Product

June 9, 2018
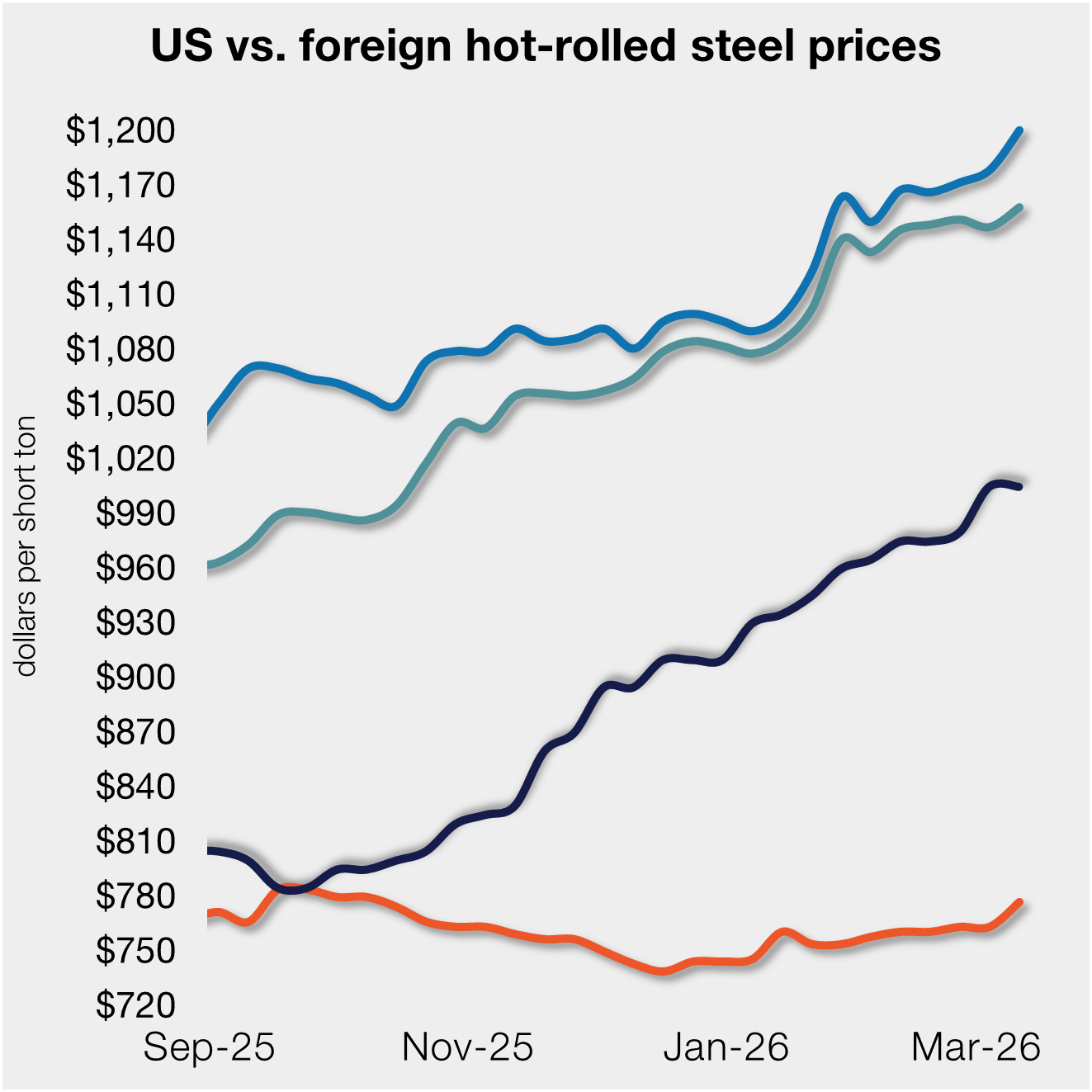
Beaulieu: What If They Return Fire?
Written by Tim Triplett
Are the markets’ fears of a trade war exaggerated or are their concerns justified? Popular economist Alan Beaulieu, president of ITR Economics, offers the following macroeconomic perspective:
Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum coming into the U.S. from Canada, Mexico and the EU are a hot topic, and with good reason. The extension of the tariffs to these regions is an open invitation for retaliation from our key trading partners and allies. Retaliatory tariffs on steel and aluminum exports from the U.S. to these nations will most likely put downward pressure on profits and job growth in key segments of the economy, and thus slow economic growth in various industries. The impact of retaliatory tariffs is consistent with ITR Economics’ forecast of slower growth in U.S. GDP, and a mild decline in U.S. Industrial production, in 2019. (It does not advance the timing for our projected 2030 Great Depression.)
Before we get to our allies, let’s put the steel issue into numerical perspective. The importation of steel into the U.S., at $38.53 billion, is 1.6% percent of all goods imported into the U.S. That is a noticeable percentage, but by way of comparison, imported auto parts are 4.8 percent of all imported goods.
As far as our allies go, it is all in the numbers in the table below:
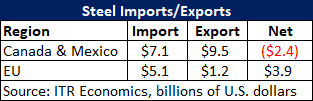
Exports of steel and iron to Canada and Mexico exceed what we buy from them. An imposition of a 25 percent tariff could negatively impact their demand for U.S. steel in those countries, which means we could feel more pain in a trade war than they might feel. A reduction in sales can be expected to put downward pressure on profits and job growth (and perhaps even lead to job loss). The EU would feel more pain in the steel industry than the U.S., which is why the EU is discussing other retaliatory tariffs over and above steel. They are discussing the imposition of tariffs on motorcycles, blue jeans, whiskey, cosmetics and peanut butter. A slowdown in the export of these items from the U.S. can be expected to have the same negative impact on U.S. manufacturers of those items. For instance, it is unlikely that the U.S. population will buy a commensurately large number of Harley-Davidsons just because they are not being bought in the EU. The same will hold true of blue jeans, cosmetics, etc. In short, keeping other countries’ goods out of the U.S. invites other nations to keep U.S. goods out of their countries.
One argument in favor of the steel tariffs, and the voluntary quotas on Australia, Argentina and Brazil in lieu of tariffs, is that the domestic demand for steel will encourage domestic manufacturers to spend capital in restarting idled facilities. That thinking only goes so far. Restarting facilities is expensive and often requires a significant investment in current technologies. There is a large unknown factor in an expensive reboot of a facility or an entire industry such as aluminum. Will corporations invest significant sums on an unknown future? What if the tariffs are lifted in the next year or two? That will not provide for an acceptable ROI and thus may make the risk unacceptable. The uncertainty of the situation may provide the reason why significant widespread investment may fail to appear.
All of which leads us to the conclusion that the U.S. economy will soon be in Phase C, Slowing Growth. That slowing growth will be more pronounced in some markets, with a potential for a mild Phase D, Recession, in other markets. Companies should analyze their budgets to make sure the cash projections are adjusted for slower growth, or worse, in 2019. They should also watch inventory levels. Concurrently, it is a great time to buy into the future by positioning the company for increased market penetration.
Beaulieu will be a featured speaker at Steel Market Update’s Steel Summit Conference Aug. 27-29 in Atlanta. For more information and to register, go to: www.SteelMarketUpdate.com/Events/Steel-Summit or call 772-932-7538.