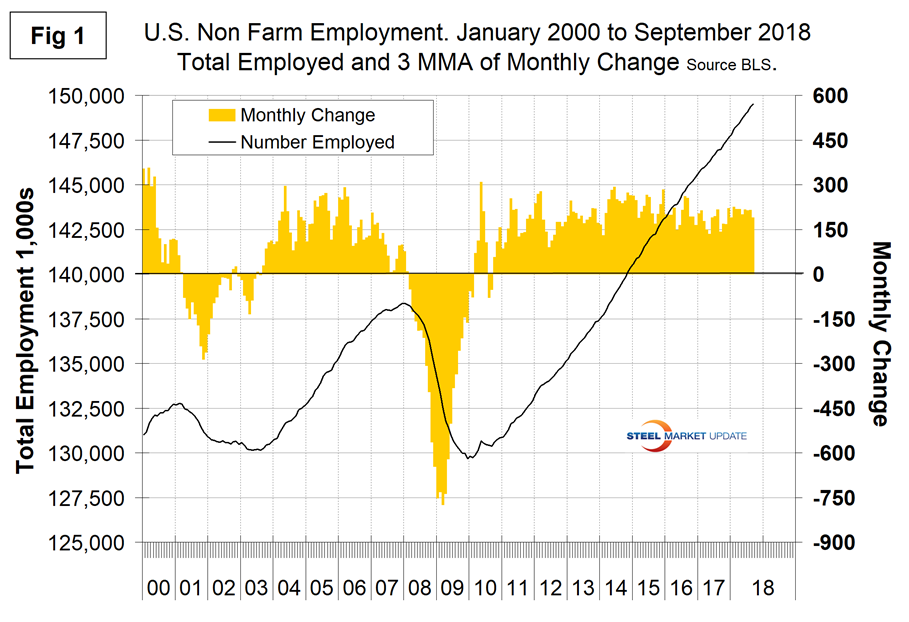
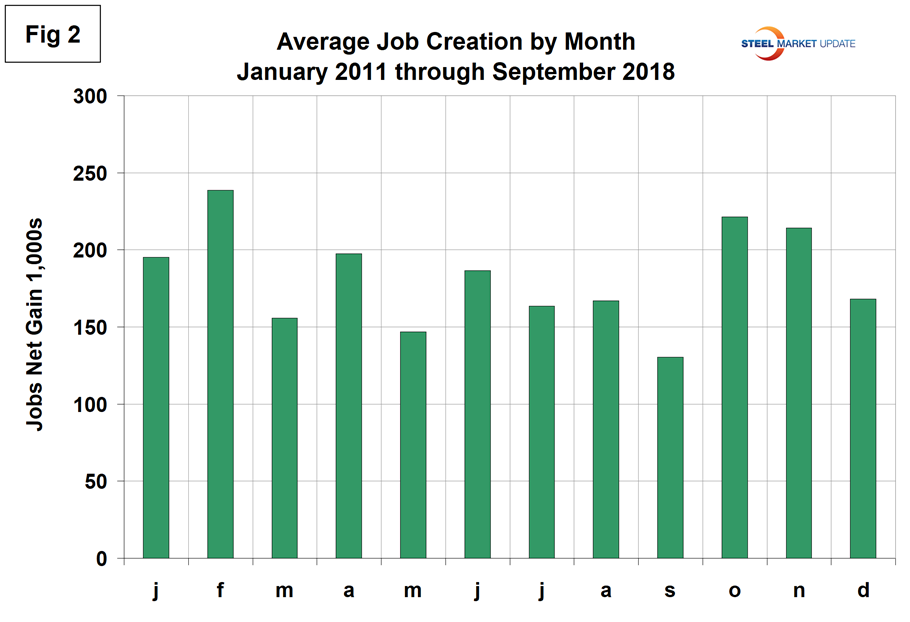
To examine if any seasonality is left in the data after adjustment, we have developed Figure 2. In the eight years since and including 2011, the September gain on average has decreased by 21.9 percent from the average August gain. This year, September was down by 50.4 percent. The BLS commissioner stated: “Hurricane Florence made landfall on the East Coast on Sept. 14 causing large-scale evacuations and severe damage to many homes and businesses. It is possible that payroll employment in some industries was affected by the hurricane; however, it is not possible to quantify the net effect.”
Historically, September on average has the smallest job gains of the year, which seems to confirm a problem with seasonal adjustment. We think it’s worth looking at the data in this way because the press will pick up on a number without any consideration of the monthly context.
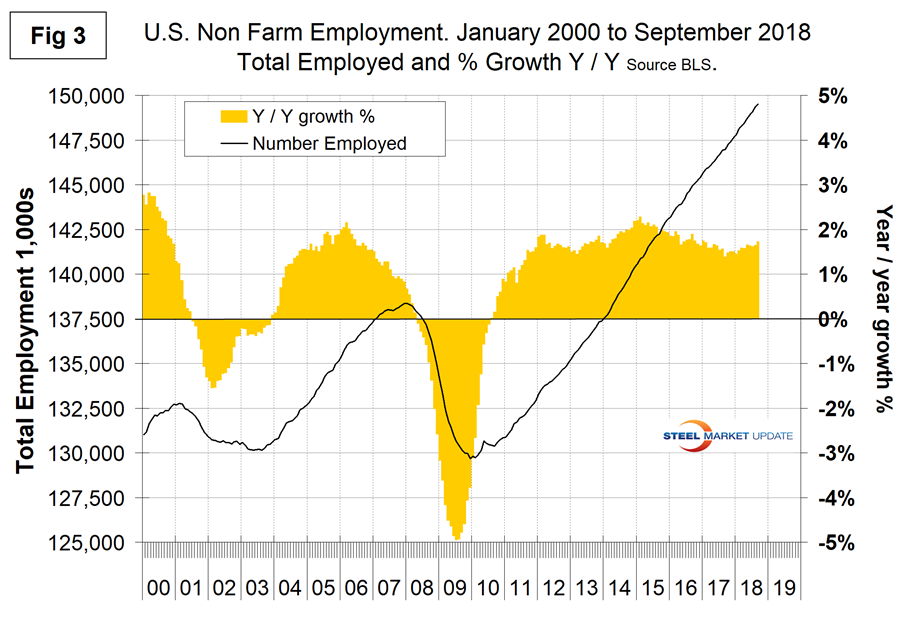
In order to get a better look at the degree of change, we have developed Figure 3. This shows the same total employment line as Figure 1, but includes the year-over-year growth on a percentage basis. From this we conclude there has been a small gradual improvement since September last year.
Total nonfarm payrolls are now 11.1 million more than they were at the pre-recession high of February 2008. Total nonfarm employment in September was 149.5 million. According to BLS data, the average workweek for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls remained unchanged at 34.5 hours in September. In manufacturing, the workweek edged down by 0.1 hour to 40.8 hours, and overtime edged down by 0.1 hour to 3.4 hours. The average workweek for production and nonsupervisory employees on private nonfarm payrolls was unchanged at 33.7 hours. In September, average hourly earnings for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls rose by 8 cents to $27.24. Over the year, average hourly earnings have increased by 73 cents, or 2.8 percent. Average hourly earnings of private-sector production and nonsupervisory employees increased by 6 cents to $22.81 in September.
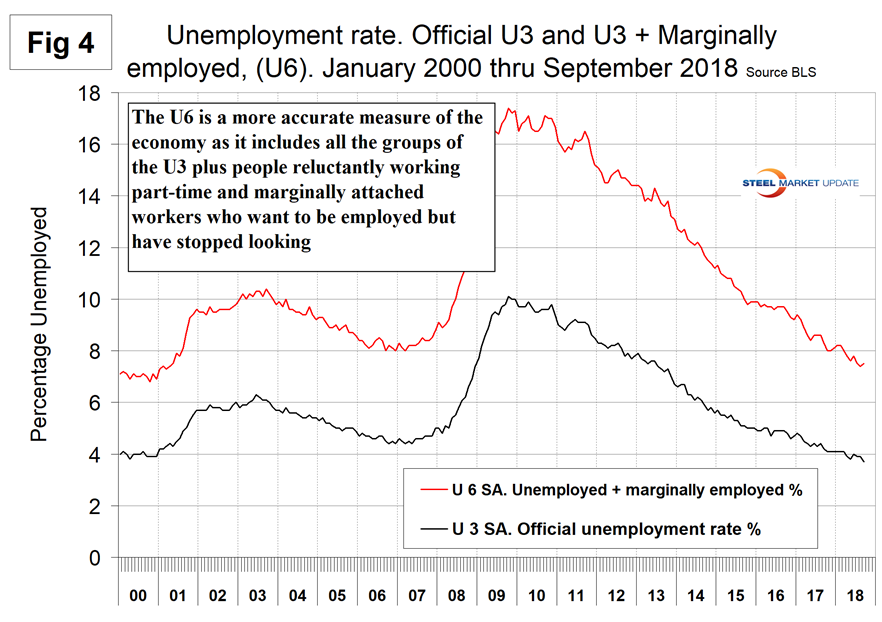
The official unemployment rate, U3, reported in the BLS Household survey (see explanation below) came in at 3.7 percent, down from 3.9 percent in August and the lowest figure since our data begins in January 2000. This is not a very representative number. The more comprehensive U6 unemployment rate declined from 9.2 percent in January last year to 7.5 percent in September (Figure 4). In September, the difference between these two measures was 3.8 percent. U6 includes individuals working part time who desire full-time work and those who want to work but are so discouraged they have stopped looking.
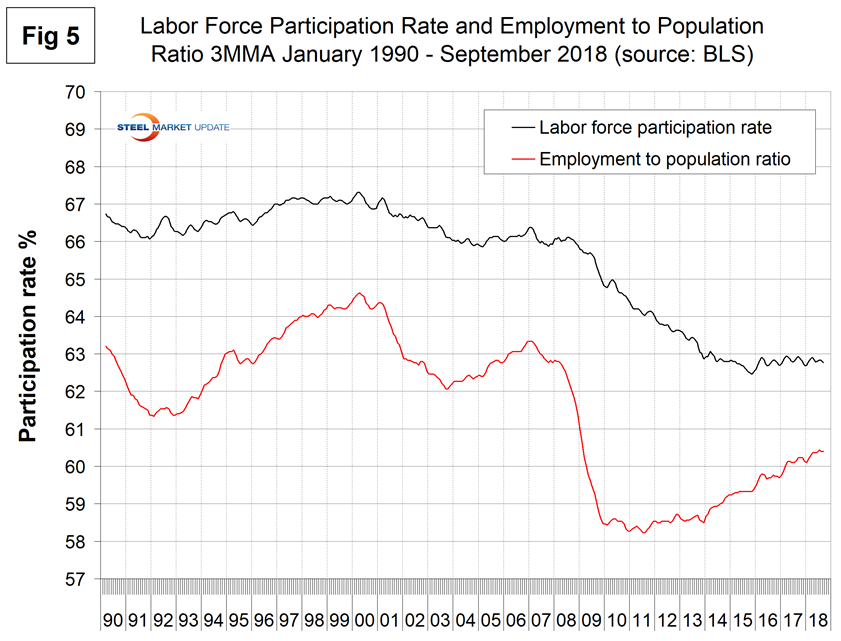
The labor force participation rate is calculated by dividing the number of people actively participating in the labor force by the total number of people eligible to participate. This measure was 62.7 percent in September, down by 0.2 percent from July, but the 3MMA at 62.8 percent hasn’t changed much in over two years. Another gauge is the number employed as a percentage of the population, which we think is more definitive. In September, the employment-to-population ratio was 60.4 percent, up from 59.7 percent in June 2016. The employment-to-population ratio has made progress for the last four years but the labor force participation rate has been stalled for two years. Figure 5 shows both measures on one graph.
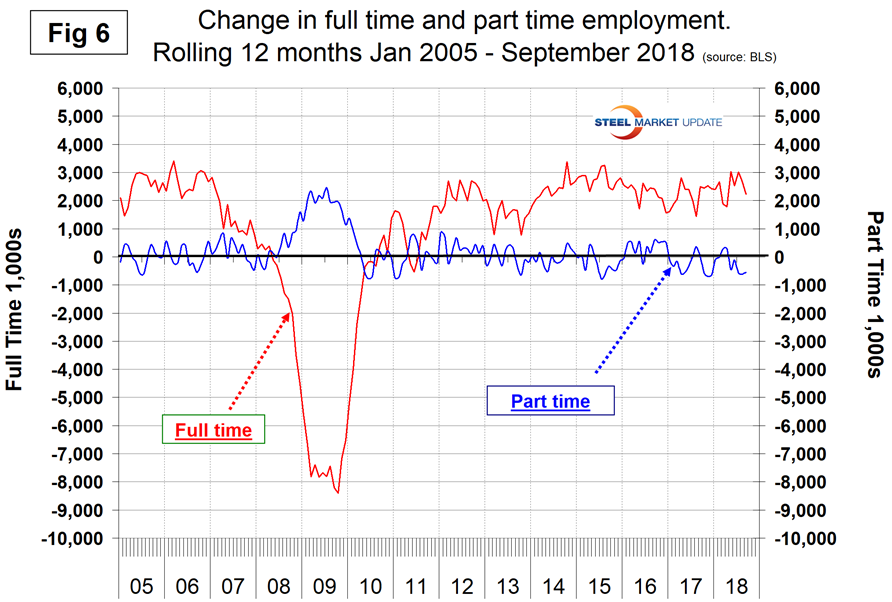
In the 33 months since and including January 2016, there has been an increase of 6,154,000 full-time and a decrease of 323,000 part-time jobs. Figure 6 shows the rolling 12-month change in both part-time and full-time employment. This data comes from the household survey and part-time is defined as less than 35 hours per week. Because the full-time/part-time data comes from the Household survey and the headline job creation number comes from the Establishment survey, the two cannot be compared in any given month. To overcome the volatility in the part-time numbers, we look at a rolling 12 months for the full-time and part-time employment picture shown in Fig. 6.
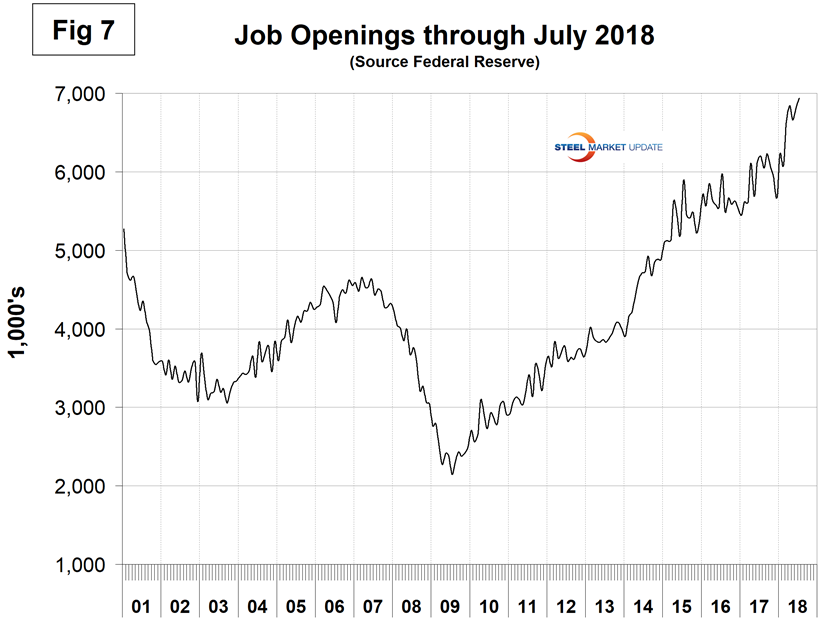
The job openings report known as JOLTS is reported on about the 10th of the month by the Federal Reserve and is over a month in arrears. Figure 7 shows the history of unfilled job openings through July when openings stood at 6,939,000. This was an all-time high. There has been an improving trend since mid-2009. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell recently stated, “For the first time since the Labor Department began collecting job openings data in 2000, there are more job vacancies than there are people counted as unemployed. In addition, the rate at which workers are quitting their jobs is elevated, a sign that workers are able to find another job when they seek one. Surveys show that businesses are finding it difficult to fill vacancies, and households perceive jobs as plentiful.”
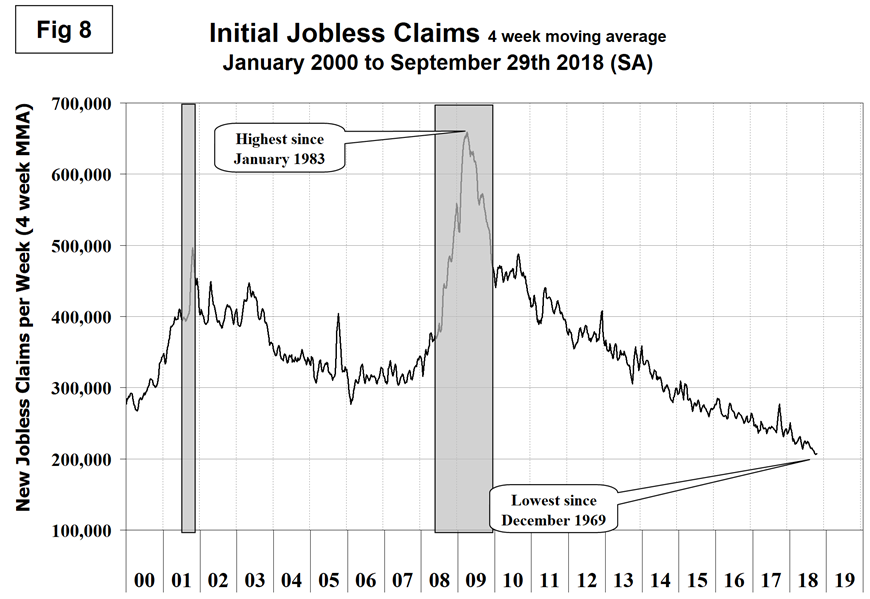
Initial claims for unemployment insurance, reported weekly by the Department of Labor, flattened in 2017 except for the hurricane-driven spike, then resumed their decline in 2018. New claims in the last few months have been at the lowest level since 1969. In the week ending Sept. 29, initial claims were 207,000 with a four-week moving average of also 207,500. This is a continuation of the longest streak since 1973 of initial claims below 300,000 (Figure 8).
SMU Comment: As 2018 unfolds, the employment situation is very good, job openings in the last three months have been at an all-time high, and new claims for unemployment are at a 44-year low. The employment situation has been described as “full” by some analysts.
Explanation: On the first Friday of each month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics releases the employment data for the previous month. Data is available at www.bls.gov. The BLS reports on the results of two surveys. The Establishment survey reports the actual number employed by industry. The Household survey reports on the unemployment rate, participation rate, earnings, average workweek, the breakout into full-time and part-time workers and lots more details describing the age breakdown of the unemployed, reasons for and duration of unemployment. At Steel Market Update, we track the job creation numbers by many different categories. The BLS database is a reality check for other economic data streams such as manufacturing and construction. We include the net job creation figures for those two sectors in our “Key Indicators” report. It is easy to drill down into the BLS database to obtain employment data for many subsectors of the economy. For example, among hundreds of sub-indexes are truck transportation, auto production and primary metals production. The important point about all these data streams is the direction they are headed. Whenever possible, we try to track three separate data sources for a given steel-related sector of the economy. We believe this gives a reasonable picture of market direction. The BLS data is one of the most important sources of fine-grained economic data that we use in our analyses. The states also collect their own employment numbers independently of the BLS. The compiled state data compares well with the federal data. Every three months, SMU examines the state data and provides a regional report, which indicates strength or weakness on a geographic basis. Reports by individual state can be produced on request.







