Analysis

June 2, 2016
Construction Expenditures through April 2016
Written by Peter Wright
Each month the Commerce Department issues its Construction Put in Place (CPIP) data, usually on the first working day covering activity two months earlier. April data was released on Wednesday June 1st.
![]() Construction Put in Place is based on spending work as it occurs, estimated for a given month from a sample of projects. In effect the value of a project is spread out from the project’s start to its completion. This is different from the starts data published by the Census Bureau for residential construction, by Dodge Data & Analytics and Reed Construction for non-residential, and Industrial Information Resources for industrial construction. In the case of starts data, the whole project is entered to the data base when ground is broken. The result is that the starts data can be very spiky which is not the case with CPIP.
Construction Put in Place is based on spending work as it occurs, estimated for a given month from a sample of projects. In effect the value of a project is spread out from the project’s start to its completion. This is different from the starts data published by the Census Bureau for residential construction, by Dodge Data & Analytics and Reed Construction for non-residential, and Industrial Information Resources for industrial construction. In the case of starts data, the whole project is entered to the data base when ground is broken. The result is that the starts data can be very spiky which is not the case with CPIP.
At SMU we analyze the CPIP provided by the Department of Commerce with the intent of providing a clear description of activity in this steel consuming sector. Please see the end of this report for more detail on how we perform this analysis and structure the data but in particular note that we are presenting NONE seasonally adjusted numbers. Much of what you will see in the press may differ from what we are presenting here because others are basing their comments on adjusted values.
Total Construction
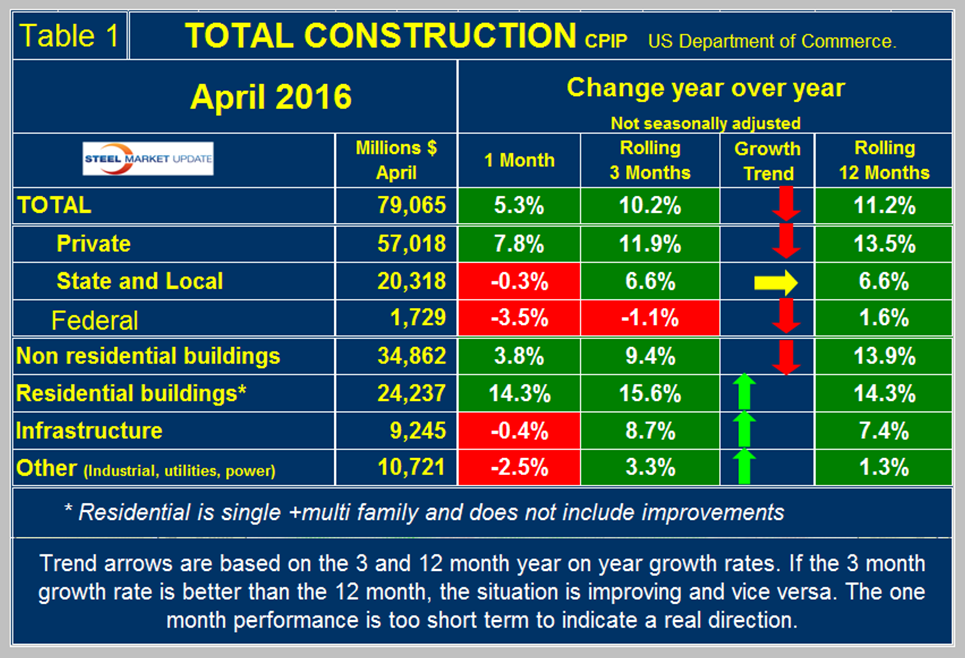
Total construction grew by 10.2 percent in three months through April year over year. This was the third consecutive month of double digit expansion. On a rolling 12 months basis construction has expanded y/y by > 10 percent for each of the last nine months. In the last twelve months construction growth has been as strong as at any time since our data stream began over twenty years ago. All growth measures included below are on a three month moving average (3MMA) basis year over year which eliminates seasonality.
April expenditures were $79.065 billion which breaks down to $57.0B of private work, $20.32B of state and locally (S&L) funded work and $1.7 B of federally funded (Table 1).
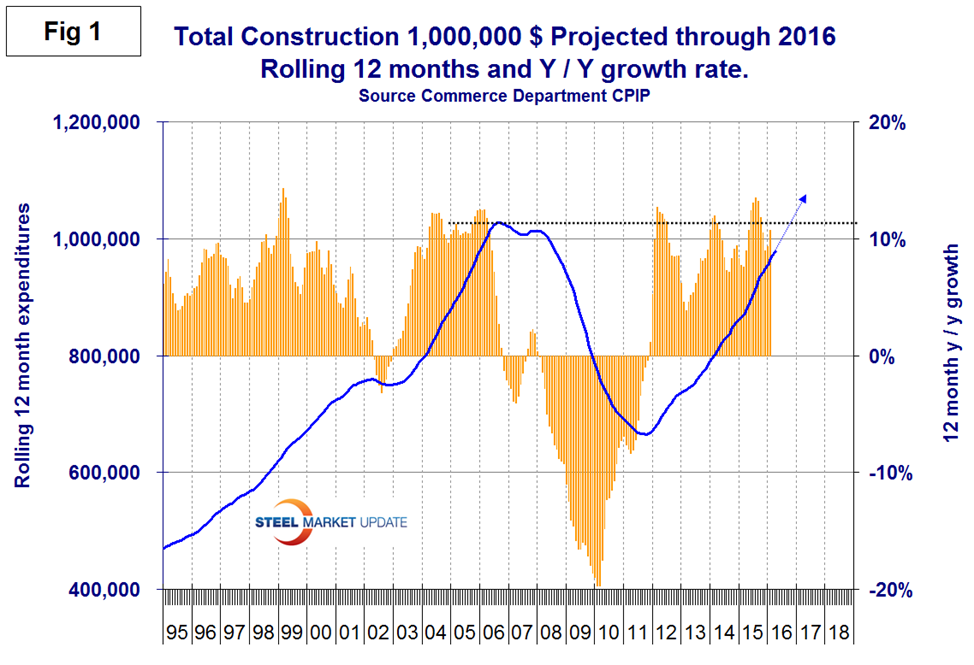
The red and green arrows in all four tables in this report show momentum. April on a 3MMA basis had an increase in year over year growth of 10.2 percent which was lower than the 11.2 percent growth on a rolling 12 months basis. This means that the growth rate has a slightly negative momentum but is still historically strong. Total construction will reach the pre-recession level before the end of this year if the present growth rate is maintained (Figure 1).
The 10.2 percent growth of total construction y/y was led by private work up by 11.9 percent. State and locally financed work was up by 6.6 percent and Federal was down by 1.1 percent. Momentum was negative for private and federal work but positive for state and local. We consider four sectors within total construction. These are non-residential, residential, infrastructure and other which is a catch all and includes industrial, utilities and power. Nonresidential building construction had negative momentum but infrastructure, accelerated in the latest data. The growth rate of non-residential and residential buildings are at double digit rates. The growth rate of “Other” became very negative at the time of the oil price collapse but has recovered to positive growth in the last eight months. The growth rate of total construction is shown by the brown bars in Figure 1. The pre-recession peak of total construction on a rolling 12 month basis was $1,028 B in 12 months through September 2006. The low point was $665.1 B in 12 months through October 2011. The 12 month total through the latest data of April 2016 was $977.8 B. July 2015 through April 2016 were the first months to exceed $900 B since March 2009 when the recession was gaining traction.
The Associated General Contractors of America had this to say in their blog dated June 1st: Officials said that data reflect relatively strong market conditions for the construction sector. The two main industry concerns remain the availability of qualified workers and the need for new investments in aging infrastructure. They added that the group would continue to push elected officials to act on its Workforce Development Plan and pass aviation and water resources development bills. “While few cities have returned to their prior peak levels, construction head counts continue to climb in most areas,” said Stephen E. Sandherr, the association’s chief executive officer. “Federal, state and local officials should focus on enacting measures to recruit and prepare future workers and improve aging airports, water systems and other public infrastructure.”
Private Construction
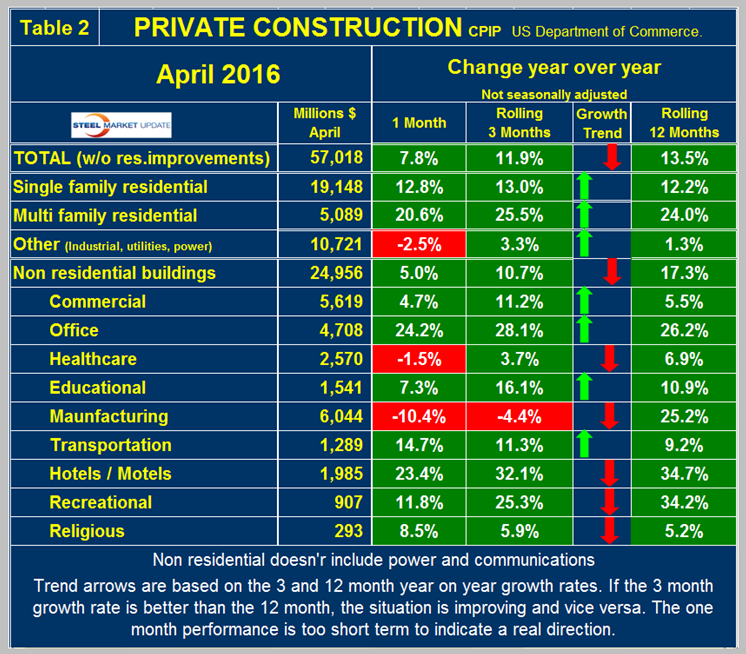
Table 2 shows the breakdown of private expenditures into residential and non-residential and subsectors of both.
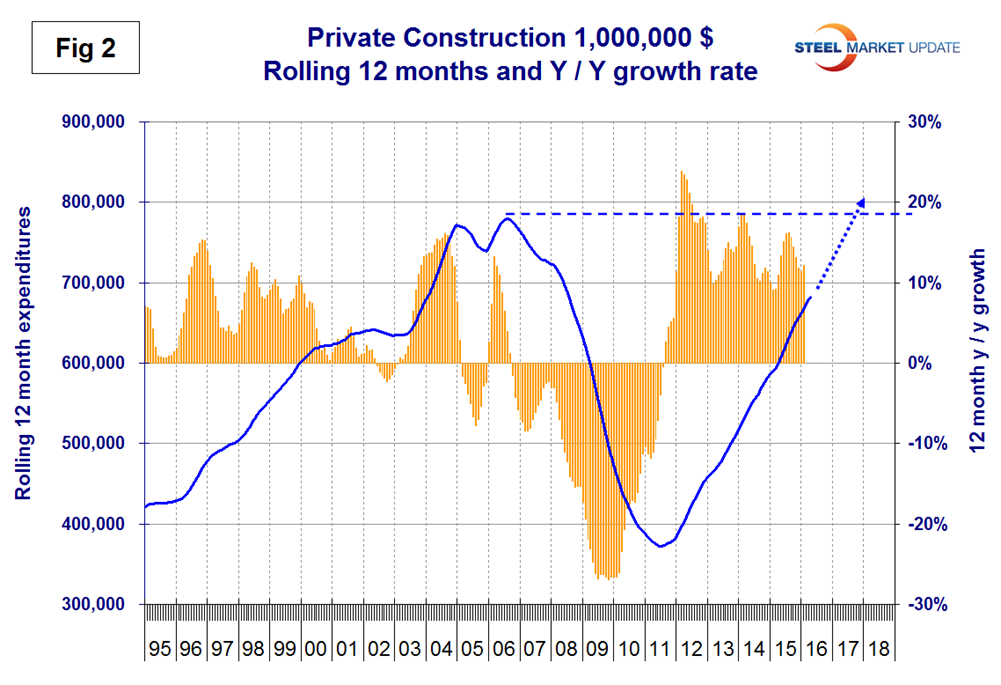
The growth rate of private construction was 11.9 percent in the last three months as shown by the brown bars in Figure 2.
The blue lines in all four graphs in this report are 12 month totals which smooths out seasonal variation. Excluding property improvements our report shows that single family residential grew at 13.0 percent and multi-family residential is still surging with a 25.5 percent growth rate. The growth of single and multifamily construction expenditures reported here are very different from the starts data as reported by the Census Bureau. (In the starts data the whole project is entered to the data base when ground is broken as described above). Single family starts grew at 21.0 percent in 3 months through April but multi family has slowed to a 2.0 percent growth rate. Within private non-residential, all sectors except manufacturing had positive growth led by hotels/motels, offices and recreational buildings, however all but four sectors had negative momentum.
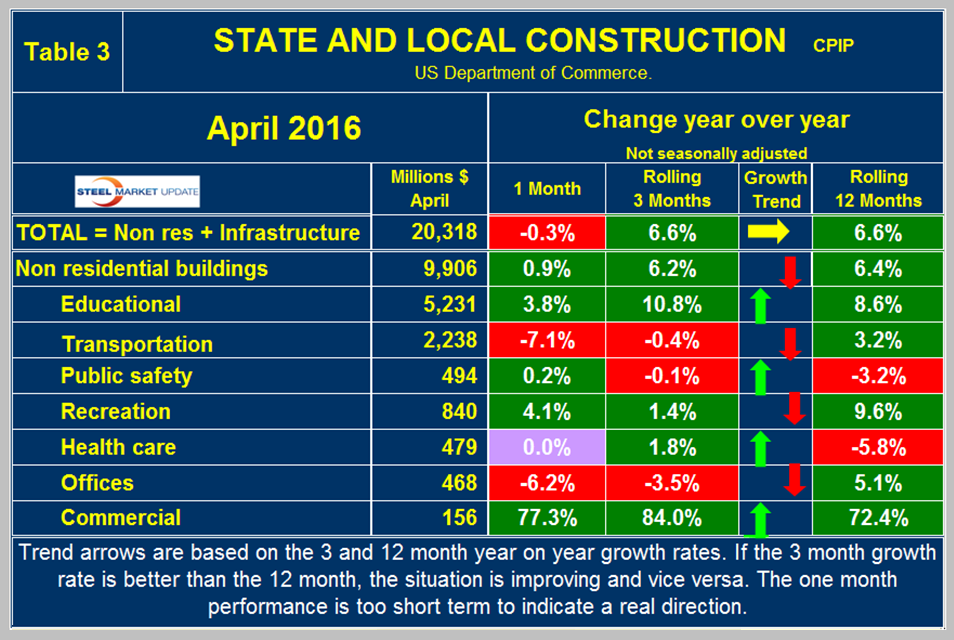
State and Local Construction
S&L work expanded by 6.6 percent in the rolling three months through April y/y with flat momentum (Table 3).
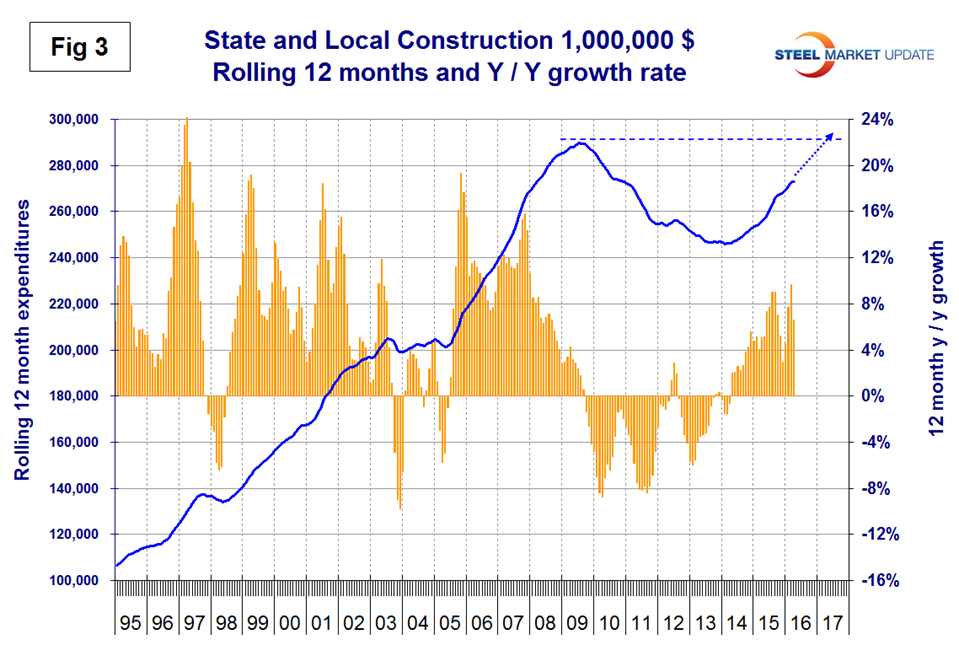
June through October 2015 had the highest growth rates for S&L construction since before the recession but growth slowed in each month of the 4th quarter of 2015 then improved in 2016. Figure 3 shows year over year growth as the brown bars.
Educational buildings are by far the largest sub sector of S&L non-residential at $5.2 billion in April and on a 3MMA basis y/y grew at 10.8 percent with positive momentum. Transportation terminals slowed to a negative 0.4 percent growth rate. All other sectors within S&L are relatively small. Recreational buildings which includes convention centers, sports arenas, theaters and miscellaneous amusements grew at 1.4 percent in the latest data with negative momentum. Public safety, which includes jails, police, courthouses and fire stations is in a slump and has contracted for 40 of the last 41 months. Table 2 shows that S&L commercial buildings grew at 84.0 percent but this is a very small volume. Comparing Figures 2 and 3 it can be seen that S&L construction did not have as severe a decline as private work during the recession and that private work bounced back faster. Both the private and S&L expenditures have now recovered to the point that they should exceed the pre-recession peak in 2017.
Drilling down into the private and S&L sectors as presented in Tables 2 and 3 shows which project types should be targeted for steel sales and which should be avoided. There are also regional differences to be considered for which data is not available from the Commerce Department.
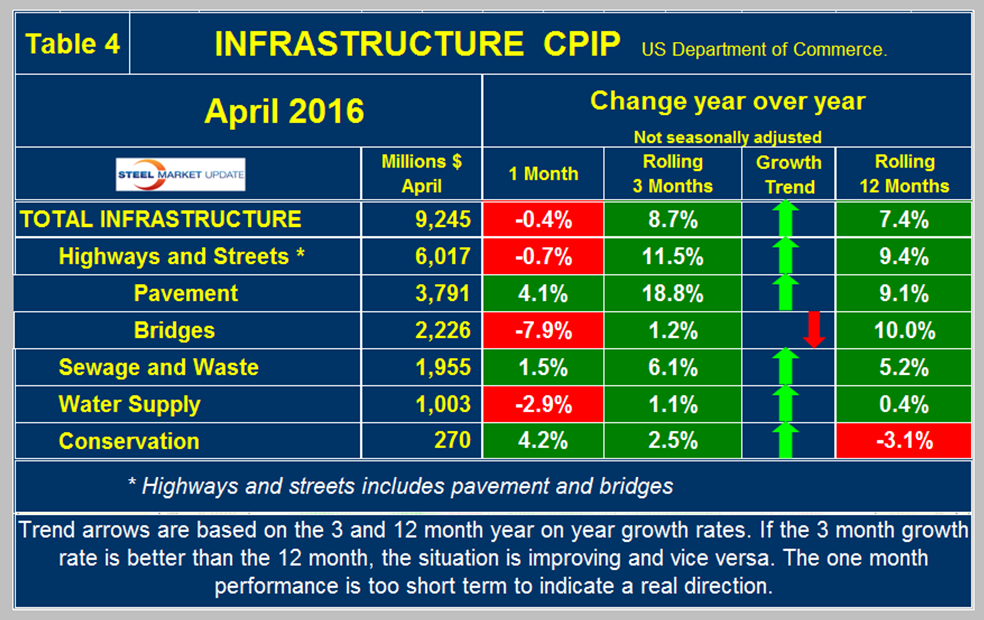
Infrastructure
Expenditures have had positive growth every month since July 2013 but growth slowed each month from August through December last year. In January there was a recovery to 3.3 percent which continued into April when y/y growth was 8.7 percent with positive momentum. Highway and streets including pavement and bridges account for about 2/3 of total infrastructure expenditures and had positive growth every month since April 2015 culminating in an 11.5 percent rate in three months through April. Highway pavement is the main subcomponent of highways and streets and had an 11.5 percent positive growth in three months through April. Bridge work has had positive growth for each of the last 17 months and exceeded $2.2 billion in the single month of April with a 1.2 percent growth rate (Table 4).
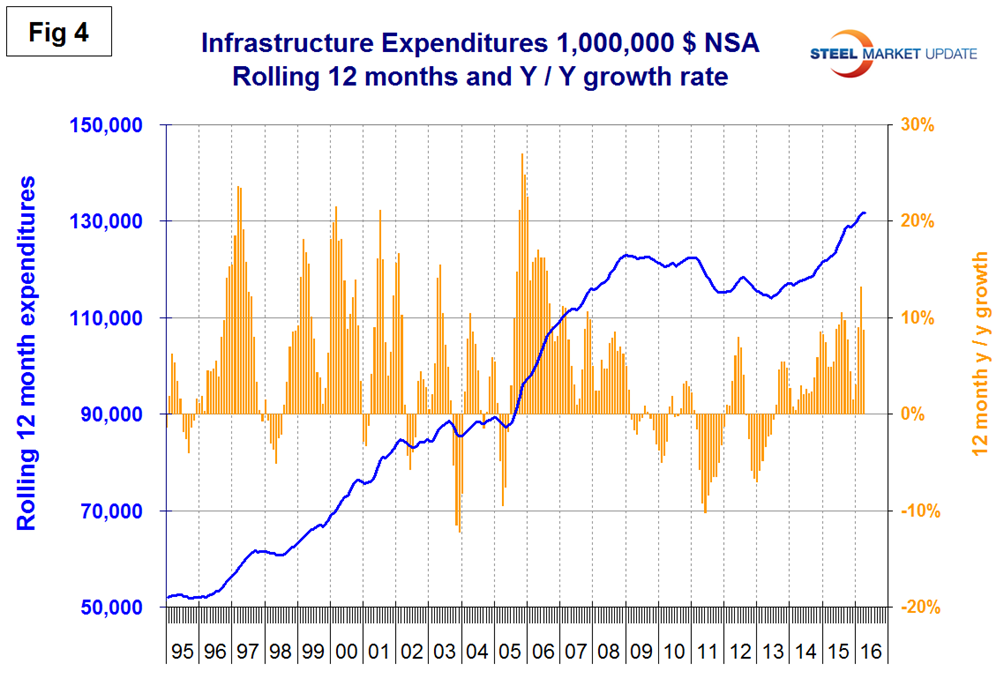
Infrastructure expenditures were slow to respond to the recession due to the magnitude of many of these projects. Growth stopped in 2009 and 2010 but it wasn’t until 2011 that an actual contraction occurred. For most of 2015 through April 2016 infrastructure expenditures exceeded the pre-recession high (Figure 4).
It looks as though the passage in late December of the congressional bill for $305 billion to fund roads, bridges, and rail lines is kicking in. The five-year infrastructure bill is the longest reauthorization of federal transportation programs that Congress has approved in more than a decade, ending an era of stopgap bills and half-measures that left the Highway Trust Fund nearly broke and frustrated local governments and business groups.
Total Building Construction Including Residential
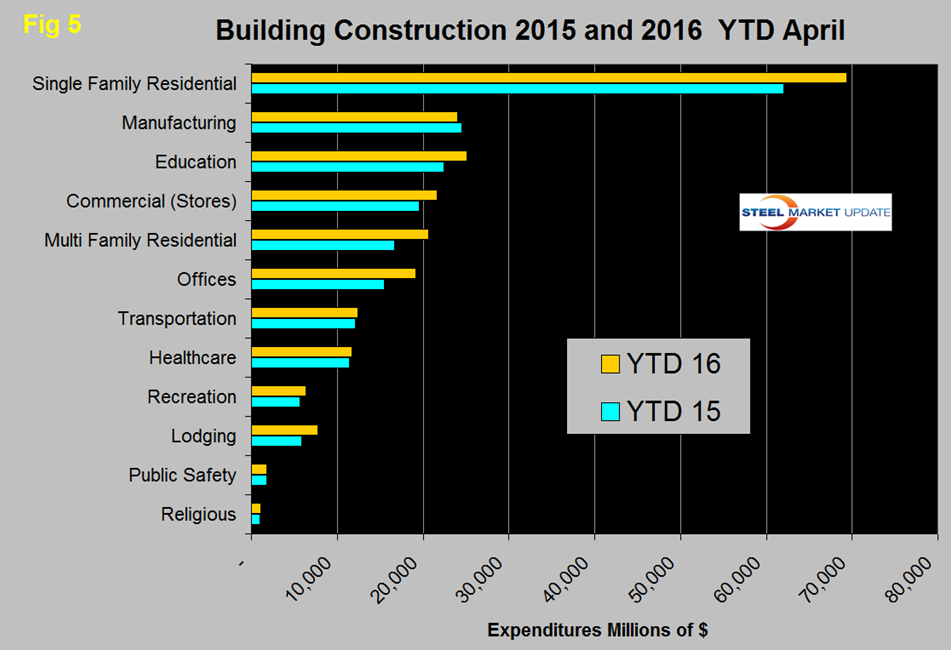
Figure 5 compares YTD expenditures for building construction for 2015 and 2016.
Single family residential is dominant and in the first four months of 2016 totaled $69.3 billion, up from $62.0 billion in the same period last year. All building sectors except public safety and manufacturing are doing better this year than last. At the other extreme lodging (hotels and motels) were up by 32.5 percent followed by multi-family residential buildings up 23.8 percent and offices up by 23.9 percent.
Explanation: The official CPIP press report gives no appreciation of trends on a historical basis and merely compares the current month with the previous one on a seasonally adjusted basis. The data is provided as both seasonally adjusted and non-adjusted. The detail is hidden in the published tables which we at SMU track and dissect to provide a long term perspective. Our intent is to provide a rout map for those subscribers who are dependent on this industry to “Follow the money.” This is a very broad and complex subject therefore to make this monthly write up more comprehensible we are keeping the information format as consistent as possible. In our opinion the absolute value of the dollar expenditures presented are of little interest. What we are after is the magnitude of growth or contraction of the various sectors. Data is reported by the Commerce Department on both a seasonally adjusted and non-adjusted basis. Their official commentary is based on adjusted numbers. In the SMU analysis we consider only the non-seasonally adjusted data because we don’t trust seasonal adjustments and in any case our businesses operate in a seasonal world. We eliminate seasonal effects by comparing rolling three month expenditures year over year. CPIP data also includes the category of residential improvements which we have removed from our analysis in the rational that such expenditures are minor consumers of steel.
In the four tables above we present the non-seasonally adjusted expenditures for the most recent month of data. Growth rates presented are all year over year and are the rate for the single months result, the rolling 3 months and the rolling 12 months. We ignore the single month year/year result in our write ups because these numbers can contain too much noise. The arrows indicate momentum. If the rolling 3 month growth rate is stronger than the rolling 12 months we define this as positive momentum and vice versa. In the text, when we refer to growth rate we are describing the rolling 3 months year over year rate. In Figures 1 through 4, the blue lines represent the rolling 12 month expenditures and the brown bars represent the rolling 3 month year over year growth rates.